Double Hashing in JavaIn programming, while we deal with data structure sometimes, we required to store two objects having the same hash value. Storing two objects having the same hash value is not possible. To overcome this problem, data structure provides collision resolution technique. In this section, we will focus only on double hashing, its advantages, example, and formula. Data structure provides the following collision resolution techniques:
What is double hashing?It is a collision resolution technique in open addressing hash table that is used to avoid collisions. A collision occurs when two keys are hashed to the same index in a hash table. The reason for occurring collision is that every slot in hash table is supposed to store a single element. Generally, hashing technique consists a hash function that takes a key and produces hash table index for that key. The double hashing technique uses two hash functions so it is called double hashing. The second hash function provides an offset value if the first hash function produces a collision. In other words, we can say that when two different objects have the same hash, is called collision. Hash FunctionA hash function is a function that accepts a group of characters (key) and maps that key to a value of a certain length (called a hash value or hash). The process is called hashing. It is done for indexing and locating items in databases. It provides an easy way to find longer value associated with the shorter hash value. It is widely used in encryption. It is also known as a hashing algorithm or message digest function. Double Hash FunctionThe first hash function determines the initial location to located the key and the second hash function is to determine the size of the jumps in the probe sequence. The following function is an example of double hashing: Or In the above function, the value of i will keep incrementing until an empty slot is found. If the table size is prime, the double hashing works well. Where PRIME is a prime smaller than tableSize. If the above functions compute an offset value that is already occupied by other object, it means there is a collision. A good hash function must have the following properties:
Advantages of Double Hashing
Double Hashing ExampleSuppose, we have a hash table of size 11. We want to insert keys 20, 34, 45, 70, 56 in the hash table. Let's insert the keys into hash table using the following double hash functions: h1(k) = k mod 11 (first hash function) h2(k) = 8 - (k mod 8) (second hash function) first, we will create a hash table of size 11. Let's insert key one by one.
*indexes that are bold denotes collision. After inserting all the keys, the hash table looks like the following. 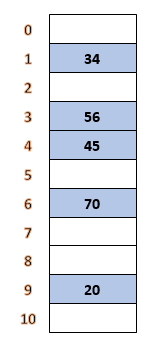
Now we have clearly understood the double hashing. So, we can easily differentiate linear and quadratic probing. In the linear probing, if collision occurs at any index, we look for the immediate next index. If the next index is also occupied, we look for the immediate next index. The process repeats until we get an empty index. In quadratic probing, if collision occurs at any index, we look for the immediate next index. If the next index is also occupied, then we jump to the i2 index. Suppose, index 2 is already occupied, then we look for 22 i.e. 4. It means look 4 indexes ahead from the current index (i.e. 2). Similarly, if index 3 is also occupied, then we look for 32 i.e. 9. It means look 9 indexes ahead from the current index (i.e. 3). Double Hashing Algorithm for Inserting an Element
Let's implement the above algorithm in a Java program. Double Hashing Java ProgramIn the following Java programs, we have implemented double hashing in hash table. DoubleHashingExample.java Output: 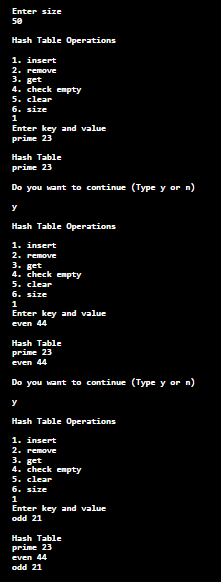
Next TopicMagic Square in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









