Equals() and Hashcode() in JavaThe equals() and hashcode() are the two important methods provided by the Object class for comparing objects. Since the Object class is the parent class for all Java objects, hence all objects inherit the default implementation of these two methods. In this topic, we will see the detailed description of equals() and hashcode() methods, how they are related to each other, and how we can implement these two methods in Java. Java equals()
Syntax:Parameter:obj: It takes the reference object as the parameter, with which we need to make the comparison. Returns:It returns the true if both the objects are the same, else returns false. General Contract of equals() methodThere are some general principles defined by Java SE that must be followed while implementing the equals() method in Java. The equals() method must be:
Java hashcode()
Syntax:Returns:It returns the hash code value for the given objects. Contract for hashcode() method in Java
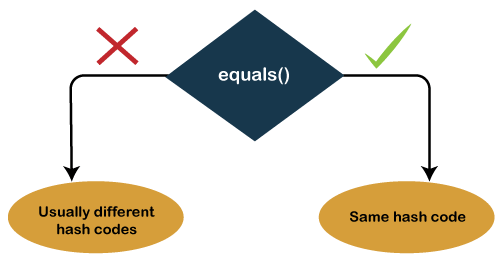
Note: As per the Java documentation, both the methods should be overridden to get the complete equality mechanism; using equals() alone is not sufficient. It means, if we override the equals(), we must override the hashcode() method.Example:Output: a & b are equal variables, and their respective hash values are: 1965574029 & 1965574029 c & d are Un-equal variables, and their respective hash values are: 74113750 & 71933245 In the above example, we have taken two 4 variables, out of which two are equal, and two are unequal. First, we have compared the objects whether they are equal or unequal, and based on that, printed their hash values.
Next TopicExternalization in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










