ES6 Decision-MakingES6 conditional statements are used to perform different actions based on various conditions. The conditional statement evaluates a condition before the execution of instructions. When you write the code, you require to perform different actions for different decisions. You can easily perform it by using conditional statements. 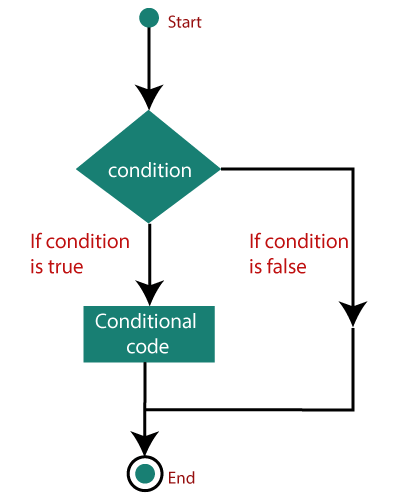
Types of Conditional StatementsThe conditional statements in JavaScript are listed below:
Let us try to elaborate on these conditional statements. The if statementIt is one of the simplest decision-making statement which is used to decide whether a block of JavaScript code will execute if a certain condition is true. Syntax If the condition evaluates to true, the code within if statement will execute, but if the condition evaluates to false, then the code after the end of if statement (after the closing of curly braces) will execute. Note: The if statement must be written in the lowercase letters. The use of Uppercase letters (If or IF) will cause a JavaScript error.Flowchart 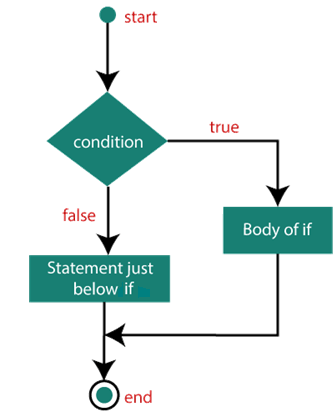
For example Output x is greater The if….else statementAn if….else statement includes two blocks that are if block and else block. It is the next form of the control statement, which allows the execution of JavaScript in a more controlled way. It is used when you require to check two different conditions and execute a different set of codes. The else statement is used for specifying the execution of a block of code if the condition is false. Syntax If the condition is true, then the statements inside if block will be executed, but if the condition is false, then the statements of the else block will be executed. Flowchart 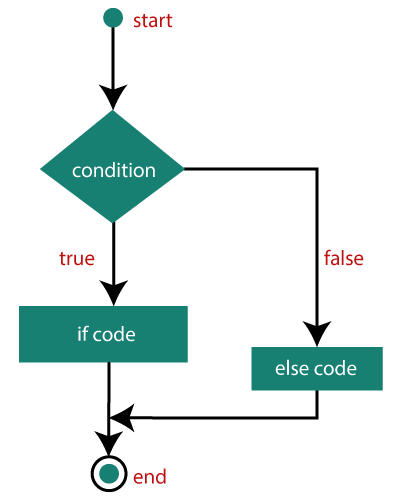
For example Let us try to understand if….else statement by the following example: Output x is greater The if….else if…..else statementIt is used to test multiple conditions. The if statement can have multiple or zero else if statements and they must be used before using the else statement. You should always be kept in mind that the else statement must come after the else if statements. Syntax Example Output c is greater The nested if statementIt is an if statement inside an if statement. Syntax Example Output 20 is greater than 10 and even number After nested if statement The switch statementIt is a multi-way branch statement that is also used for decision-making purposes. In some cases, the switch statement is more convenient than if-else statements. It is mainly used when all branches depend upon the value of a single variable. It executes a block of code depending upon the different cases. The switch statement uses the break or default keywords, but both of them are optional. Let us define these two keywords: break: It is used within the switch statement for terminating the sequence of a statement. It is optional to use. If it gets omitted, then the execution will continue on each statement. When it is used, then it will stop the execution within the block. default: It specifies some code to run when there is no case match. There can be only a single default keyword in a switch. It is also optional, but it is recommended to use it as it takes care of unexpected cases. If the condition passed to switch doesn't match with any value in cases, then the statement under the default will get executed. Some points to remember
Syntax Flowchart 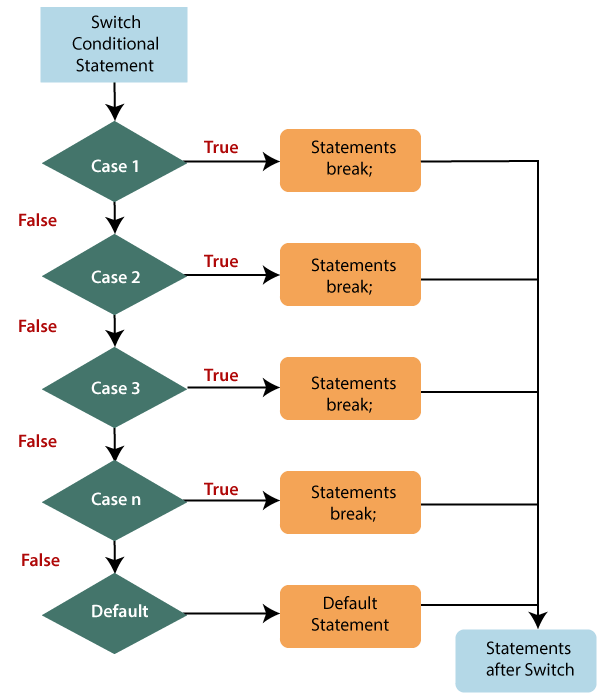
Example Output Friday
Next TopicES6 Functions
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










