Fail-fast and Fail-safe in JavaFail-fast and Fail-safe are the iterators or collections in Java. Java SE specification doesn't use the Fail-safe term. We use the Fail-safe to segregate between the Non-Fail-fast and Fail-fast iterators. The Fail-Fast system terminates the operation as-fast-as-possible that are exposing failures and stop the entire operation. Whereas, Fail-Safe system doesn't terminate the operation that are exposing failures. The Fail-safe system tries to avoid raising Failures as much as possible. 
Fail-fast and Fail-safe are the concepts of concurrent modification. Concurrent modification is a process in which an object is modified concurrently when a different task is running over it. Fail-fast and Fail-safe are the iterators to iterate over the Collection objects. Let's dive into detail about Fail-fast and Fail-safe one by one: Fail-fast IteratorWhen we use the Fail-fast iterator, it immediately throws ConcurrentModificationException when an element is added or removed from the collection while the thread is iterating over the collection. Examples: Iterator in HashMap, Iterator on ArrayList, etc. The Fail-fast iterators use modCount, i.e., an internal flag to check whether the collection is structurally modified or not. When the Fail-fast iterator gets the next value using the next() method, it checks the modCount flag's value. When the iterator finds the modified modCount value, it throws the ConcurrentModificationException. Let's take an example of Fail-fast iterator to understand how it works in Java. FailFastIterator.java Output 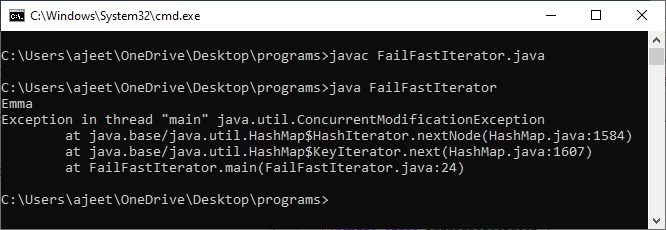
Let's take another example of a Fail-fast iterator in which we will use the iterator on the ArrayList. FailFastIterator2.java Output 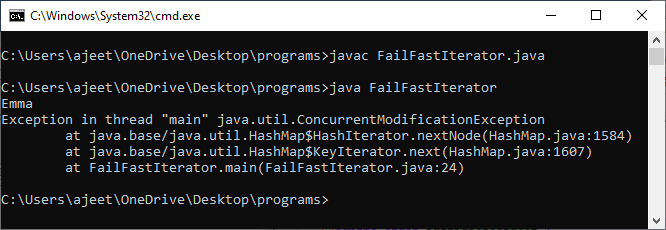
Fail-safe IteratorThe Java SE specification doesn't use the Fail-safe term. It is better to call it a Non-Fail-fast Iterator. The Fail-safe iterator doesn't throw the ConcurrentModificationException, and it tries to avoid raising the exception. The Fail-safe iterator creates a copy of the original collection or object array and iterates over that copied collection. Any structural modification made in the iterator affects the copied collection, not the original collection. Therefore, the original collection remains structurally unchanged. Below are some key points related to the Fail-safe:
Let's take an example Fail-safe iterator to understand how it actually works in Java. FailSafeIterator.java Output 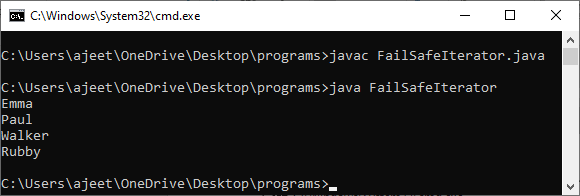
Let's take another example of a Fail-safe iterator in which we will use the Iterator on CopyOnWriteArrayList. FailSafeIterator2.java Output 
Difference between Fail-safe and Fail-fastWe define some main difference between Fail-safe and Fail-fast iterators based on some key factors:
Next TopicFind unique elements in array Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










