flatMap() Method in Java 8The Stream API was introduced in Java 8 that is used to process the collections of objects. It can be used by importing the java.util.stream package. In this section, we will discuss the Stream.flatMap() method of the Stream API. Also, we will discuss the key differences between the Stream.flatMap() and Stream.map() method in Java 8. 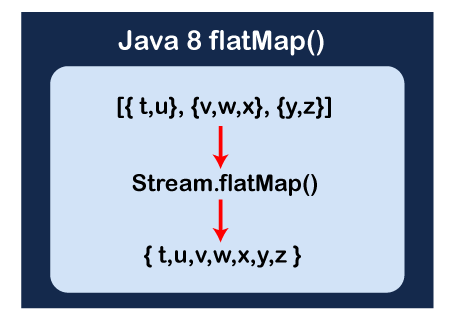
Before moving to the topic, first, we will understand the Stream.map() method. Because the flatMap() method is based on the map() method. Java Stream.map() MethodThe Stream.map() method performs an intermediate operation by using the mapper function. It produces a new stream for each element. It transforms all the streams into a single stream to provide the result. therefore, each element of the stream gets converted into a new stream. Syntax: R: It is a type parameter that represents the element type of the new stream. mapper: It is a parameter that is non-interfering, stateless function to apply to each element. Example of the map() MethodConsider the above statement for a map of the stream. It creates a resulting stream using the map(). In each iteration, map() creates a separate stream with the result by executing the mapper function. At last, map() transforms all streams into a single stream. MapExample.java Output: Stream After applying the map() function: 24 90 134 38 174 4 18 Java Stream.flatMap() MethodIn Java 8 Streams, the flatMap() method applies operation as a mapper function and provides a stream of element values. It means that in each iteration of each element the map() method creates a separate new stream. By using the flattening mechanism, it merges all streams into a single resultant stream. In short, it is used to convert a Stream of Stream into a list of values. Syntax: The method takes a function as an argument. It accepts T as a parameter and returns a stream of R. R: It is a type parameter that represents the element type of the new stream. mapper: It is a parameter that is a non-interfering, stateless function to apply to each element. It produces a stream of new values. In short, we can say that the flatMap() method helps in converting Stream<Stream<T>> to Stream<T>. It performs flattening (flat or flatten) and mapping (map), simultaneously. The Stream.flatMap() method combines both the operations i.e. flat and map. Let's understand the meaning of flattening. What is flattening?Flattening is the process of converting several lists of lists and merge all those lists to create a single list containing all the elements from all the lists. Flattening Example Consider the following lists of lists: Before Flattening: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [7, 8, 9, 0], [5, 6], [12, 18, 19, 20, 17], [22]] After Flattening: [1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 0, 5, 6, 12, 18, 19, 20, 17, 22] Example of the flatMap() MethodWe can use a flatMap() method on a stream with the mapper function List::stream. On executing the stream terminal operation, each element of flatMap() provides a separate stream. In the final phase, the flatMap() method transforms all the streams into a new stream. In the above stream, we observe that it does not contain duplicate values. Let's create a Java program and use the flatMap() method. FlatMapExample.java Output: List Before Applying mapping and Flattening: [Printer, Mouse, Keyboard, Motherboard, Scanner, Projector, Lighten, Pen Drive, Charger, WIFI Adapter, Cooling Fan, CPU Cabinet, WebCam, USB Light, Microphone] List After Applying Mapping and Flattening Operation: [Printer, Mouse, Keyboard, Motherboard, Scanner, Projector, Light Pen, Pen Drive, Charger, WIFI Adapter, Cooling Fan, CPU Cabinet, WebCam, USB Light, Microphone] Now, we have understood both the methods of the Stream class. Since we can easily point out the key differences between them. Stream.flatMap() Vs. Stream.map()The following table describes the key differences between Stream.flatMap() and Stream.map(). 
Next TopicHow to Print Table in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










