How to Open Java Control Panel?In this section, we will learn different ways to open the Java control panel. Also, we will discuss the uses of the Java Control Panel. Java Control PanelThe Java Control Panel is a multipurpose control panel. It allows us to view and set a wide range of control parameters. The uses of the Java control panel are as follows:
How to open Java Control Panel?There are many ways to open the Java control panel.
Using Control Panel Window
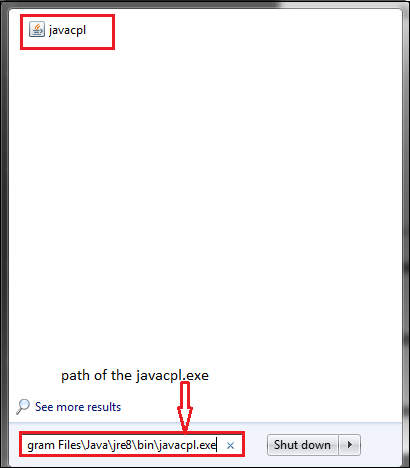
Java Control Panel appears on the screen. Directly Access javacpl.exe
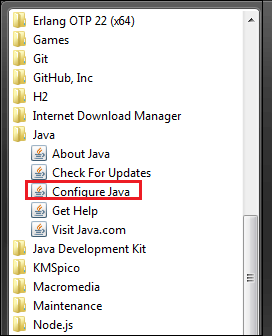
Java Control Panel appears on the screen. Using Windows Button
Java Control Panel appears on the screen. Another way is:
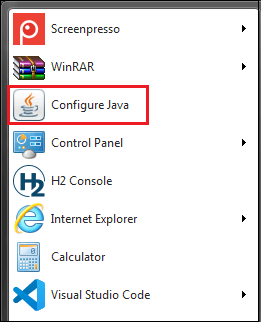
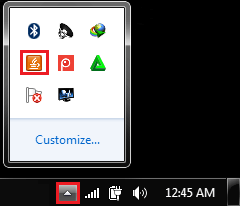
Java Control Panel appears on the screen. Using System Tray Icon
Java Control Panel appears on the screen. 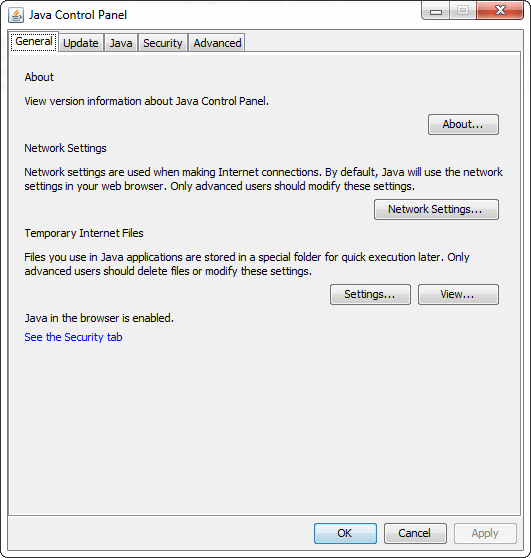
The Java Control Panel includes the following separately viewable panels:
Let's discuss the purpose of each tab one by one. GeneralThe General tab is subdivided into three panels that are About, Network Setting, and Temporary Internet Files. Since Java 7 another security feature is added to the Control panel that informs that Java is enabled in the browser or not. 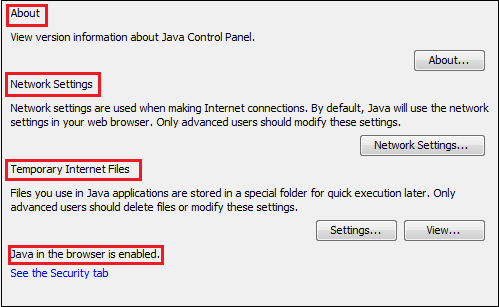
About: By clicking on the About button, we can see the version information for the JRE that is installed in the system. 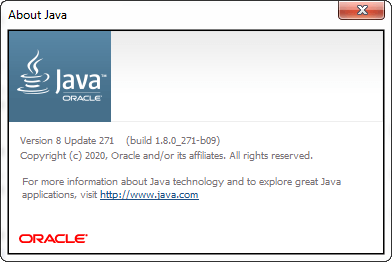
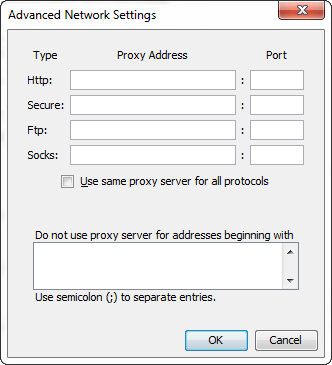
Network Setting: It provides the network-related setting if the system is connected to the network. By default, it uses the network setting of the web browser. Click on the Network Setting button to get the network setting dialog box. 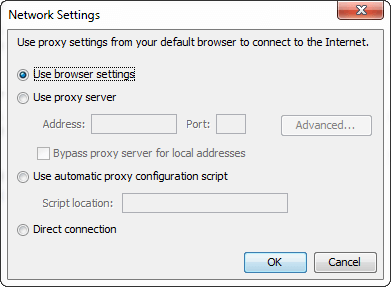
It provides the following four options:
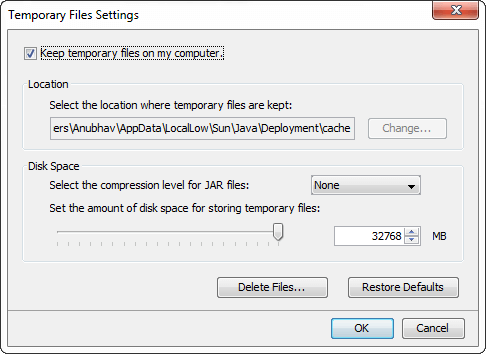
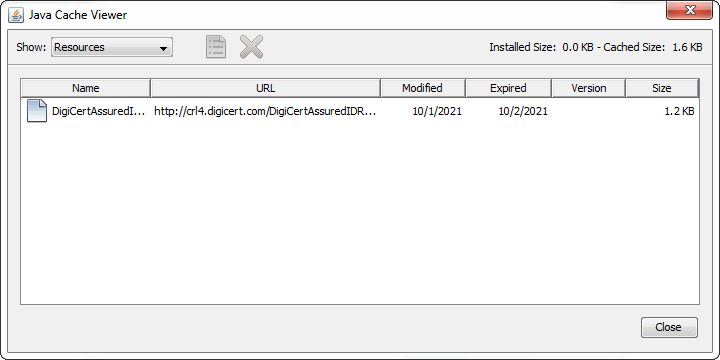
Temporary Internet Files:
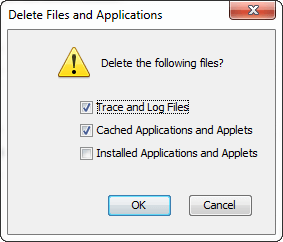
In addition, we can perform the following:
UpdateThe Update panel, in conjunction with the Java Update Scheduler (jusched.exe), is used to provide the latest Java updates to the end-user. It uses the Java Update Scheduler (jusched.exe) for launching the automatic updates. 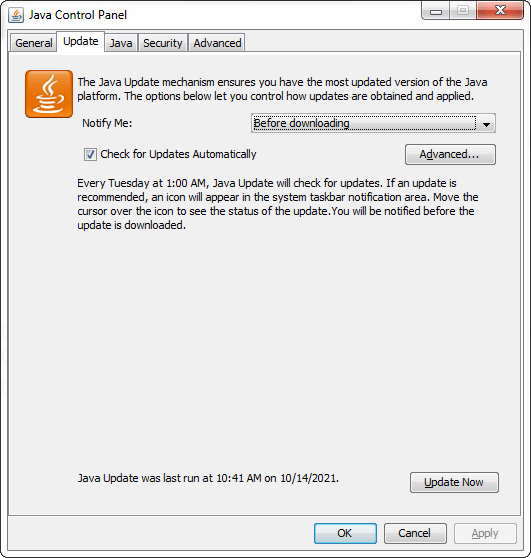
Uncheck the auto-update if you do not want to get the notification from time to time. In addition, we can also set the time, date, and frequency (daily, weekly, or monthly) for update notification by clicking on the Advanced button that opens the Automatic Update Advanced Settings. 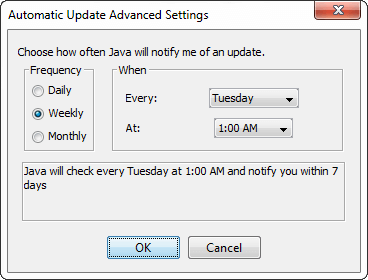
Click on the Update Now button to get the latest Java update. JavaIt is used to manage the Java Runtime versions, settings for Java applications, and applets. 
Click on the View button to get the Java Runtime Environment Settings. It enlists all the versions that are installed in the system. 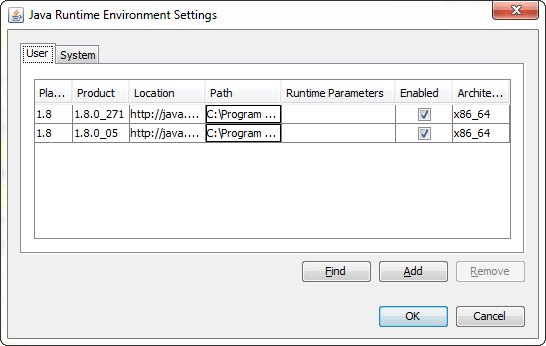
Note: If all Java apps are disabled from running in the browser, by de-selecting Enable the Java content in the browser in the Security panel, enabling the JRE here has no effect.Click on the Find button to launch the JRE Finder. It searches for unregistered private Java Runtime Environments installed in the system and adds them to the Java Runtime Versions panel. 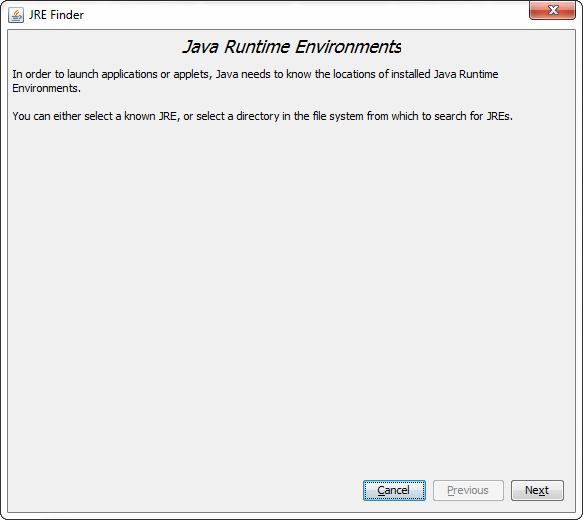
Click on the Add button to manually add a Java Runtime Environment to the Java Runtime Versions panel. When we click on the Add button, a new row appears in the Java Runtime Versions panel. However, there are no values for Platform, Product, Path, Runtime Parameters, and Enabled; we must specify these parameters. 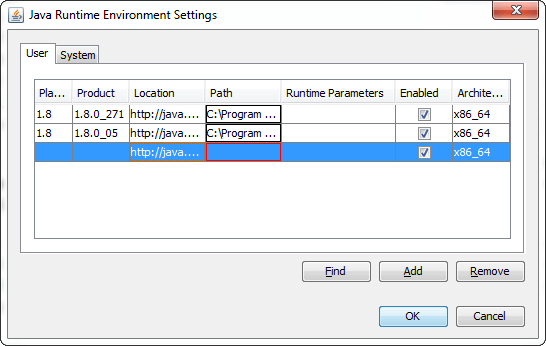
Click on the Remove button to remove the selected Java Runtime Environment from the Java Runtime Versions panel. Note: There will always be at least one entry.SecurityUncheck the Enable Java content in the browser button, which is selected by default, will prevent any Java application from running in the browser. 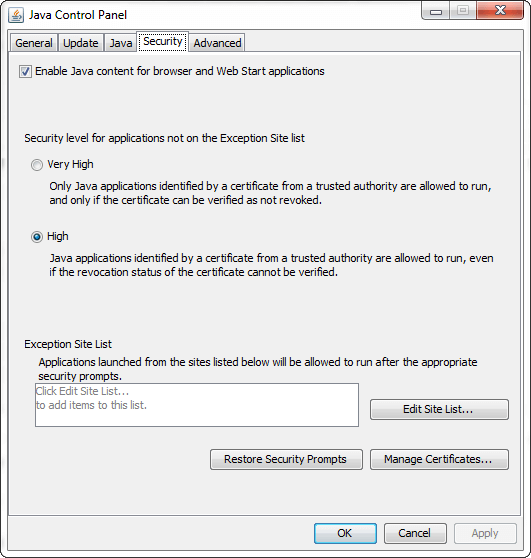
It provides the following two security levels, Very High and High.
Note: There was another security level in the previous versions of the Java called Medium. It is degraded in the later versions.Exception Site List: The exception site list contains a list of URLs that host RIAs (Rich Internet Applications) that users want to run even if the RIAs are normally blocked by security checks. RIAs from the sites listed are allowed to run with applicable security prompts. Click on the Edit Site List button to add, edit, and remove items. 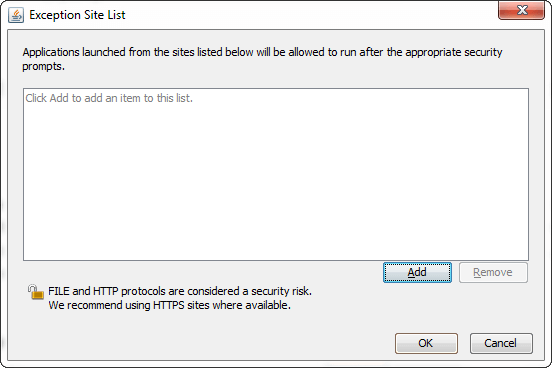
Restore Security Prompts: An option to hide a prompt in the future is included in some security prompts that are shown when an application starts. It is recommended that we must periodically restore the prompts that were hidden. It ensures the continued security of the system. Seeing the prompts again provides an opportunity to review the applications and ensure that you still want them to run. To restore the prompts that were previously hidden, click on the Restore Security Prompts button. It confirms the selection, click on the Restore All button, else click on the Cancel button. When we start the application again, the security prompt for that application is shown. 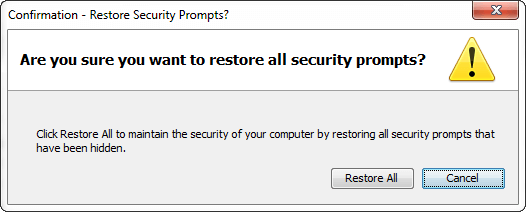
Certificates: Click Manage Certificates to get the Certificates dialog that looks like the following. 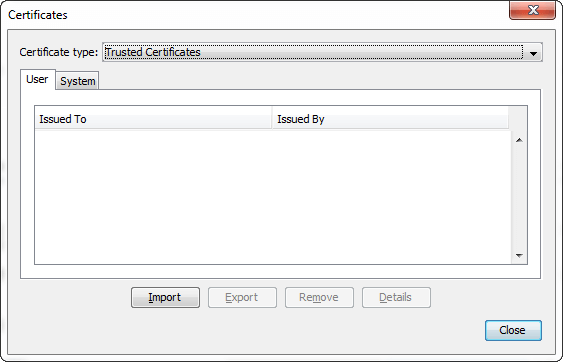
It handles both User and System-Level (enterprise-wide) certificates of the following types:
AdvancedIt includes options for Debugging, Java console, Default Java for browsers, Shortcut Creation, JNLP File/MIME Association, Application Installation, Secure Execution Environment, Mixed code security verification, Certificate revocation checks, Advanced Security Settings, and other Miscellaneous options. 
Next TopicHow to Reverse Linked List in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share