How to Use Eclipse for JavaEclipse is the most popular IDE for Java application development. In order to use eclipse effectively, we must familiar with the workbench, concepts, and components of Eclipse IDE. Before moving ahead in this section, we will understand what is eclipse in Java, eclipse platform overview, and how to use eclipse for Java. What is eclipse in Java?In 2001, IBM formed a consortium to support the development of Eclipse IDE. In 2004, it become the Eclipse Foundation whose main vision was to guide, implement, and share the development of open-source (software whose source code is released under a license) Eclipse projects in a vendor-natural environment. It is an open-source Integrated Development Environment (IDE). It is written in Java. It is used to develop Java applications (Java SE and Java EE). It is also used to develop applications in other languages, such as C, C++, PHY, Python, Perl, and other web projects with the help of extensible plug-ins. We can run it on different platforms, like Windows, Linux, and macOS. Presently, it is the widely used IDE for developing Java applications. Eclipse Platform OverviewIt itself structured as a subsystem because it implements one or more plug-ins. These subsystems are built on the top of the small runtime engine or system. The runtime engine is based on Equinox. It is an implementation of the OSGi core framework specification. It allows eclipse to be used with other programming languages, typesetting languages such as LaTeX, and networking applications, such as database management system. The following figure shows the simplified architecture of the eclipse. 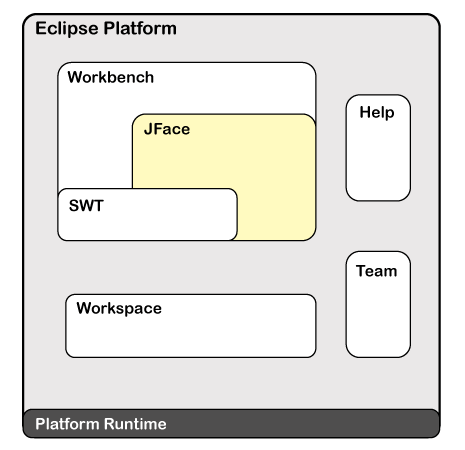
How to use Eclipse for Java?Eclipse Foundation has a long history of development, since it has released many versions. It uses an astronomy name for its versions, such as Juno, neon, Kepler, Oxygen, Photon, Mars, etc. the latest version uses a naming scheme, i.e. year-month format, such as 20219-20. We recommend you to download and install the latest version of Eclipse IDE i.e. Eclipse 2020-06. Note: Before installing the eclipse, make sure that JDK is installed in the system and the path is properly set. It is because eclipse depends on JDK/ JRE.Before moving to the eclipse IDE let's understand some key concepts and components in the IDE. WorkbenchIn eclipse, workbench (desktop development environment) is a window instance of IDE. It consists of one or more perspectives to achieve seamless tool integration and provides a common paradigm for the creation, navigation, and management of workspace resources. Further, perspectives consist of editors and views. It allows us to open multiple workbenchs windows for projects, simultaneously. Remember that all the workbenches use the same workspace. The following window shows the Eclipse workbench. 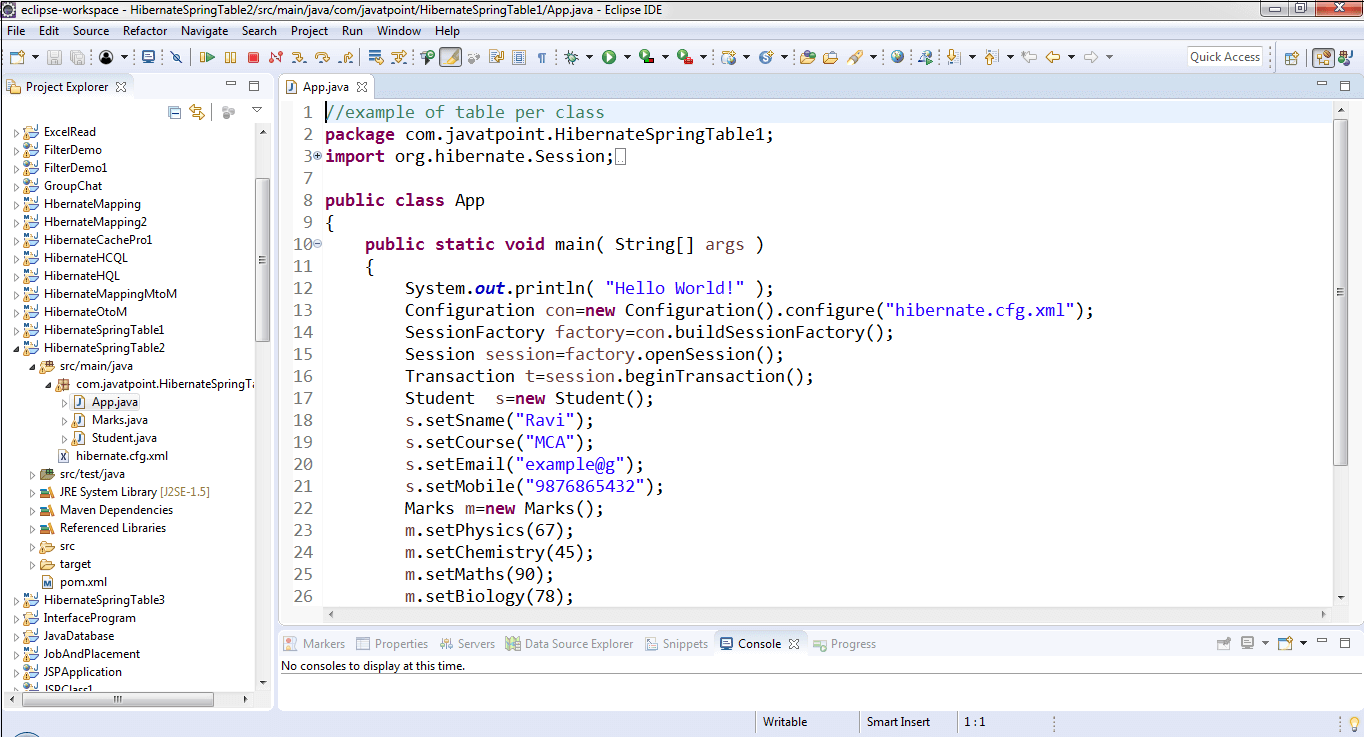
WorkspaceIn IDE, workspace is a directory or folder where the projects are stored. Before starting the IDE, we must select the workspace. The IDE allows us to create multiple workspace, if needed. We can also switch among the IDEs without closing the application. The advantage of workspace is that it allows us to work with multiple projects at a time. Eclipse stores each workspace preferences separately in the .metadata directory which is located in the workspace root. 
PerspectivesThe perspective provides the initial layout that helps the programmer to accomplish the work and task. Each perspective provides different sets of views and editors. We can open the perspective by clicking on the Windows menu -> Perspective -> Open Perspective. 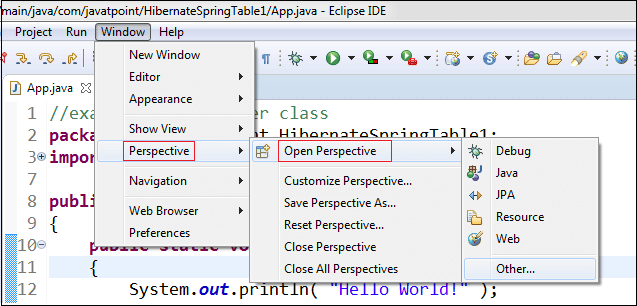
The Java perspectives provide the following editors and views:
Eclipse provides the following Java perspective: 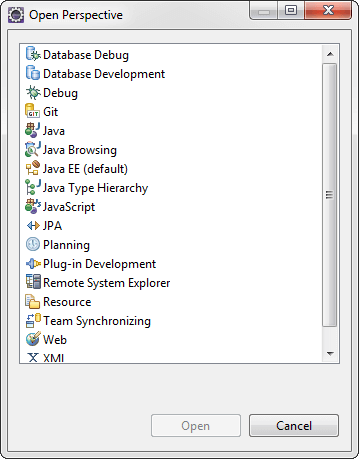
EditorsEditors are the center of the workbench. It allows us to edit the source files. When we click on the .java file it opens in the editor. In eclipse, we can open multiple editors simultaneously. But we can work on a single editor at a time. The title bar shows the name of the file. When we add something in the file, the unsaved changes indicate by an asterisk (*). We can switch among the editors by pressing the Ctrl+F6 key. The following image shows the editor. 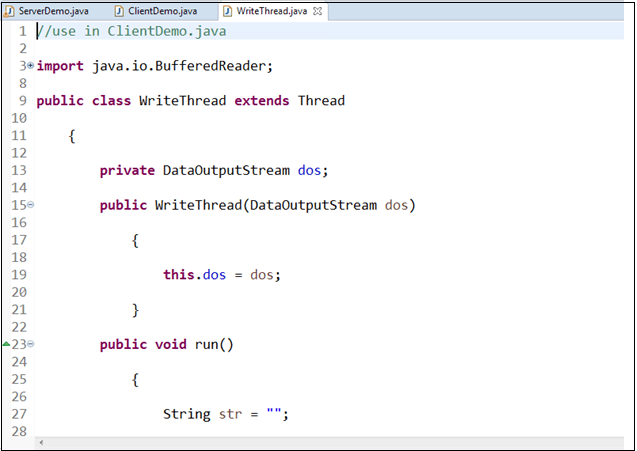
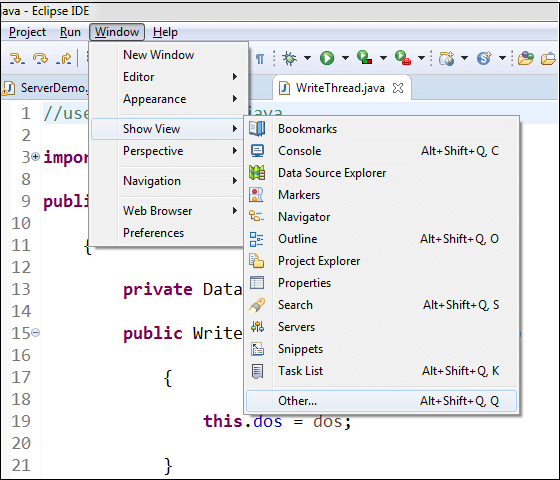
ViewIn eclipse, we use the view to navigate the information in workbench. Using an outline view, we can quickly jump to the specific element of the source file. examples of view are Bookmarks, Console, Navigator, Search, Project Explorer, etc. If we want to open view in eclipse, click on the Window menu -> Show View. It shows the list of views available in eclipse. We can switch among the multiple views by pressing the Ctrl+F7.
ToolbarsThere are four types of toolbars available in eclipse:
Main Toolbar: The main tollbar is placed just below the main menu. It contains the buttons in pictorial form. The buttons are grouped in different sections, like save, create, open, run, debug, etc. 
Individual Toolbar: Each view in eclipse has its own toolbar that is displayed at the top right corner. The following image shows the tollbar for the Servers view. 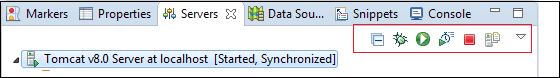
Perspective Search Toolbar: It is placed on the right side of the main toolbar. It contains the button that allows us to switch among open perspectives in workbench. 
View Stack Toolbar: It is a tollbar that appears on minimizing a view in a stack. The icons on this bar allow us to open an individual view in the stack. The toolbar shown in the following image appears when we minimize the Console view. 
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










