Invert a Binary tree in JavaInverting or mirroring a binary tree is common in computer science and programming. It reverses the arrangement of left and right subtrees at each node, effectively creating a mirror image of the original tree. 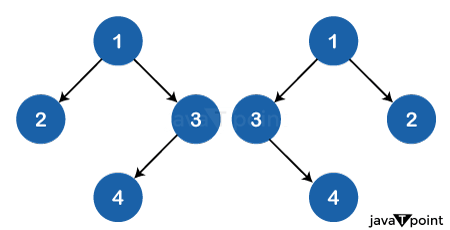
The process essentially mirrors the tree across its vertical axis. In binary tree manipulation, inversion is a frequently used operation that plays a key role in optimizing various algorithms related to trees. The concept involves recursively navigating the tree and exchanging the positions of the left and right children for each node. Approach: Recursive Tree TraversalRecursive Tree Traversal is a method used to explore and process a tree-like structure's nodes (or boxes). The approach involves breaking down the task of navigating the tree into smaller, more manageable steps. Algorithm:Step 1: Create a BinaryTreeNode class representing a binary tree point. It has a number (value), a left child, and a right child. It also has a way to start with a value when it's created. Step 2: Make a class called BinaryTreeMirrorConverter that will help us change a binary tree to its mirror image. The class has a variable called root that points to the starting point of the tree. Step 3: Inside BinaryTreeMirrorConverter, make a method called convertToMirror. It just changes the root to whatever the result is when we use a helper method. Step 4: Make a helper method called convertToMirror. It takes a point in the tree (a node) and does the following:
Step 5: Inside BinaryTreeMirrorConverter, make a method called inorderTraversal. It helps us go through the tree in a specific order. Step 6: Make a helper method called inorderTraversal. It takes a point in the tree (a node) and if the point isn't empty, go to the left, print the value, and then go to the right. Step 7: In the main part of our program, create a new BinaryTreeMirrorConverter named tree. Build a tree with some numbers in a specific order. Show the numbers in the tree in a certain order (inorder traversal). Change the tree to its mirror. Show the numbers in the mirrored tree in the same order. ImplementationFilename: BinaryTreeMirrorConverter.java Output: Inorder traversal of the original tree: 4 2 5 1 3 Inorder traversal of the mirrored tree: 3 1 5 2 4 Time Complexity: The time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. Each node is visited once during the mirror conversion process. Auxiliary Space: The auxiliary space complexity is O(h), where h is the height of the binary tree. The recursion stack space contributes to the auxiliary space. Approach: Level Order TraversalLevel Order Traversal is a tree traversal algorithm that visits nodes level by level, from left to right, starting from the root of the tree. The approach employs a queue to manage the order of node exploration, enqueuing the root initially. Algorithm:Step 1: Define a class TreeNode with attributes int data, TreeNode left, and TreeNode right. Step 2: Define a class BinaryTree with static methods. Step 3: In the main Method, create a sample binary tree. Step 4: Print the inorder traversal of the original binary tree. Step 5: Call the convertToMirror method with the root of the binary tree. Step 6: Inside convertToMirror:
Step 7: Print the inorder traversal of the mirrored binary tree. Implementation:Filename: BinaryTree.java Output: Original Binary Tree (Inorder Traversal): 4 2 5 1 3 Mirrored Binary Tree (Inorder Traversal - Mirror Image): 3 1 5 2 4 Time Complexity: The time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. It is because each node is visited once during the level order traversal. Auxiliary Space: The auxiliary space complexity is O(w), where w is the binary tree's maximum width (number of nodes at any level).
Next TopicJava Template Engine
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









