Difference Between List and Set in JavaIn JDK 2.0, we used to use Vectors, Arrays, and Hashtable to group the objects into a single unit. In JDK 8, Collection framework come in to existence that provides several interfaces to work with a collection of data. List and Set interfaces are one of them that are used to group the object. Both interfaces extend the Collection interface. The main difference between List and Set is that Set is unordered and contains different elements, whereas the list is ordered and can contain the same elements in it. Let's discuss in detail. List InterfaceThe java.util package provides the List interface for maintaining the ordered collection. A List can contain the null and duplicate values. The methods of the List are based on the index, so all the operations like insert, delete, update, and search is based on the index. ArrayList, LinkedList, Stack, and Vector are the implementation classes available in the List interface. In Java, we mostly used the ArrayList and LinkedList implementation classes to design a list. Let's use the List interface in a Java program. ListExample.java Output: 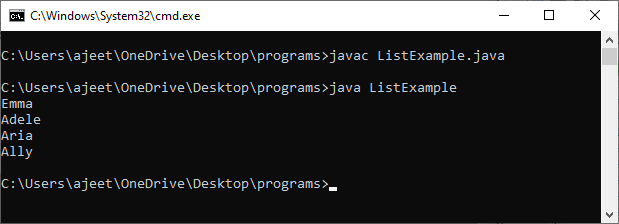
Set InterfaceThe Set interface belongs to the java.util package that extends the Collection interface. It restricts us from entering the distinct value in it. It stores the value in a sorted way, so it doesn't maintain the insertion order. The set interface is used to design the mathematical Set in Java. Let's see an example to understand how to create a set in Java. SetExample.java Output: 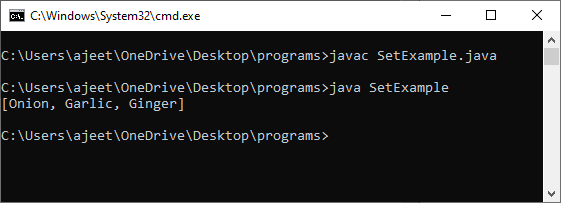
List Vs Set InterfaceIn Java, both the List and the Set are available in the Collection framework. In order to store the collection of objects as a single unit, Set and List interface are used. Apart from these similarities, both the interfaces have so many differences too, which are as follows:
Next TopicHow many days required to learn Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










