Literals in JavaIn Java, literal is a notation that represents a fixed value in the source code. In lexical analysis, literals of a given type are generally known as tokens. In this section, we will discuss the term literals in Java. LiteralsIn Java, literals are the constant values that appear directly in the program. It can be assigned directly to a variable. Java has various types of literals. The following figure represents a literal. 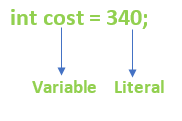
Types of Literals in JavaThere are the majorly four types of literals in Java:
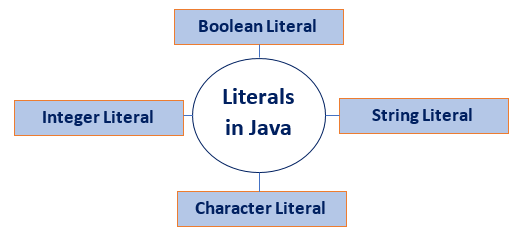
Integer LiteralsInteger literals are sequences of digits. There are three types of integer literals:
Real LiteralsThe numbers that contain fractional parts are known as real literals. We can also represent real literals in exponent form. For example, 879.90, 99E-3, etc. Backslash LiteralsJava supports some special backslash character literals known as backslash literals. They are used in formatted output. For example: \n: It is used for a new line \t: It is used for horizontal tab \b: It is used for blank space \v: It is used for vertical tab \a: It is used for a small beep \r: It is used for carriage return \': It is used for a single quote \": It is used for double quotes Character LiteralsA character literal is expressed as a character or an escape sequence, enclosed in a single quote ('') mark. It is always a type of char. For example, 'a', '%', '\u000d', etc. String LiteralsString literal is a sequence of characters that is enclosed between double quotes ("") marks. It may be alphabet, numbers, special characters, blank space, etc. For example, "Jack", "12345", "\n", etc. Floating Point LiteralsThe vales that contain decimal are floating literals. In Java, float and double primitive types fall into floating-point literals. Keep in mind while dealing with floating-point literals.
Floating: Decimal: Decimal in Exponent form: Boolean LiteralsBoolean literals are the value that is either true or false. It may also have values 0 and 1. For example, true, 0, etc. Null LiteralsNull literal is often used in programs as a marker to indicate that reference type object is unavailable. The value null may be assigned to any variable, except variables of primitive types. Class LiteralsClass literal formed by taking a type name and appending .class extension. For example, Scanner.class. It refers to the object (of type Class) that represents the type itself. Invalid LiteralsThere is some invalid declaration of literals. Restrictions to Use Underscore (_)
Why use literals?To avoid defining the constant somewhere and making up a label for it. Instead, to write the value of a constant operand as a part of the instruction. How to use literals?A literal in Java can be identified with the prefix =, followed by a specific value. Let's create a Java program and use above discussed literals. LiteralsExample.java Output: 987 4534.99 19765.567 2020 26 p Java true 55 null ! backslash literal ?
Next TopicSquare Free Number in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









