MVC Architecture in JavaThe Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a well-known design pattern in the web development field. It is way to organize our code. It specifies that a program or application shall consist of data model, presentation information and control information. The MVC pattern needs all these components to be separated as different objects. In this section, we will discuss the MVC Architecture in Java, alongwith its advantages and disadvantages and examples to understand the implementation of MVC in Java. What is MVC architecture in Java?The model designs based on the MVC architecture follow MVC design pattern. The application logic is separated from the user interface while designing the software using model designs. The MVC pattern architecture consists of three layers:
In Java Programming, the Model contains the simple Java classes, the View used to display the data and the Controller contains the servlets. Due to this separation the user requests are processed as follows: 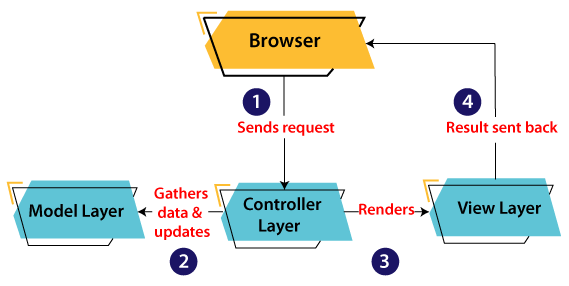
Advantages of MVC ArchitectureThe advantages of MVC architecture are as follows:
Implementation of MVC using JavaTo implement MVC pattern in Java, we are required to create the following three classes.
MVC Architecture LayersModel LayerThe Model in the MVC design pattern acts as a data layer for the application. It represents the business logic for application and also the state of application. The model object fetch and store the model state in the database. Using the model layer, rules are applied to the data that represents the concepts of application. Let's consider the following code snippet that creates a which is also the first step to implement MVC pattern. Employee.java The above code simply consists of getter and setter methods to the Employee class. View LayerAs the name depicts, view represents the visualization of data received from the model. The view layer consists of output of application or user interface. It sends the requested data to the client, that is fetched from model layer by controller. Let's take an example where we create a view using the EmployeeView class. EmployeeView.java Controller LayerThe controller layer gets the user requests from the view layer and processes them, with the necessary validations. It acts as an interface between Model and View. The requests are then sent to model for data processing. Once they are processed, the data is sent back to the controller and then displayed on the view. Let's consider the following code snippet that creates the controller using the EmployeeController class. EmployeeController.java Main Class Java fileThe following example displays the main file to implement the MVC architecture. Here, we are using the MVCMain class. MVCMain.java The MVCMain class fetches the employee data from the method where we have entered the values. Then it pushes those values in the model. After that, it initializes the view (EmployeeView.java). When view is initialized, the Controller (EmployeeController.java) is invoked and bind it to Employee class and EmployeeView class. At last the updateView() method (method of controller) update the employee details to be printed to the console. Output: Employee Details: Name: Anu Employee ID: 11 Employee Department: Salesforce Employee Details after updating: Name: Nirnay Employee ID: 11 Employee Department: Salesforce In this way, we have learned about MVC Architecture, significance of each layer and its implementation in Java.
Next TopicNarcissistic Number in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










