POJOPOJO in Java stands for Plain Old Java Object. It is an ordinary object, which is not bound by any special restriction. The POJO file does not require any special classpath. It increases the readability & re-usability of a Java program. POJOs are now widely accepted due to their easy maintenance. They are easy to read and write. A POJO class does not have any naming convention for properties and methods. It is not tied to any Java Framework; any Java Program can use it. The term POJO was introduced by Martin Fowler ( An American software developer) in 2000. it is available in Java from the EJB 3.0 by sun microsystem. Generally, a POJO class contains variables and their Getters and Setters. The POJO classes are similar to Beans as both are used to define the objects to increase the readability and re-usability. The only difference between them that Bean Files have some restrictions but, the POJO files do not have any special restrictions. Example:POJO class is used to define the object entities. For example, we can create an Employee POJO class to define its objects. Below is an example of Java POJO class: Employee.java: The above employee class is an example of an employee POJO class. If you are working on Eclipse, you can easily generate Setters and Getters by right click on the Java Program and navigate to Source-> Generate Getters and Setters. 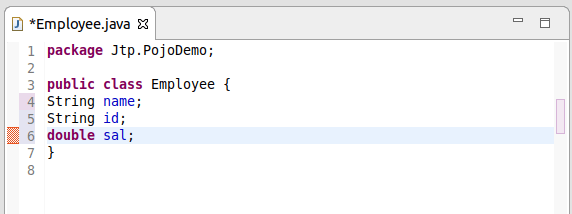
Right-click on the Java Program and Select Generate Getters and Setters. 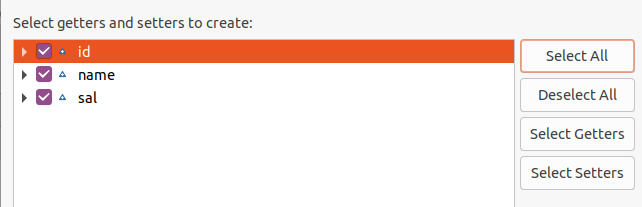
Now, click on the Generate option given at the bottom of the Generate window. It will auto-generate setters and getters. Properties of POJO classBelow are some properties of the POJO class:
Working of POJO ClassThe POJO class is an object class that encapsulates the Business logic. In an MVC architecture, the Controller interacts with the business logic, which contacts with POJO class to access the data. Below is the working of the POJO class. 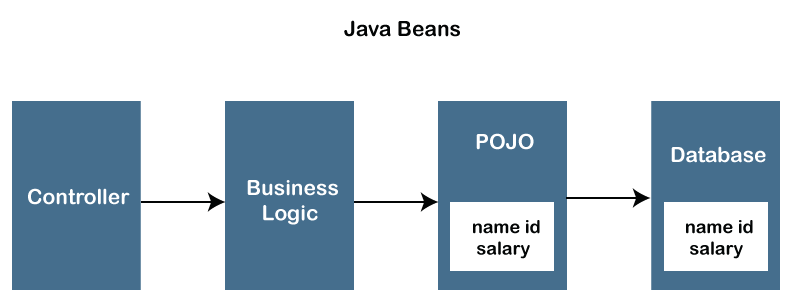
How to use POJO class in a Java ProgramThe POJO class is created to use the objects in other Java Programs. The major advantage of the POJO class is that we will not have to create objects every time in other Java programs. Simply we can access the objects by using the get() and set() methods. To access the objects from the POJO class, follow the below steps:
For example, create a MainClass.java class file within the same package and write the following code in it: MainClass.java: Output: Name: Alisha Id: A001 Salary: 200000.0 From the above example, we can see we have accessed the POJO class properties in MainClass.java. POJO is similar to Bean Class, so people often get confused between them; let's see the difference between the POJO and Bean. Java BeanJava Bean class is also an object class that encapsulates several objects into a single file ( Bean Class File). There are some differences between POJO and Bean. Java POJO and Bean in a nutshell:
POJO Vs. Bean
Next TopicPower Function in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










