Private Constructor in JavaIn Java, the constructor is a special type of method that has the same name as the class name. Internally, a constructor is always called when we create an object of the class. It is used to initialize the state of an object. In the same way, Java also allows us to create a private constructor. In this section, we will discuss private constructors in Java, rules for creating a private constructor, and its use cases. Also, we will see its implementation. What is a private constructor?Java allows us to declare a constructor as private. We can declare a constructor private by using the private access specifier. Note that if a constructor is declared private, we are not able to create an object of the class. Instead, we can use this private constructor in Singleton Design Pattern. Rules for Private ConstructorThe following rules keep in mind while dealing with private constructors.
Use Cases of Private ConstructorThe main purpose of using a private constructor is to restrict object creation. We also use private constructors to implement the singleton design pattern. The use-cases of the private constructor are as follows:
Let's see the implementation of the private constructor. Implementation of a Private ConstructorA.java Output: 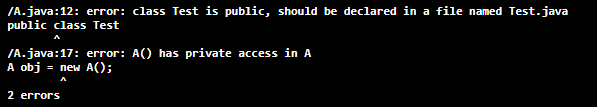
PrivateConstructorDemo.java Output: true
Next TopicScope of Variables in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










