Selection Statement in JavaSelection statements in Java are control flow statements that allow you to make decisions in your Code based on certain conditions. These statements enable your Java programs to execute different blocks of Code depending on whether specific conditions are true or false. Selection statements are fundamental to programming, allowing you to create dynamic, flexible, and responsive applications. There are three main types of selection statements in Java: 1. if Statement:The "if" statement is an essential component of programming that enables conditional execution of instructions based on a specified condition. The "if" statement assesses a specified condition, executing a predefined set of commands when the condition is true and skipping them otherwise. Essentially, it functions as a way to pose a question in code and generate a corresponding response based on the condition's evaluation. 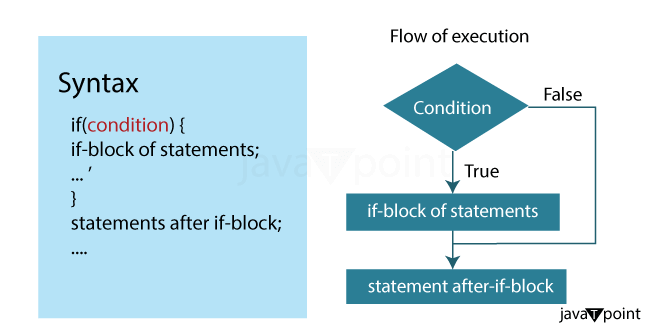
Syntax:
Filename: NumberClassifier.java Output: The entered number is positive. 2. if-else Statement:In Java programming, the if-else statement serves as a control flow construct that allows for the efficient implementation of conditional logic. By providing two separate blocks of code to execute based on whether a specified condition is met or not, this statement expands upon the functionality of the traditional if statement. Essentially, it offers a means of handling both true and false outcomes of a condition with ease. 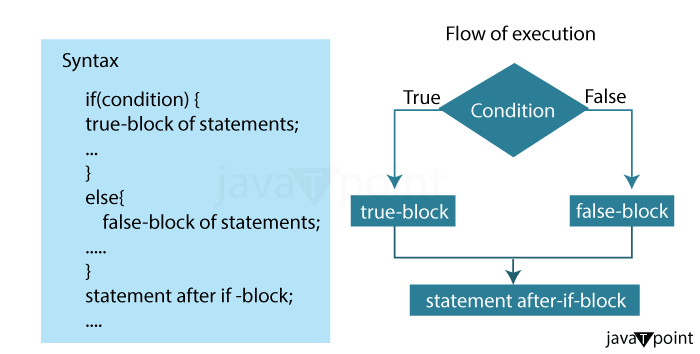
Syntax:
Filename: EligibilityChecker.java Output: Apologies, you are currently not eligible to vote. You will achieve voting eligibility in 8 year(s). 3. Nested if StatementIn Java, a nested if Statement is an if Statement that is inside another if Statement. It means you can have one or more if statements inside another if Statement's block. The inner if statements are executed only if the outer if Statement's condition is true. 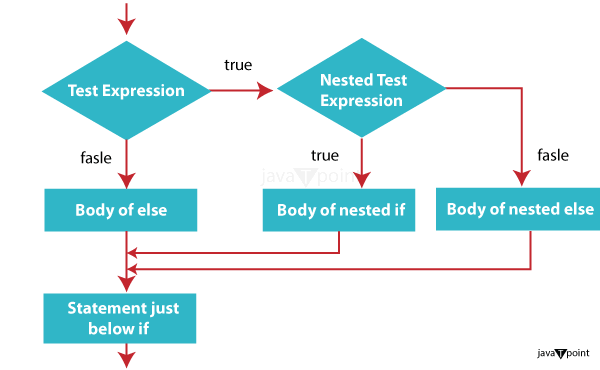
Syntax: In this structure, the condition is evaluated first. If it is true, the inner block of the Code is executed. Inside the inner block, condition2 is considered. If it is also true, the Code inside the inner if Statement is executed. Filename: NestedIfStatementExample.java Output: The given number is less than 100. It is a multiple of 5. Exiting the nested if-else block. 4. if- else if- else StatementIn Java, the if-else if-else Statement acts as a decision-making tool, enabling you to execute different code blocks based on various conditions. It's a versatile tool for handling multiple possible outcomes in your program. Think of it as a branching path where you choose the appropriate direction based on specific criteria. 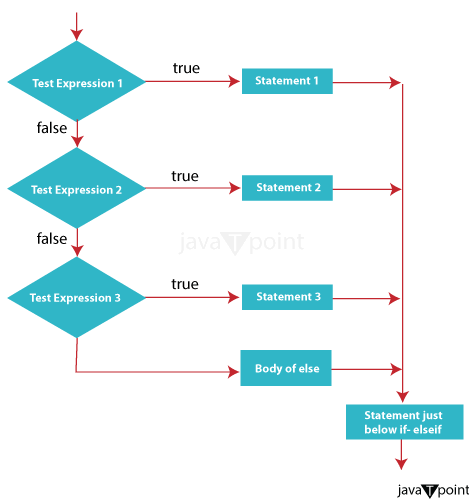
Syntax:
Filename: GradeCalculator.java Output: The student's exam score is: 85 Based on the score, the student's grade is: B 5. Switch StatementIn Java, the switch statement is a useful tool for controlling the flow of program execution based on a given expression's evaluation. It enables developers to simplify their code by condensing numerous conditional statements into a single statement. The switch statement assesses the value of the specified expression and subsequently matches it against various predefined constants (known as case labels) located inside the switch block. If a matching case is found, the corresponding code is executed. 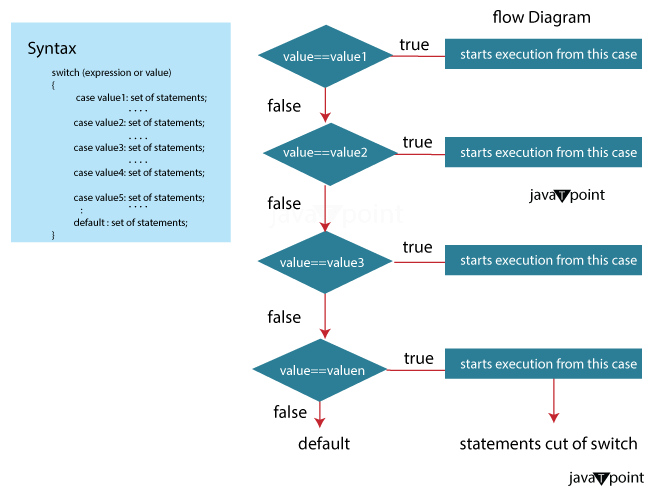
Syntax:
Filename: DayOfWeek.java Output: The entered day number corresponds to: Tuesday 6. JumpJump statements in Java are used to alter the normal flow of control in a program. These statements transfer the program's control to another part of the code based on specific conditions or requirements. Java provides three types of jump statements: break, continue, and return. a. break: In Java, the break statement is used to terminate the loop or switch statement it is within. When a break statement is encountered, the program exits the loop or switch Statement immediately, and the control is transferred to the following Statement after the loop or switch block. Filename: BreakExample.java Output: The first even number found in the range is: 2 b. continue: The continue statement is used to skip the current iteration of a loop and move to the next iteration. It is often used to bypass some specific logic within a loop iteration. 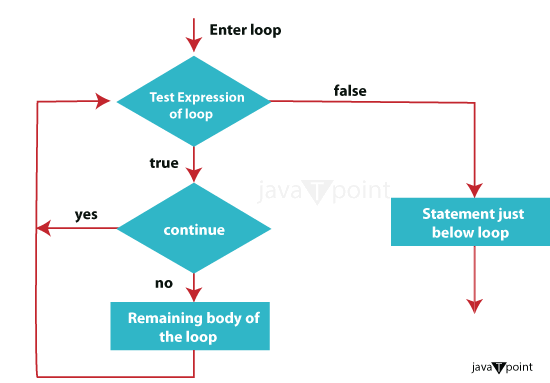
Filename: ContinueExample.java Output: Current number is: 1 Current number is: 2 Current number is: 4 Current number is: 5 c. return: The return statement is not limited to selection statements but is used to exit from a method and return a value. It can be used in various conditional and control flow scenarios to exit a method early. Filename: ReturnExample.java Output: Sum: 15 ConclusionSelection statements, also known as branching statements or conditional statements or decision-making statements, are vital components in Java programming. They allow developers to control the flow of a program's execution based on specific conditions, making the Code dynamic and responsive. In Java, there are several types of selection statements:
In Java, these are statements that control programs. They are used to choose an execution path if a given condition is satisfied.
Next TopicDifference Between Java 8 and Java 9
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









