Set Matrix Zeros in JavaIn this section, we will create Java programs to set matrix elements to zero with different logics. It is the most important problem usually asked in coding round interviews. Given a m*n matrix. If any element of the matrix is 0, set it's entire row and column to 0. Note that no extra array should be used to perform the operation. For example, consider the following matrix. 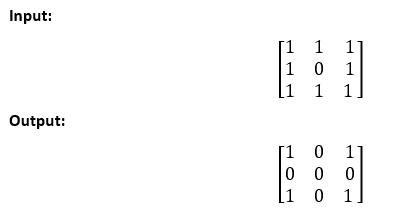
In the above array, the element of the second row and second column is 0. Hence, we will set all the elements of the second row and column to 0. Let's consider another matrix. 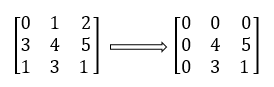
The problem can be solved in the following three ways:
Let's discuss the above approaches one by one. Brute Force ApproachIt is naive approach to set matrix zeros. In this approach, we traverse over the matrix and for every 0, we update the corresponding row and column to 0. The approach is very easy but it may lead to wrong answer. Then, what's the correct solution. Solution Steps
Pseudo Code In above approach, we have traversed each row and column of the corresponding cell of the matrix. The time complexity for the above approach is O(n*m(n+m)) and the space complexity is O(n*m), for storing the auxiliary matrix. But our task is to perform the same without using extra space. The following approaches demonstrate the same. Using HashTableIn this perform the same, we will use HashTable. First, we will create a HashTable for all rows and columns of the matrix and set them to false. If the value updated to true in any row and column, it means update that particular row and column's value to 0. Solution Steps
Let's converts the above steps into logic. Pseudo Code For the above approach the time complexity is O(n*m). Because Creating and filling values in two Hash Tables [O(n+m)] + Traversing the matrix [O(n*m)] + Updating the matrix [O(n*m)]. Hence, the time complexity is O(n*m). The space complexity is O(n+m) because we are using two HashTable for storing the elements. The above approach is also not optimized. The optimized solution can be achieved by using the in-place hashing. Using In-Place HashingIn this approach, we store hash for row and column in the matrix itself. We can use the first row and first column of the matrix to store the status of the rows and columns respectively. The problem will occur for the status of first row and column that can be handled using two variables. Solution Steps
Let's convert the above steps into logic. Pseudo Code The time complexity for the above approach is O(m*n) because we have traversed over the first row and first column i.e. O(m) and O(n), traversing and updating the matrix i.e. O(m*n), and at last updating the first row and first column i.e. O(m) + O(n). Therefore, the time complexity is O(m*n). We have not used an auxiliary array for the matrix, so the space complexity is O(1). Java Program to Set Matrix ZerosThe following Java program use extra space to set elements to zeros. SetMatrixZeros.java Output: 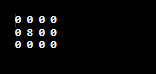
Let's see another Java program in which we have not used auxiliary space to set matrix elements to zeros. SetMatrixToZero.java Output: 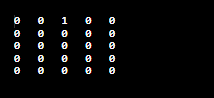
Let's solve the same problem using Set. SetMatrixElementsToZero.java Output: 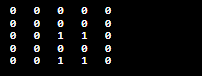
We observe that in the above approach, we have not used any extra space. So, it is an efficient approach. We must consider while setting a matrix to zeros.
Next TopicFind Number of Island in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










