What is JNDI in JavaThe interface used by the Java programming language is by the name Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI). It is an API (application programming interface) that communicates with servers and uses naming conventions to get files from databases. A word or a single phrase might serve as the naming convention. It can also be added to a socket in order to use servers that transfer flat files or data files in a project to perform socket programming. In browsers with a lot of directories, it can also be used on web pages. Using the Java programming language, JNDI gives Java users the ability to search Java objects. The architecture of JNDI in the Java Interface:The Service Provider Interface (SPI) which is made up of an API and an interface known as JNDI. 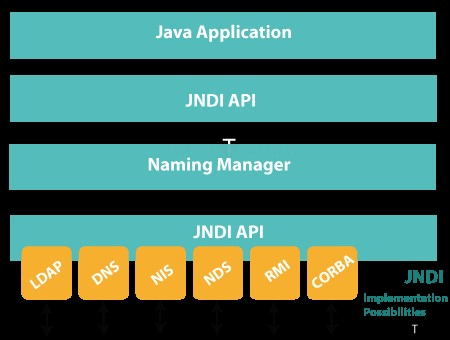
JNDI, is visible in the architecture as a series of various directories. There is a connection between the Java program and the JNDI architecture, as seen in this diagram. Since the interface is used to connect to many directories, the levels make it apparent that the JNDI API is above it. The following lists a few of the directory services.
The JNDI SPI connects with the directories listed above to create a platform with the JNDI implementation choices. JNDI Packages:In Java, JNDI SPI is specifically used by five packages. Some of the packages use the javax.naming language. There are classes and interfaces for name service access in the package known as javax.naming. Lookup, list Bindings, and Name are a few of the available functions. Java.naming.directory is the second one. This package is a more sophisticated version of Java.naming directory that helps in obtaining the data as objects. The packages java. Naming. event and Java. naming. spi are two more examples. Additionally, JNDI is a key component of three of the newest Java technologies. They are as follows:
In the Java programming language, there are two functions called bind() and lookup() that are used to name objects and look them up in directories, respectively. Context.bind("name", object) Any name can be given to the current object in the directory in this case by changing the name. In this instance of the bind function, the object's name has been set. Object hello= Context.lookup("name") The hello object in this function searches the directory for the item's name. Depending on the type of directory supported, different types of serialized or non-serialized data are also used. Example of JNDI Interface in Java:This program, which operates through a menu system, asks the user to input the principal amount before printing the simple interest, compound interest, and the difference between the simple and compound interest based on the user's preferences. Additionally, the program ends if the user decides not to utilize it any further. The amount of time it takes for interest to start accruing is 7 years, and the rate of interest is fixed at 8.5 percent. All interest rates are calculated as a result. The development of a menu-driven application that allows users to enter a principal amount and calculate simple interest, compound interest, and the absolute difference between the two. Implementation:FileName: JndiExample.java Output: 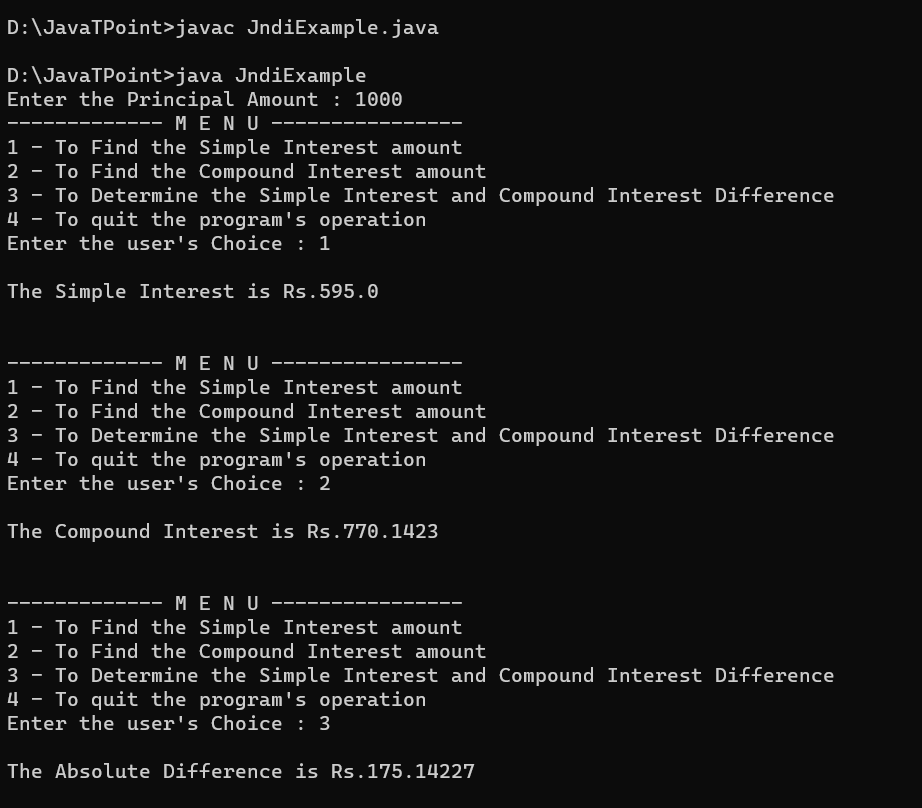
Benefits of JNDI Interface in Java:The advantages of a JNDI naming service include:
Limitations of JNDI Interface in Java:JNDI has some restrictions and, regrettably, is not intended for high-performance environments:
Next TopicBacktracking in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









