Design of JDBCJava Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an Application Programming Interface (API), from Sun microsystem that is used by the Java application to communicate with the relational databases from different vendors. JDBC and database drivers work in tandem to access spreadsheets and databases. Design of JDBC defines the components of JDBC, which is used for connecting to the database. Components of JDBC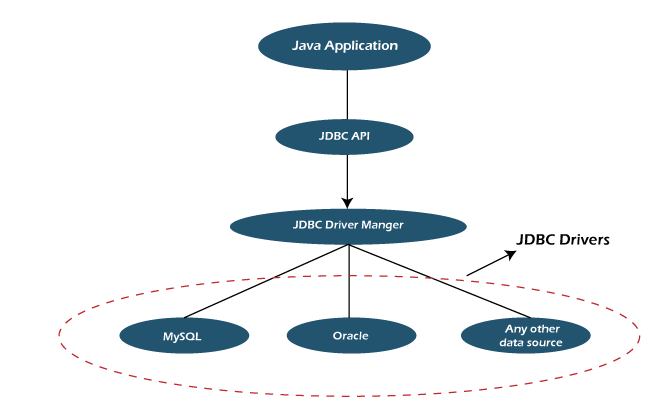
JDBC has four major components that are used for the interaction with the database.
1) JDBC API: JDBC API provides various interfaces and methods to establish easy connection with different databases. 2) JDBC Test suite: JDBC Test suite facilitates the programmer to test the various operations such as deletion, updation, insertion that are being executed by the JDBC Drivers. 3) JDBC Driver manager: JDBC Driver manager loads the database-specific driver into an application in order to establish the connection with the database. The JDBC Driver manager is also used to make the database-specific call to the database in order to do the processing of a user request. 4) JDBC-ODBC Bridge Drivers: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Drivers are used to connect the database drivers to the database. The bridge does the translation of the JDBC method calls into the ODBC method call. It makes the usage of the sun.jdbc.odbc package that encompasses the native library in order to access the ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) characteristics. Note: Since Java 8, the JDBC-ODBC drivers have been removed. Oracle suggests using drivers provided by the vendor of the database.Architecture of JDBC1) Application: It is the Java servlet or an applet that communicates with the data source. 2) The JDBC API: It allows the Java programs to perform the execution of the SQL statements and then get the results. A few of the crucial interfaces and classes defined in the JDBC API are the following:
3) DriverManager: DriverManager plays a crucial role in the architecture of JDBC. It uses database-specific drivers to connect the enterprise applications to various databases. 4) JDBC drivers: To interact with a data source with the help of the JDBC, one needs a JDBC driver which conveniently interacts with the respective data source. Different Types of Architecture of JDBCThe architecture of the JDBC consists of two and three tiers model in order to access the given database. Two-tier model: In this model, the application interacts directly with the source of data. The JDBC driver establishes the interaction between the data source and the application. When a query is sent by the user to the data source, the reply of those sent queries is sent directly to the user. The source of data can be located on a different machine, and that machine is connected to the user machine following a client-server paradigm, where the machine which is sending the query is the client machine, and the machine that is sending the result of those queries is acting as the server. Three-tier model: In this model, the queries of the user are being sent to the middle-tier services, from where the commands are sent again to the source of data. The answers to those queries are reverted to the middle tier, and from there, it is again sent to the user. JDBC WorkingAny Java application that needs to interact with a database needs to be programmed using the JDBC API. The JDBC driver that supports the data sources like Oracle or MySql needs to be added; then, only the interaction happens with the data source. FileName: JDBCExample.java Output: Database connection established Employee ID: 100, Employee Name: Nitesh Singh, Department: Project Management Employee ID: 104, Employee Name: Amit Kumar, Department: Game Development Employee ID: 105, Employee Name: Amrit Kumar, Department: Database Management Employee ID: 109, Employee Name: Rohit Kumar, Department: Software Testing Employee ID: 120, Employee Name: Ajeet Chouhan, Department: Software Design Employee ID: 155, Employee Name: Aman Jatt, Department: Art Integration The Connection is closed. Explanation: The above Java application connects to the MySQL Database System. Therefore, we need the driver for MySQL in order to access the data. That driver (com.mysql.jdbc.Driver) is provided in the mysqlconnector.jar file, which must be included in the classpath when the above program is executed. Similarly, if instead of MySQL had we used Oracle, then the drivers corresponding to Oracle must be used.
Next TopicJava Anon Proxy
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









