DevOps Architecture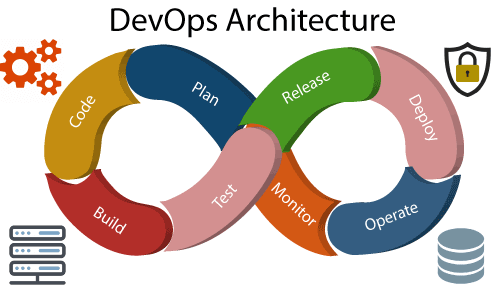
Development and operations both play essential roles in order to deliver applications. The deployment comprises analyzing the requirements, designing, developing, and testing of the software components or frameworks. The operation consists of the administrative processes, services, and support for the software. When both the development and operations are combined with collaborating, then the DevOps architecture is the solution to fix the gap between deployment and operation terms; therefore, delivery can be faster. DevOps architecture is used for the applications hosted on the cloud platform and large distributed applications. Agile Development is used in the DevOps architecture so that integration and delivery can be contiguous. When the development and operations team works separately from each other, then it is time-consuming to design, test, and deploy. And if the terms are not in sync with each other, then it may cause a delay in the delivery. So DevOps enables the teams to change their shortcomings and increases productivity. Below are the various components that are used in the DevOps architecture: 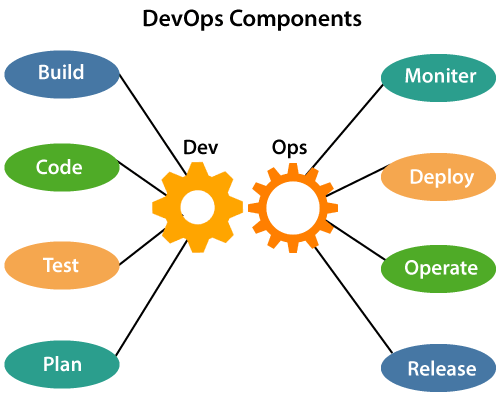
1) BuildWithout DevOps, the cost of the consumption of the resources was evaluated based on the pre-defined individual usage with fixed hardware allocation. And with DevOps, the usage of cloud, sharing of resources comes into the picture, and the build is dependent upon the user's need, which is a mechanism to control the usage of resources or capacity. 2) CodeMany good practices such as Git enables the code to be used, which ensures writing the code for business, helps to track changes, getting notified about the reason behind the difference in the actual and the expected output, and if necessary reverting to the original code developed. The code can be appropriately arranged in files, folders, etc. And they can be reused. 3) TestThe application will be ready for production after testing. In the case of manual testing, it consumes more time in testing and moving the code to the output. The testing can be automated, which decreases the time for testing so that the time to deploy the code to production can be reduced as automating the running of the scripts will remove many manual steps. 4) PlanDevOps use Agile methodology to plan the development. With the operations and development team in sync, it helps in organizing the work to plan accordingly to increase productivity. 5) MonitorContinuous monitoring is used to identify any risk of failure. Also, it helps in tracking the system accurately so that the health of the application can be checked. The monitoring becomes more comfortable with services where the log data may get monitored through many third-party tools such as Splunk. 6) DeployMany systems can support the scheduler for automated deployment. The cloud management platform enables users to capture accurate insights and view the optimization scenario, analytics on trends by the deployment of dashboards. 7) OperateDevOps changes the way traditional approach of developing and testing separately. The teams operate in a collaborative way where both the teams actively participate throughout the service lifecycle. The operation team interacts with developers, and they come up with a monitoring plan which serves the IT and business requirements. 8) ReleaseDeployment to an environment can be done by automation. But when the deployment is made to the production environment, it is done by manual triggering. Many processes involved in release management commonly used to do the deployment in the production environment manually to lessen the impact on the customers.
Next TopicDevOps Lifecycle
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









