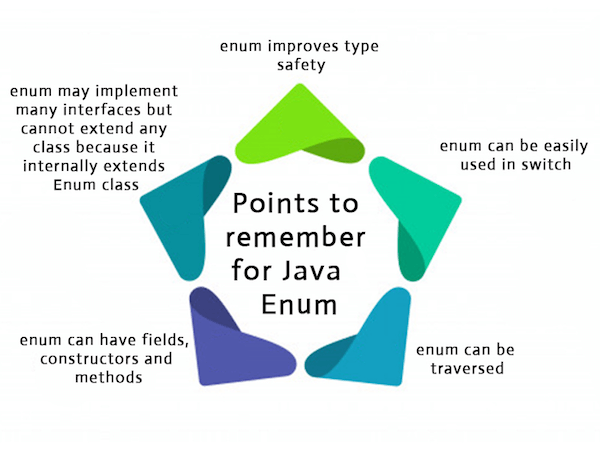
Java EnumsThe Enum in Java is a data type which contains a fixed set of constants. It can be used for days of the week (SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, and SATURDAY) , directions (NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, and WEST), season (SPRING, SUMMER, WINTER, and AUTUMN or FALL), colors (RED, YELLOW, BLUE, GREEN, WHITE, and BLACK) etc. According to the Java naming conventions, we should have all constants in capital letters. So, we have enum constants in capital letters. Java Enums can be thought of as classes which have a fixed set of constants (a variable that does not change). The Java enum constants are static and final implicitly. It is available since JDK 1.5. Enums are used to create our own data type like classes. The enum data type (also known as Enumerated Data Type) is used to define an enum in Java. Unlike C/C++, enum in Java is more powerful. Here, we can define an enum either inside the class or outside the class. Java Enum internally inherits the Enum class, so it cannot inherit any other class, but it can implement many interfaces. We can have fields, constructors, methods, and main methods in Java enum. Points to remember for Java Enum
Simple Example of Java EnumTest it NowOutput: WINTER SPRING SUMMER FALL Let us see another example of Java enum where we are using value(), valueOf(), and ordinal() methods of Java enum. Output: WINTER SPRING SUMMER FALL Value of WINTER is: WINTER Index of WINTER is: 0 Index of SUMMER is: 2 Note: Java compiler internally adds values(), valueOf() and ordinal() methods within the enum at compile time. It internally creates a static and final class for the enum. What is the purpose of the values() method in the enum?The Java compiler internally adds the values() method when it creates an enum. The values() method returns an array containing all the values of the enum. What is the purpose of the valueOf() method in the enum?The Java compiler internally adds the valueOf() method when it creates an enum. The valueOf() method returns the value of given constant enum. What is the purpose of the ordinal() method in the enum?The Java compiler internally adds the ordinal() method when it creates an enum. The ordinal() method returns the index of the enum value. Defining Java EnumThe enum can be defined within or outside the class because it is similar to a class. The semicolon (;) at the end of the enum constants are optional. For example: Or, Both the definitions of Java enum are the same. Java Enum Example: Defined outside classTest it NowOutput: WINTER Java Enum Example: Defined inside classTest it NowOutput: WINTER Java Enum Example: main method inside EnumIf you put main() method inside the enum, you can run the enum directly. Output: WINTER Initializing specific values to the enum constantsThe enum constants have an initial value which starts from 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. But, we can initialize the specific value to the enum constants by defining fields and constructors. As specified earlier, Enum can have fields, constructors, and methods. Example of specifying initial value to the enum constantsTest it NowOutput: WINTER 5 SPRING 10 SUMMER 15 FALL 20 Constructor of enum type is private. If you don't declare private compiler internally creates private constructor.Internal code generated by the compiler for the above example of enum typeCan we create the instance of Enum by new keyword?
Can we have an abstract method in the Enum?Yes, Of course! we can have abstract methods and can provide the implementation of these methods. Java Enum in a switch statementWe can apply enum on switch statement as in the given example: Example of applying Enum on a switch statement Test it NowOutput: monday
Next TopicJava Annotation
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










