Java ConstantAs the name suggests, a constant is an entity in programming that is immutable. In other words, the value that cannot be changed. In this section, we will learn about Java constant and how to declare a constant in Java. What is constant?Constant is a value that cannot be changed after assigning it. Java does not directly support the constants. There is an alternative way to define the constants in Java by using the non-access modifiers static and final. How to declare constant in Java?In Java, to declare any variable as constant, we use static and final modifiers. It is also known as non-access modifiers. According to the Java naming convention the identifier name must be in capital letters. Static and Final Modifiers
The syntax to declare a constant is as follows: For example, price is a variable that we want to make constant. Where static and final are the non-access modifiers. The double is the data type and PRICE is the identifier name in which the value 432.78 is assigned. In the above statement, the static modifier causes the variable to be available without an instance of its defining class being loaded and the final modifier makes the variable fixed. Here a question arises that why we use both static and final modifiers to declare a constant? If we declare a variable as static, all the objects of the class (in which constant is defined) will be able to access the variable and can be changed its value. To overcome this problem, we use the final modifier with a static modifier. When the variable defined as final, the multiple instances of the same constant value will be created for every different object which is not desirable. When we use static and final modifiers together, the variable remains static and can be initialized once. Therefore, to declare a variable as constant, we use both static and final modifiers. It shares a common memory location for all objects of its containing class. Why we use constants?The use of constants in programming makes the program easy and understandable which can be easily understood by others. It also affects the performance because a constant variable is cached by both JVM and the application. Points to Remember:
Let's see some examples in which we have used constants. Example 1: Declaring Constant as PrivateConstantExample1.java Output: 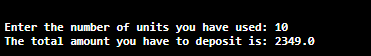
Example 2:ConstantExample2.java Output: 
Example 3: Declaring Constant as PublicIn the following example, we have declared constant PI as public. Inside the main() method, we have assigned 3.15 in the constant PI. After that, we have invoked the printValue() method. When we execute the program, it shows an error cannot assign a value to the final variable PI. ConstantExample3.java Output: 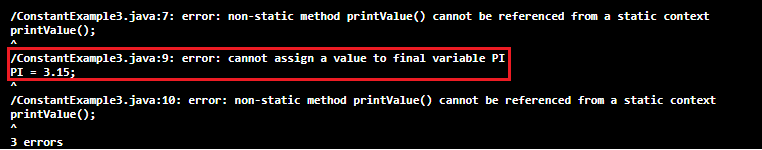
Using Enumeration (Enum) as Constant
Example of EnumerationOutput: 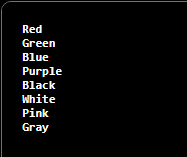
Next TopicJava Tokens
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









