Sudoku in JavaSudoku is a logic-based puzzle that uses combinatorial-number placement. In a classic Sudoku puzzle, the task is to fill the numbers in a 9 x 9 grid laced in such a way that each row, each column, and each of the sub-grid of the size 3 x 3 contains all the numbers from 1 to 9 (1 and 9 inclusive). Pictorially, a classic Sudoku puzzle is represented as follows: 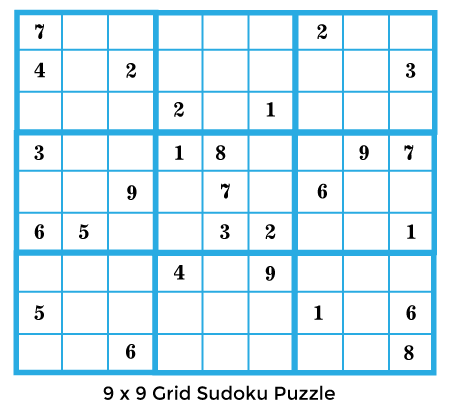
In the code, we will provide the input of the above-mentioned 9 x 9 grid as: The grid has a lot of 0's in it. It indicates that the cells of the grid containing 0 are empty and need to be filled. To fill the numbers in the empty cells, we will use backtracking approach to solve the puzzle. Using Backtracking ApproachIn this approach, we assign numbers one-by-one to empty cells. Before assigning any number, we check whether the same is present in the current column, current row, or the current 3 x 3 sub-grid or not. If the same number is present, then we take another number and check its safety. If the same number is not present, then the number is assigned, and then we check recursively whether this assignment leads to the solution or not. If the assignment does not lead to the solution, then we take another number and repeat the process. If none of the numbers from 1 to 9 leads to a solution, then false is returned, and the message "the solution does not exit" is displayed. AlgorithmStep 1: Create a function whose work is to check whether the grid is safe or not when a number is assigned to the current index. For the boxes, column, and row, create a HashMap for storing the frequency of the numbers. If the HashMap shows the frequency of any number greater than 1, then return false, else return true. Instead of HashMap, one can use loops also. Step 2: Write a recursive function that accepts the grid as the input. Step 3: Look for the unassigned location in the grid. If the unassigned location is present, then assign a number from 1 to 9, check if the number that is assigned to the current index makes the grid safe or not If the grid is safe, then recursively invoke the method for all the safe cases from 1 to 9. if any of the recursive calls return true, then terminate the loop by returning true. If there is no recursive call that returns true, then return false. Step 4: If the total number of unassigned locations in the grid is zero, then return true. ImplementationLet's see the implementation based on the algorithm defined above. FileName: SudokuPuzzle.java Output: The grid is: 7 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 4 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 3 0 0 1 8 0 0 9 7 0 0 9 0 7 0 6 0 0 6 5 0 0 3 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 4 0 9 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 8 The solution of the grid is: 7 6 5 8 4 3 2 1 9 4 1 2 6 9 7 8 5 3 9 3 8 2 5 1 7 6 4 3 2 4 1 8 6 5 9 7 1 8 9 5 7 4 6 3 2 6 5 7 9 3 2 4 8 1 8 7 1 4 6 9 3 2 5 5 9 3 7 2 8 1 4 6 2 4 6 3 1 5 9 7 8 Time complexity: For every empty cell, there are 9 options available, so the time complexity is O(9 ^ (n x n)). Space Complexity: O(n x n). It is because the output grid also has to be stored.
Next TopicChristmas Tree Pattern in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










