CRC Program in JavaCRC stands for Cyclic Redundancy Check. It was invented by W. Wesley Peterson in 1961. It is an error detecting technique through which we can detect the error in digital networks(or communication channel or digital data) and storage devices. It is used to trace the accidental changes in the digital data. In this section, we will learn how to calculate and perform CRC through a Java program. Let's understand CRC in detail. CRC MechanismIt is an error detection mechanism in which a special number is added to the block of data. The primary goal to add the number is to identify the changes during the transmission or storage. It is calculated twice, once at the sender side during the data transmission and recalculated at the receiver side. It compares data bit by bit with originally transmitted values. If any error (corrupted bit) occurs during the transmission of data, the CRC does not match with the originally transmitted value. We can easily understand the CRC mechanism by the following figure. 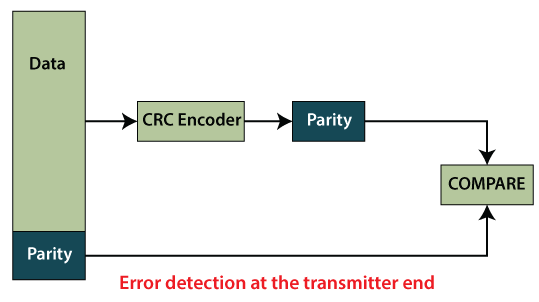
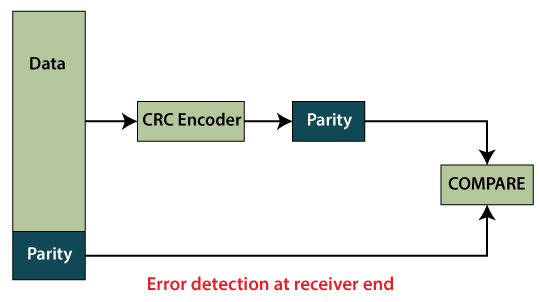
For example, a single corrupted bit in the data results in a one-bit change in the calculated CRC, but multiple corrupted bits may cancel each other out. If multiple bits are corrupted or changed is known as a burst error. There is some other error detection mechanism like Vertical Redundancy Check (VRC)and Longitudinal Redundancy Check (LRC), but CRC is more powerful in comparison with others. The algorithm of CRC is more complex because it uses binary division to calculate CRC. The divisor is generated using polynomials. So, CRC is also called polynomial code checksum. Following are the steps used in CRC for error detection:
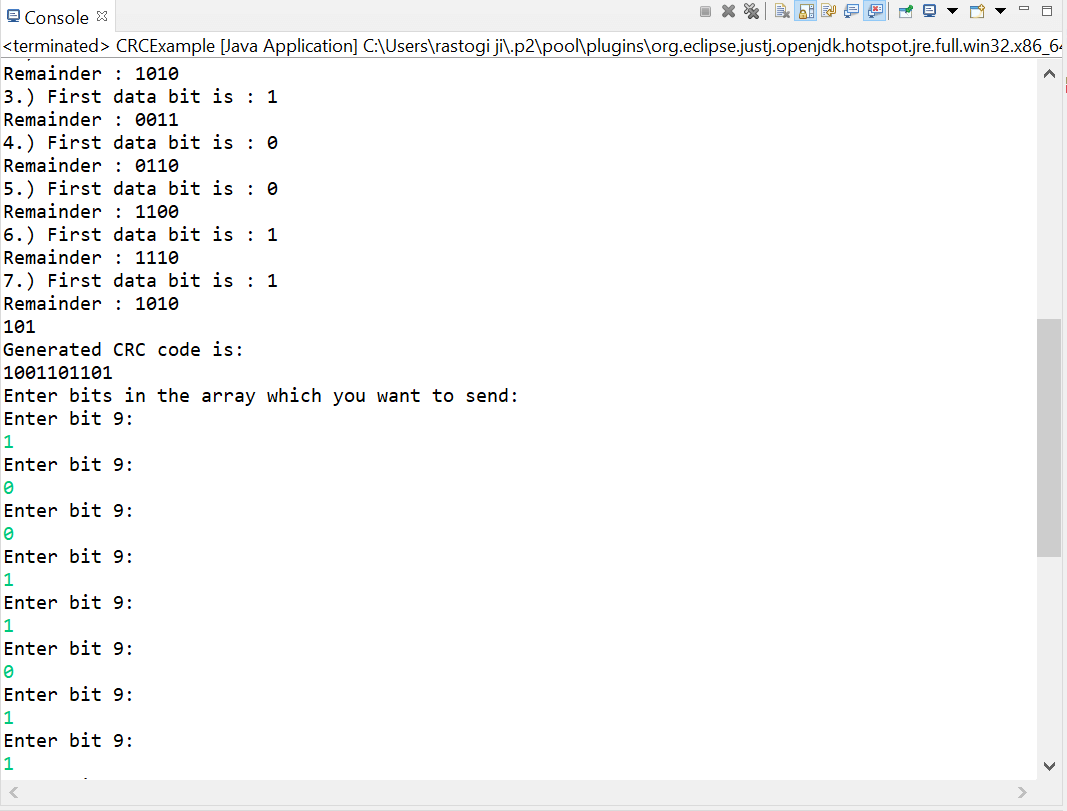
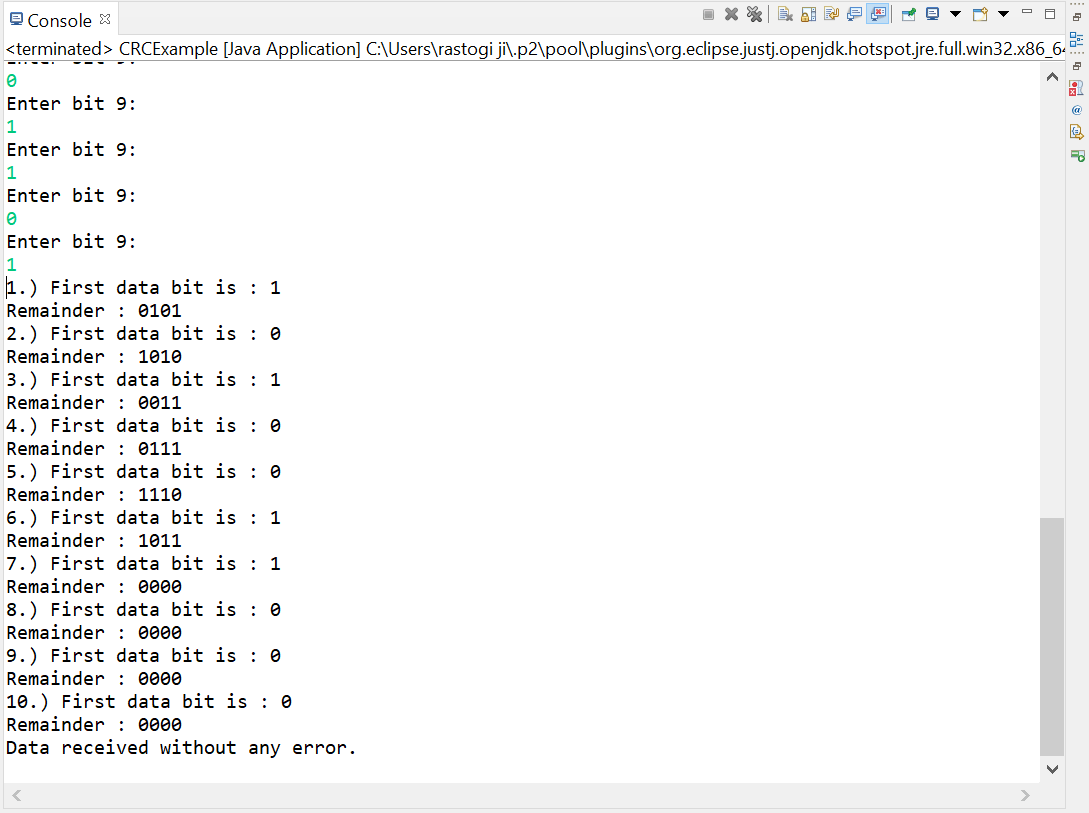
Let's take an example and understand how CRC works: Suppose the original data is 11100 and the divisor is 1001.
CyclicRedundancyCheck.java Output: 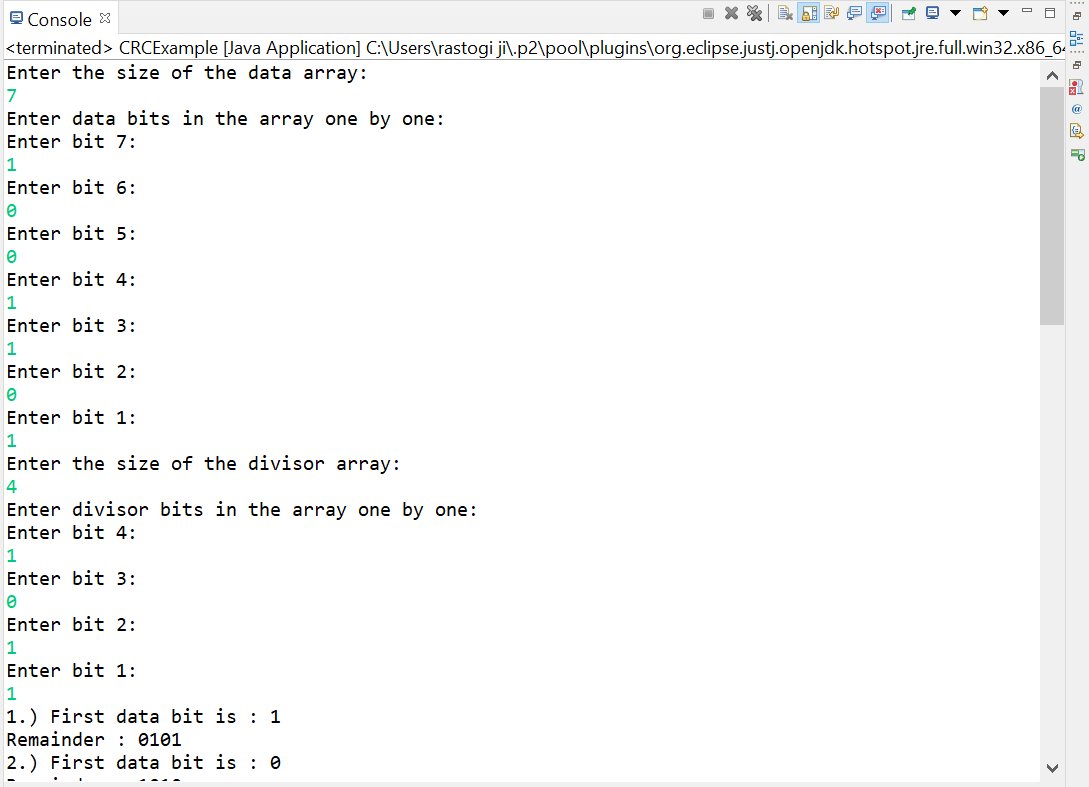
Next TopicFileNotFoundException in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










