Linux File OwnershipEvery Linux system have three types of owner:
Users and groups can be locally managed in /etc/psswd or /etc/group. Syntax: 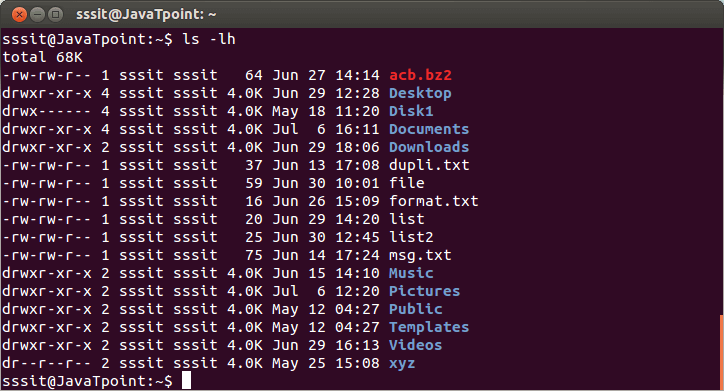
Look at the above snapshot, all the listed files and directories have the same user and group that is sssit.First sssit column denotes the user and second column denotes the group. Listing User AccountsTo know the local users account, following command can be used. It list out all the local users from the system. Syntax: 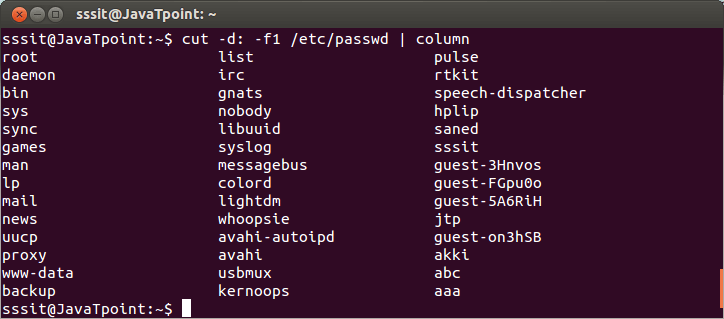
Linux chgrp: change groupThe chgrp command can be abbreviated as change group. You can change the group owner of the file using chgrp command. Syntax: Example: 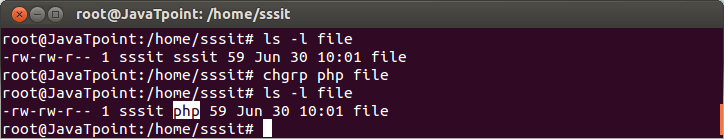
Look at the above snapshot, earlier 'file' group was sssit. But after passing the command "chgrp php file" , we have changed the group to php (we have highlighted php just to show you). Note: Only root user have the permissison to change the owner or group of the files in the system.Linux chown: change ownerCommand chown is used to change the owner of the file. Syntax: Example: 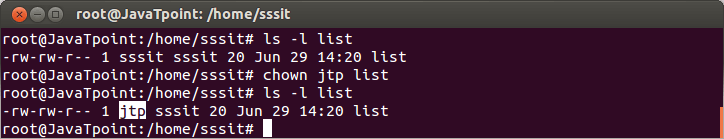
Look at the above snapshot, we have changed the owner of the file list from sssit to jtp. Command chown can also be used to change both user owner and group. Syntax: Example: 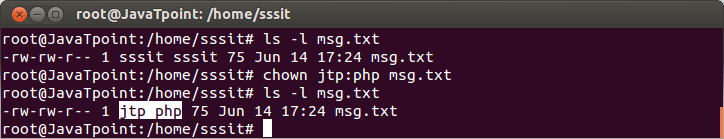
Look at the above snapshot, both user owner and group are changed to jtp and php respectively. List of Special FilesWhen we type ls -l command, ten characters are displayed before user owner and group. First character tells us about the type of the file. Following are the file types:
Examples of file type: 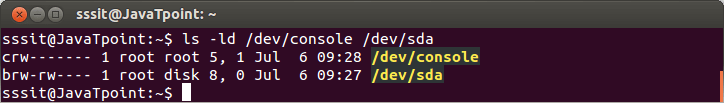
Look at the above snapshot, first letter c denotes the character device and b denotes the blocked device. 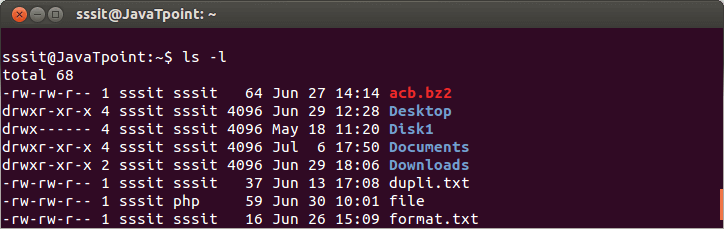
Look at the above snapshot, first letter (-) denotes the normal file and d denotes the directory.
Next TopicLinux chgrp Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









