Linux Shell CommandsIn Linux, commands are ways or instructions through which you can instruct your system to do some action. Commands are executed in the command line. Syntax: There are some commands which don't have any option or don't accept any argument such as 'clear' and 'pwd'. clear The 'clear' command clears out all the previous commands and outputs from terminal display. pwd The 'pwd' command stands for 'print working directory'. It doesn't accept any option or argument and displays the detail of current working directory. Types of CommandsExternal or built-in commands Built-in commands are internal commands that are built-in the shell. Built-in commands are called from the shell and executed directly within the shell itself. You can list all built-in commands with the help of 'help' and 'compgen -b' command. Some example of built-in commands are 'pwd', 'help', 'type', 'set', 'unset', etc. External commands are other than built-in commands. These commands are programs which have their own binary and located in the filesystem. These are the commands that your system offer and are totally shell independent. Mostly these commands reside in /bin, /sbin, /usr/sbin. type commandLinux 'type' command tell us whether a command given to the shell is a built-in or external command. Syntax: Example: 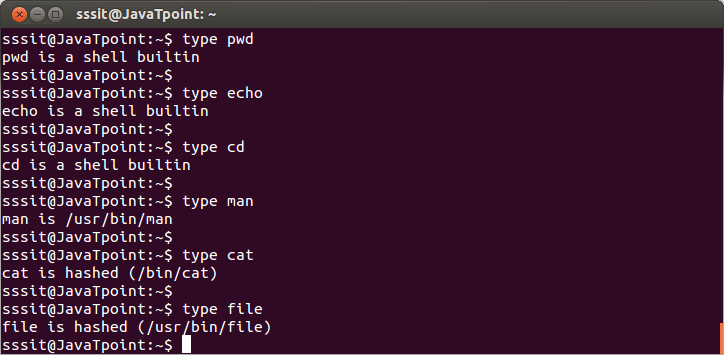
Look at above snapshot, commands like 'pwd' and 'cd' are built-in commands while commands 'man', 'cat', and 'file' are external commands. Linux 'type' command also tells whether a command is aliased or not. Example: 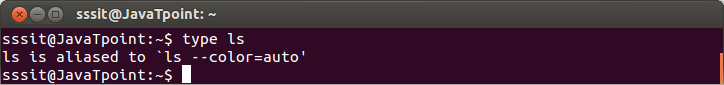
Look at the above snapshot, 'type' command shows that 'ls' is an aliased command. type -aThe 'type -a' option tells about all type of command whether it is built-in, external, or aliased. Some commands are both external and built-in commands. But built-in command will always takes priority until and unless path of external command is mentioned. Syntax: Example: 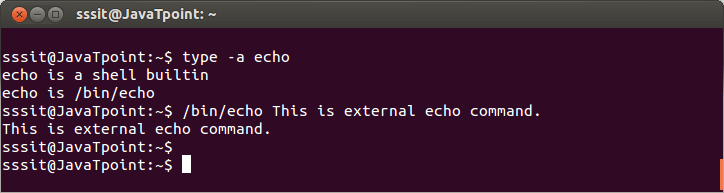
Look at the above snapshot, 'echo' command is internal as well as external. To use external 'echo' command, path "/bin/echo" is mentioned. whichLinux 'which' command locates the path of a command. Syntax: Example: 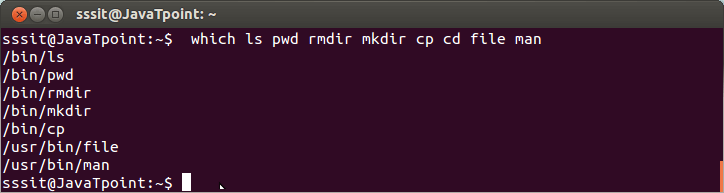
Look at the above snapshot, except 'cd' command, all other commands are external commands because bash has displayed their external path.
Next TopicLinux Aliases
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










