Linux I/O RedirectionRedirection can be defined as changing the way from where commands read input to where commands sends output. You can redirect input and output of a command. For redirection, meta characters are used. Redirection can be into a file (shell meta characters are angle brackets '<', '>') or a program ( shell meta characters are pipesymbol '|'). Standard Streams In I/O RedirectionThe bash shell has three standard streams in I/O redirection:
Redirection Into A FileEach stream uses redirection commands. Single bracket '>' or double bracket '>>' can be used to redirect standard output. If the target file doesn't exist, a new file with the same name will be created. Overwrite Commands with a single bracket '>' overwrite existing file content.
Note: Writing '1>' or '>' and '0<' or '<' is same thing. But for stderr you have to write '2>'. Syntax: Example: 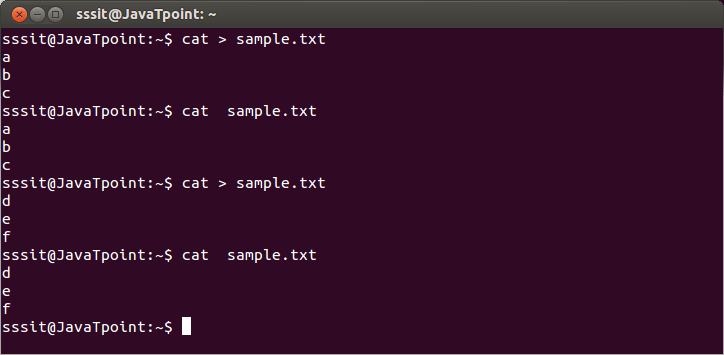
Look at the above snapshot, command "cat > sample.txt" has created 'sample.txt' with content 'a, b, c'. Same file 'sample.txt' is created again with command "cat > sample.txt" and this time it overwrites earlier file content and only displays 'd, e, f '. AppendCommands with a double bracket '>>' do not overwrite the existing file content.
Syntax: Example: 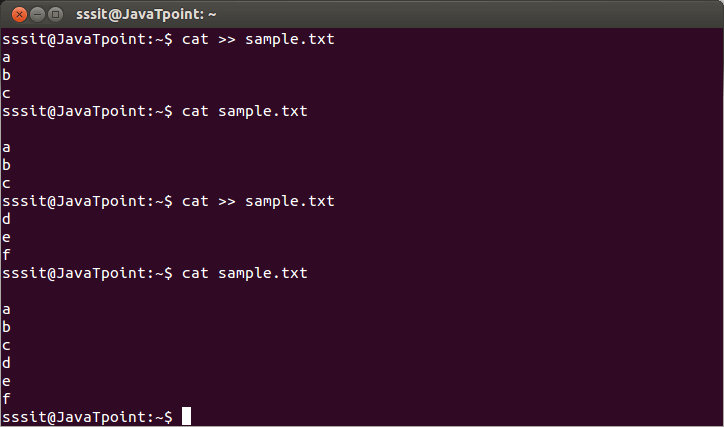
Look at the above snapshot, here again we have created two files with the same name using '>>' in command "cat >> sample.txt". But this time, content doesn't overwrite and everything is displayed. Redirection Into A ProgramPipe redirects a stream from one program to another. When pipe is used to send standard output of one program to another program, first program's data will not be displayed on the terminal, only the second program's data will be displayed. Although the functionality of pipe may look similar to that of '>' and '>>' but has a significance difference. Pipe redirects data from one program to another while brackets are only used in redirection of files. Example: 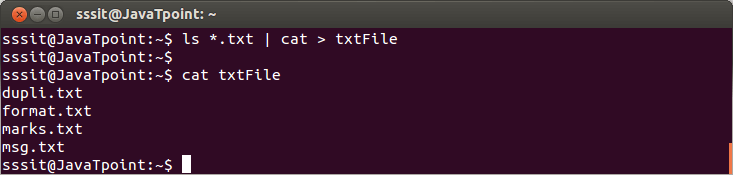
Look at the above snapshot, command "ls *.txt | cat > txtFile" has put all the '.txt' files into a newly created file 'txtFile'.
Next TopicLinux Input Redirection
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









