Linux aliasesLinux 'alias' command replaces one string from the shell with another string. It is a shell built-in command. It converts a complicated command into a simpler command or in other words, it creates a shortcut by replacing it with the simpler one. Making 'alias' in command line creates a temporary 'alias'. Temporary aliases are only available until you exit the shell. To make permanent 'alias' store it in bash startup files. Note: There will be no space on either side of (=) sign while typing 'alias' command. Quotes are necessary if there are more than one word in the string being aliased. alias syntax: Creating an aliasHere, we are going to use following options for creating an alias.
1) Creating alias for 'file' command as 'fi'Syntax: Example: 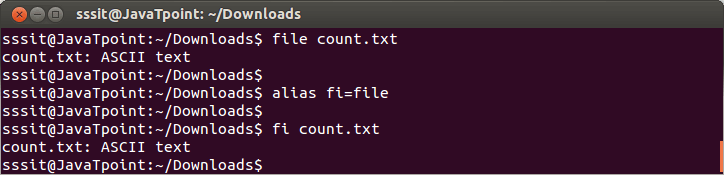
Look at the above snapshot, 'file' command is aliased as 'fi' through command "alias fi=file". 2) Creating alias for 'ls-l' command as 'll'Syntax: Example: 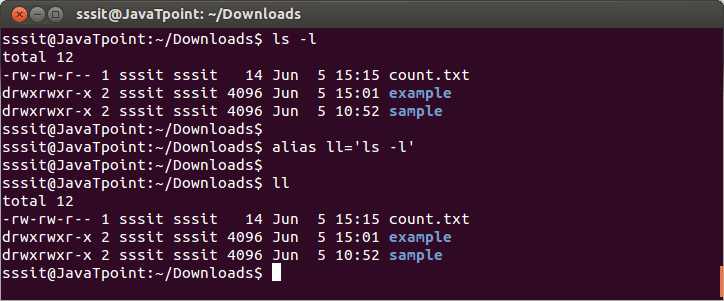
Look at the above snapshot, 'ls -l' command is aliased as 'll' through command "alias ll='ls -l' ". 3) Creating alias with two argumentsSyntax: Example: 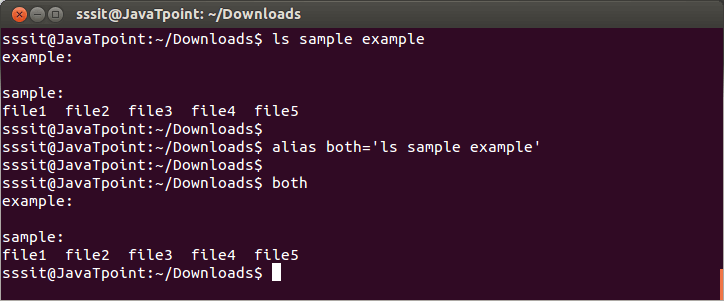
Look at the above snapshot, 'ls sample example' command is aliased as 'both' through command "alias both='ls sample example' ". 4) Creating alias for a pathSyntax: Example: 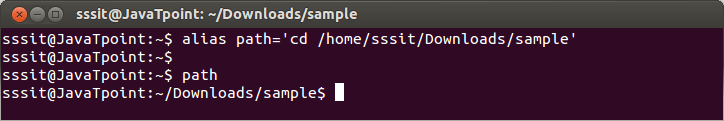
Look at the above snapshot, 'cd /home/sssit/Downloads/sample' command is aliased as 'path' through command "alias path='cd /home/sssit/Downloads/sample' ". How to remove aliasWith the help of 'unalias' command you can remove created alias. Syntax: Example: 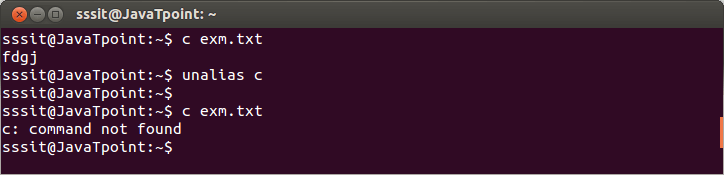
Look at the above snapshot, alias 'c' work as 'cat' command. After removing 'c' by the command "unalias c" we got an error message.
Next TopicLinux Arguments
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










