vi Text buffersA buffer is a computer's memory, that acts as a temporary holding place for data that is being sent to or received from an external device like keyboard, hard disk, printer etc. There are 36 buffers in vi to store text. Command starts with (") character. The vi editor doesn't allow direct modification of the file, instead it makes a copy of the edited file which is saved in buffer. Example: "add Here a is one of the buffer out of 36 buffers, dd is the command to delete a line. This command will delete the current line and will save it in buffer a. 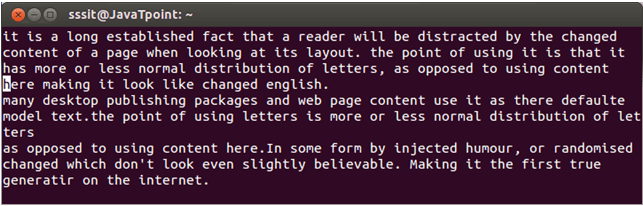
Look at the above snapshot, currently we're at line number four. 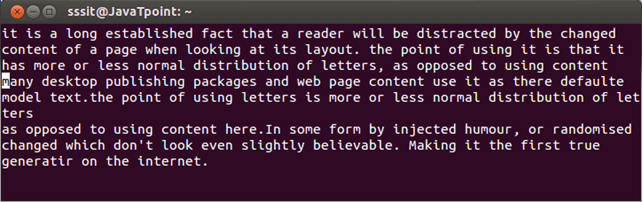
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing command "add, current line (fourth line) is deleted and is saved in buffer a. "ap Here also a is one of the buffer out of 36 buffers, p is the command to paste. This command will paste a line from buffer a after the current cursor position. 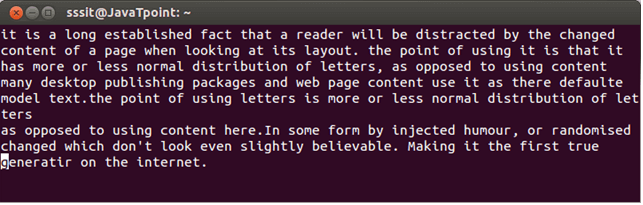
Look at the above snapshot, we want to paste a line from buffer a after the current cursor position. 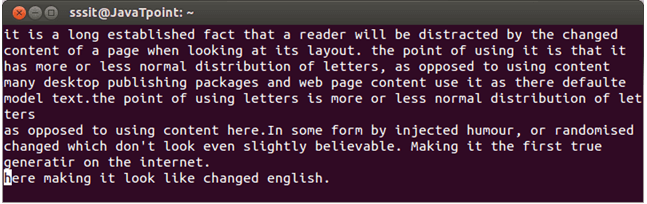
Look at the above snapshot, after passing "ap command, line which was saved in buffer a (in last example) is pasted back after the current position that is at the last.
Next TopicLinux vi Abbreviations
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









