Node.js BuffersNode.js provides Buffer class to store raw data similar to an array of integers but corresponds to a raw memory allocation outside the V8 heap. Buffer class is used because pure JavaScript is not nice to binary data. So, when dealing with TCP streams or the file system, it's necessary to handle octet streams. Buffer class is a global class. It can be accessed in application without importing buffer module. Node.js Creating BuffersThere are many ways to construct a Node buffer. Following are the three mostly used methods:
Node.js Writing to buffersFollowing is the method to write into a Node buffer: Syntax: Parameter explanation: string: It specifies the string data to be written to buffer. offset: It specifies the index of the buffer to start writing at. Its default value is 0. length: It specifies the number of bytes to write. Defaults to buffer.length encoding: Encoding to use. 'utf8' is the default encoding. Return values from writing buffers: This method is used to return number of octets written. In the case of space shortage for buffer to fit the entire string, it will write a part of the string. Let's take an example: Create a JavaScript file named "main.js" having the following code: File: main.js Open the Node.js command prompt and execute the following code: Output: 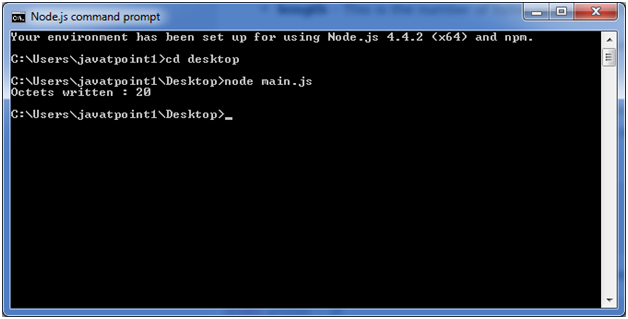
Node.js Reading from buffersFollowing is the method to read data from a Node buffer. Syntax: Parameter explanation: encoding: It specifies encoding to use. 'utf8' is the default encoding start: It specifies beginning index to start reading, defaults to 0. end: It specifies end index to end reading, defaults is complete buffer. Return values reading from buffers: This method decodes and returns a string from buffer data encoded using the specified character set encoding. Let's take an example: File: main.js Open Node.js command prompt and execute the following code: Output: 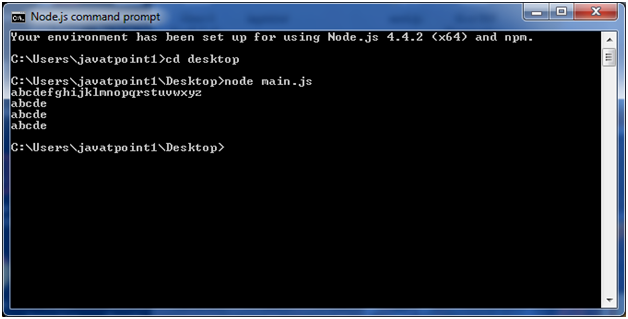
Next TopicNode.js Stream
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










