Types of single phase induction motorsThe single-phase induction motor is started by using some methods. Mechanical methods are not very practical methods that is why the motor is started temporarily by converting it into a two-phase motor. Single-phase induction motors are classified according to the auxiliary means used to start the motor. They are classified as follows:
1. Split-phase induction motor:The split-phase induction motor is also known as a resistance-start motor. It consists of a single-cage rotor, and its stator has two windings ? the main winding and a starting (also known as an auxiliary) winding. Both the windings are displaced by 90° in space like the windings in a two-phase induction motor. The main winding of the induction motor has very low resistance and high inductive reactance. 
Figure: Split-phase induction motor (a) Circuit diagram (b) Phasor diagram Motor Characteristics:The starting torque of a resistance-start induction motor is about 1.5 times full-load torque. The maximum or pull-out torque is about 2.5 times full-load torque at about 75% of synchronous speed. The split-phase motor has a high starting current which is usually 7 to 8 times the full-load value. Applications:Split-phase motors are most suitable for easily started loads where the frequency of starting is limited, and these are very cheap.
Capacitor motors:Capacitor motors are the motors that have a capacitor in the auxiliary winding circuit to produce a greater phase difference between the current in the main and auxiliary windings. There are three types of capacitor motors. 2. Capacitor-start motor:The capacitor-start motor develops a much higher starting torque, i.e. 3.0 to 4.5 times the full-load torque.To obtain a high starting torque, the value of the starting capacitor must be large, and the resistance of starting winding must be low. Because of the high VAr rating of the capacitor required, electrolytic capacitors of the order of 250 �F are used. The capacitor Cs is short-time rated. These motors are more costly than split-phase motors because of the additional cost of the capacitor. 
Figure: Capacitor start motor (a) circuit diagram (b) Phasor diagram Applications:
3. Two-Value Capacitor MotorThis motor has a cage rotor, and its stator has two windings namely the main winding and the auxiliary winding. The two windings are displaced 90?in space. The motor uses two capacitors Cs and CR. In the initial stage, the two capacitors are connected in parallel. 
Figure: Two-value capacitor motor Applications:
4. Permanent-split Capacitor (PSC) motor:These motors have a cage rotor, and its rotor consists of two windings namely, the main winding and the auxiliary winding. The single-phase induction motor has only one capacitor C which is connected in series with the starting winding. The capacitor C is permanently connected in series with the starting winding. The capacitor C is permanently connected in the circuit at starting and running conditions. 
AdvantagesA single-value capacitor motor has the following advantages:
Limitations of permanent-split capacitor motor:
Applications:
5. Shaded pole motor:A shaded-pole motor is a simple type of self-starting single-phase induction motor. It consists of a stator and a cage-type rotor. The stator is made up of salient poles. Each pole is slotted on the side, and a copper ring is fitted on the smaller part. This part is called the shaded pole. The ring is usually a single-turn coil and is known as shading coil. 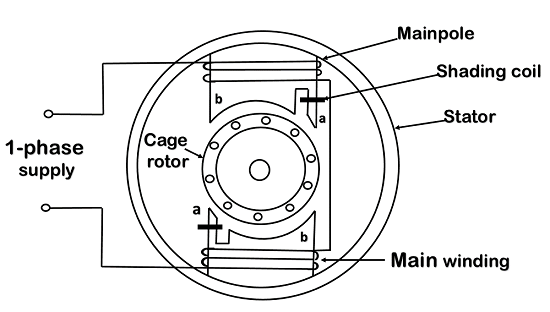
Figure: Shaded-pole motor with two stator poles. Applications:
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









