Why String is Immutable or Final in JavaIn object-oriented programming, the immutable string or objects that cannot be modified once it is created. But we can only change the reference to the object. We restrict to change the object itself. The String is immutable in Java because of the security, synchronization and concurrency, caching, and class loading. The reason of making string final is to destroy the immutability and to not allow others to extend it. The String objects are cached in the String pool, and it makes the String immutable. The cached String literals are accessed by multiple clients. So, there is always a risk, where action performs by one client affects all other clients. For example, if one client performs an action and changes the string value from Pressure to PRESSURE, all remaining clients will also read that value. For the performance reason, caching of String objects was important, so to remove that risk, we have to make the String Immutable. 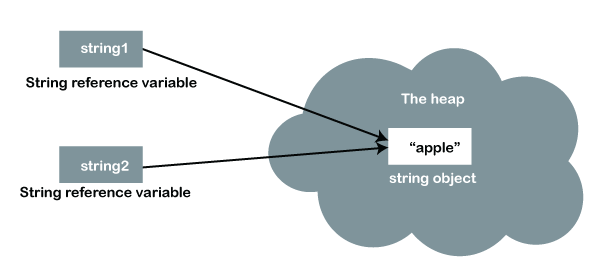
These are some more reasons of making String immutable:
Let's understand the concept of immutable through an example. ImmutableString.java Output: 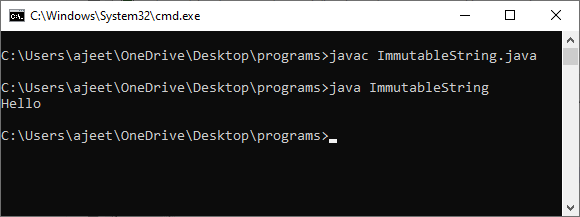
Description: We can understand the above example with the help of the following diagram: 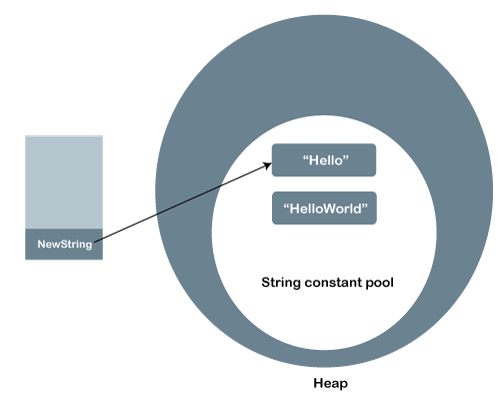
In the string constant pool, the Hello remains unchanged, and a new string object is created with HelloWorld. It shows that the strings are immutable. The reference variable points to the Hello not to the HelloWorld. If we want that it refers to the HelloWorld, we have to explicitly assign it to that variable. For example: Output: 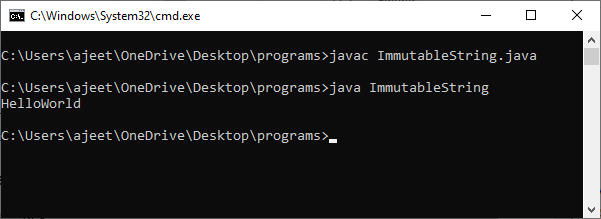
Next TopicJava Vs Kotlin
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










