Linux pwd CommandIntroduction to pwd CommandPWD stands for Print Working Directory. It writes the complete path name of the working directory to standard output in UNIX-like and other operating systems. Implementations of pwd CommandMultics had a command, i.e., pwd (which was an abbreviated name of the command, i.e., print_wdir), from which the Unix pwd command was produced. The PWD command is a shell builtin into almost every Unix shell, like zsh, ksh, bash, ash, and Bourne shell. It can be easily implemented with the POSIX C functions getwd() or getcwd (). Also, it is available in many operating systems, including KolibriOS, PANOS, and SpartaDOS X. The cd command, along with no arguments, is equivalent on Microsoft Windows (cmd.exe) and DOS Windows (COMMAND.com). Windows PowerShell offers the same GET-LOCATION cmdlet with the pwd and gl standard aliases. On the 5.0 version of Windows CE, the command processor shell cmd.exe has the pwd command. Since issue 2 of 1987, pwd has been a component of the X/Open Portability Guide as detected on Unix systems. It was acquired into the first version of the Single Unix Specification and POSIX.1. It occurred in the Version 5 Unix. The pwd version was specified by Jim Meyering and loaded with GNU coreutils. The GNU Octave and MATLAB numerical computing environments contain a pwd function with the same functionality. The OpenVMS is the same as the show default. Introduction to Woking Directory (Current)The current working directory is a directory where the user is working currently. Each time we interact with our command prompt, we are working inside a directory. When we log into our Linux system, our current working directory is our home directory by default. We can use the cd command to change our working directory. For example, we need to enter the below command in the terminal window to change the working directory to /tmp: If you have a customized zsh or bash prompt, the current working directly path may be displayed in the shell prompt. PWD Syntaxpwd takes the below syntax: The options are explained in the below section. Exit Status pwd contains the following exit statuses:
PWD Options and their Explanation
Note: POSIX needs that are default nature be as if the -L option was provided.Examples of PWD Command

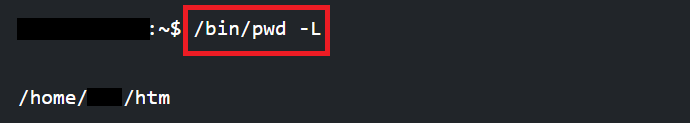
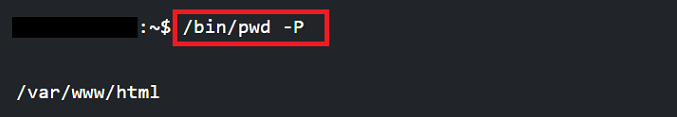
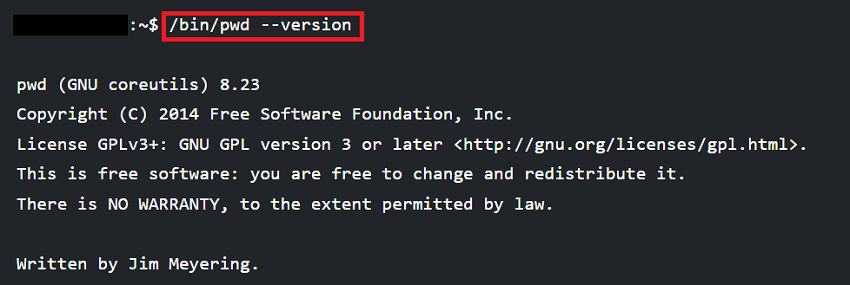
Note: The pwd command is never applied with arguments and is used often without options.Important: We might have seen that we are running the command as /bin/pwd, not pwd, which is mentioned above. So, what is the difference? pwd alone describes shell built-in pwd. Our shell may contain different pwd versions. We recommend referencing the manual. We are calling a binary version of the command if we are using /bin/pwd. Both the binary and the shell versions of the command will print the current working directory, so the binary version contains more options.

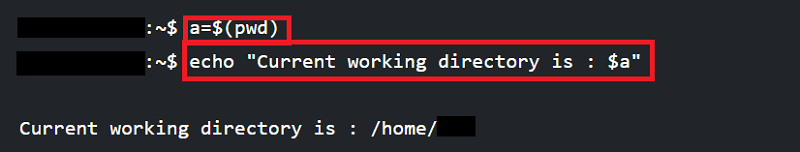
Next TopicLinux CD Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









