Linux Home DirectoryThe Linux home directory is a directory for a particular user of the system and consists of individual files. It is also referred to as the login directory. This is the first place that occurs after logging into a Linux system. It is automatically created as "/home" for each user in the directory'. It is a standard subdirectory of the root directory. The root directory contains all other directories, subdirectories, and files on the system. It is denoted by a forward slash (/). The home directory can be said as a personal working space for all the users except root. There is a separate directory for every user. For example, two users 'jtp1' and 'jtp2' will have directories like "/home/jtp1" and "/home/jtp2". These users will have all the rights under their directory files. The root (administrative) user is the only user who has its home directory in a different location by default. The path of the root user is '/root/', where it has control under all the directories and files. How to find the Home Directory?There are multiple ways to access and return to the home directory. Some commands are very helpful for the directories such as cd, pwd, mkdir, pwd, ls, and rmdir. To access the home directory graphically, open the files application, and click on the Home option from the left side menu. Consider the below image: 
Here, we can explore our home directory. Generally, our terminal opens with the user's particular directory. To change directory to home directory, execute the cd command as follows: The above command will change the directory to home. To list the home directory, execute the ls command as follows: Consider the below output: 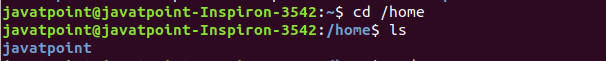
We can get back to our home directory by executing the cd command without any argument. It will back to our home directory from any directory we are working on. Execute it as follows: Consider the below output: 
From the above output, we were in /Directory/files, by executing only cd command, we reached to our home directory. We can use the "cd ~ or cd $HOME" commands as well, to do the same. Consider the below commands: To display the current working directory, execute the pwd command as follows: Consider the below output: 
To create a directory under a directory, execute the mkdir command as follows: Consider the below output: 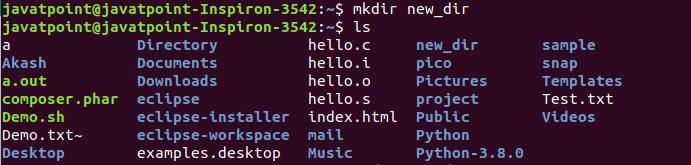
From the above output, we have created a directory as 'new_dir', and displayed it by executing the ls command. We can remove a directory as well. To remove a directory, execute the rmdir command as follows: Consider the below output: 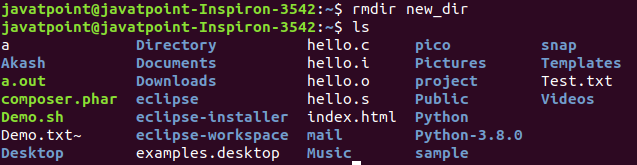
From the above output, we have removed the 'new_dir' directory. Difference between Root and Home DirectorySome key differences between root and home directory are as following:
Next TopicLinux PWD
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









