SSH Linux | Linux ssh commandIn Linux, ssh is a protocol, which stands for Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell. The secure shell is useful for security while connecting to a remote server. The ssh command uses a ssh protocol, which is a secure protocol, as the data transfer between the client and the host takes place in encrypted form. It transfers the input through the client to the host and returns the output transferred by the host. It executes through TCP/IP port 22. The encrypted connection is also used to run the commands on a Linux server, port forwarding, tunnelling, and more. There are lots of SSH clients that are available for both commercial and free. The OpenSSH is its most widely used client. It is available for all the most used platforms such as Windows, Linux, macOS, OpenBSD, and more. Syntax: Components of ssh commandThe ssh command consists of three different types of components:
How SSH works?To establish an SSH connection, we need two primary components; a client and a host, which can be a server, domain name, IP address, and more. Also, we require a ssh client to connect with another computer or server. The client uses the specified host information to establish the connection; if the provided credential verified, it will establish an encrypted connection. 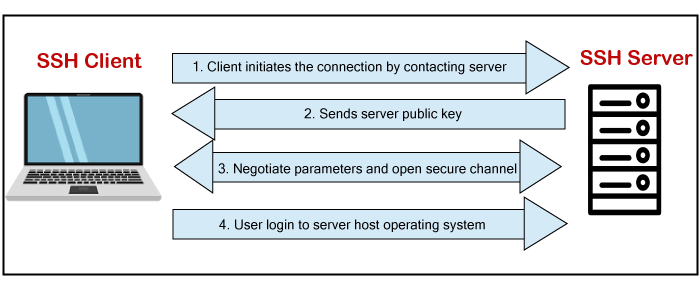
The server (Host) contains an SSH process that is ready to take a request for the client connection through a TCP/IP port. Once the client initiates a connection, the host responds with the necessary information and exchanges the credentials. If the provided information is verified, the SSH protocol establishes a new connection for the available environment. The default SSH protocol version for SSH server and SSH client communication is version 2. Install OpenSSH client on Linux (Ubuntu)The OpenSSH client is a connectivity tool for the systems to connect two systems with the ssh protocol. It is also called as ssh and can be invoked from the Linux terminal. This client package contains other SSH utilities like sftp, scp, and ssh that are installed by default with the ssh command. It performs remote operations using these ssh utilities. The OpenSSH client comes preinstalled with most Linux distributions. If any Linux system does not have the ssh client, we can install it manually by using the package manager. To install the OpenSSH client, execute the below command: The above sudo command will update the package of the Linux system. Consider the below snap of the output: 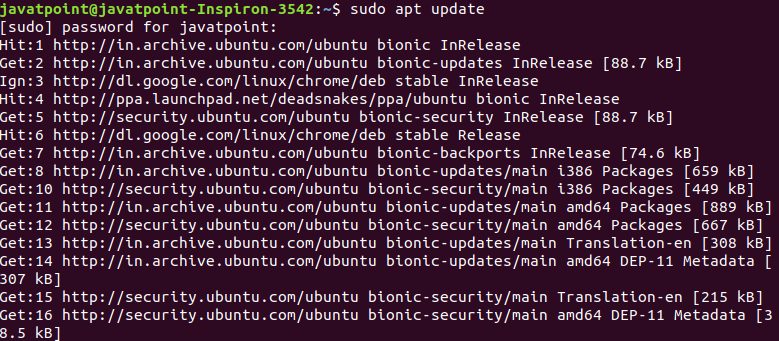
After updating the Linux system, execute the below command to install the OpenSSH client: The above command will install the latest package of the OpenSSH client. Consider the below output: 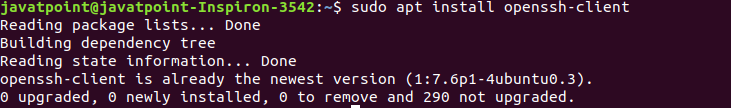
As we can see from the above output, a daemon process is running to install the OpenSSH client. As in our machine, OpenSSH client is already installed, so it has displayed the message 'openssh-client is already the newest version.' Note: The macOS carries the Openssh client by default.Install OpenSSH server on Linux(Ubuntu)To make an SSH connection, we need to have the server-side part of the SSH software in our machine. To check the installation status of the server, open the terminal and execute the below command: If our machine does not have the server tool kit of the OpenSSH client, then it will display the output as follows: 
In the above case, we have to install the OpenSSH server. To install the SSH server, execute the below command: The above command will prompt for the system administrative password, type the password, and press ENTER key to start the installation process. Next, it will confirm the installation type 'y' key and press ENTER key. Consider the below output: 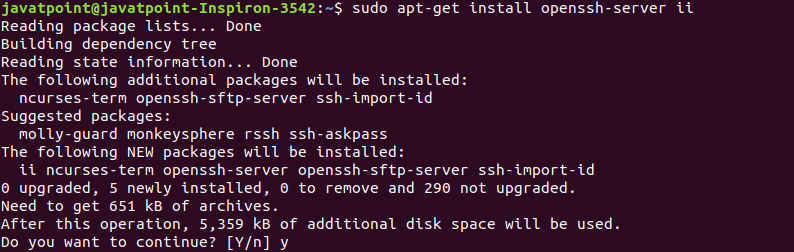
After confirming the installation, a daemon process will begin and install the OpenSSH server on your machine. To verify the installation, execute the below command: The above command will display the status of the installation. If the installation is successful, it will display the output as follows: 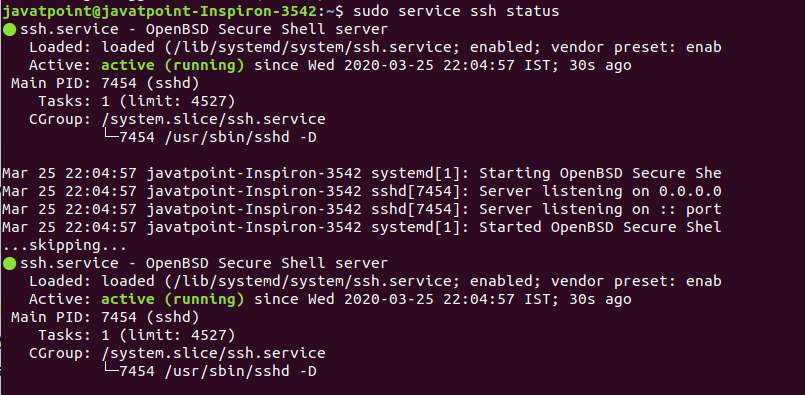
There is another way to test the installation by ssh localhost command: The above command will verify the connectivity type 'yes' to continue. Consider the below output: 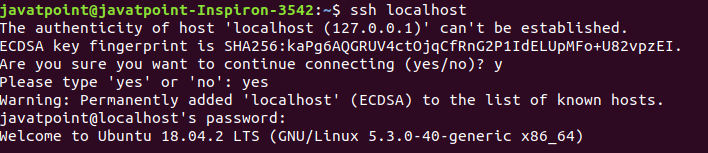
Now, we have successfully installed the OpenSSH server on our machine. SSH Key GenerationTo create a connection with the host client, we need a specific key for an encrypted connection. Logging in to remote host computer by ssh key is more secure than using a password. After logging in the host, computer commands will only work if these commands will be written to the host computer directly. To generate the ssh key, execute the below command: The above command will generate the public and private keys for creating a connection to the host system. Consider the below output: 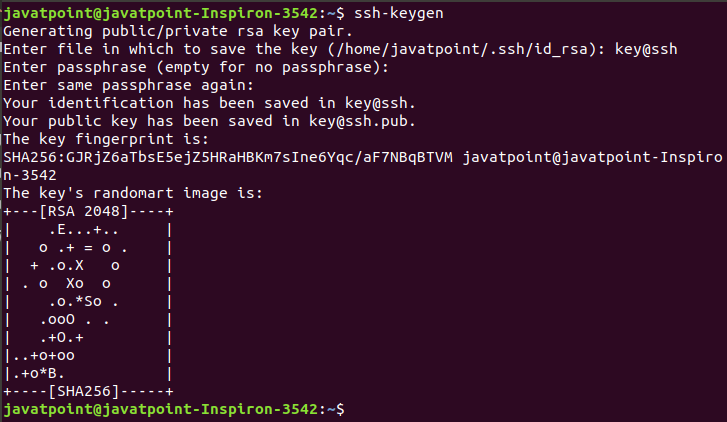
we can see from the above output, the ssh keys have generated. The ssh-keygen command creates two files, key@ssh, and [email protected], which contain private and public key, respectively. It is recommended to hide the private key for security purposes, copy the public key to the remote host. After copying this key to a remote host, we can establish a connection using the SSH key, not by the password. Techniques of SSH ProtocolThe SSH protocol is more secure as compared to other protocols such as telnet, and the encryption techniques are quite good than other protocols. There are three major encryption techniques which are used by the SSH. They are as following:
SSH CommandsThe client ssh has many functions for the ssh command, such as creating a key, configuring a key, opening an SSH server, holding a key for single sign-on, file transfer client, and more. Some most useful ssh commands are as follows:
Options: There are many command-line options are available to specify the different specification of SSH output. Some useful options are as following:
How to connect via SSHAs we have installed the SSH client and server, we can establish a secure connection with other machines. For a secure connection between two machines, they both have ssh client and server installed. To establish a connection, execute the below command: If the user name is verified by the machine that you want to connect, execute the below command: The above command will ask for the password, type the password, and press ENTER key. If we are making a connection for the first time, it will ask for the continue connecting; type yes and press Enter. It will add an ECDSA (Elliptical curve Digital Signature Algorithm) key and connect you to a remote server. You are now eligible to control and manage a remote machine by your terminal. If you face any difficulty in establishing a connection, consider the following points:
Next TopicLinux mail Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









