Linux mtr CommandThe mtr command is a combination of ping and traceroute commands. It is a network diagnostic tool that continuously sends packets showing ping time for each hop. It also displays network problems of the entire route taken by the network packets. Syntax:The basic syntax for the mtr command is as follows: Options:The mtr command supports the following command-line options: -h, --help: It is used to display the help manual having a brief description of usage and command-line options. -v, --version: It is used to display the installed version information. -4: It is used for IPv4 addresses. -6: It is used for IPv6 addresses. -F FILENAME, --filename FILENAME: It is used to access the domain names( paths) from the file. -r, --report: it is used to set the mtr into report mode. It is useful for displaying network statistics quality. -w, --report-wide: It is used to set the mtr into wide report mode. -x, --xml: It is used to specify the xml output format. -t, --curses: It is used to specify the use of curses-based terminal interface forcefully. --displaymode MODE: It is used to select the initial display mode. The display modes are as follows: 0: selects statistics (The default) 1: selects the stripchart without latency information 2: selects the stripchart with latency information -g, --gtk: It is used to specify the use of the GTK+ based X11 window interface. -l, --raw: It is used to specify the raw output format. -C, --csv: It is used to specify the "Comma-Separated-Value (CSV)" output format. -j, --json: It is used to specify the JSON output format. -p, --split: It is used to specify the spit out a format. It is suitable for a split-user interface. -n, --no-dns: It is used to display numeric IP numbers and not try to resolve the hostnames forcefully. -b, --show-ips: It is used to display both the domain names and IP addresses. -o FIELDS, --order FIELDS: It is used to specify the fields and their orders to display. -y n, --ipinfo n: It is used to display the information of each IP hop. -z, --aslookup: It is used to display the Autonomous System (AS) number with each hop. It is similar to the "--ipinfo 0" command. -i SECONDS, --interval SECONDS: It is used to describe the positive number of seconds between ICMP ECHO requests. -c COUNT, --report-cycles COUNT: It is used to specify the number of sent pings. -s PACKETSIZE, --psize PACKETSIZE: It is used to describe the packet size for probing. -B NUM, --bitpattern NUM: It is used to specify the bit pattern for payload. -G SECONDS, --gracetime SECONDS: It is used to specify the response time in a positive number of seconds after the final request.by default, it is five seconds. -Q NUM, --tos NUM: It is used to specify the type of service field value in Ip header. -e, --mpls: It is used to specify the information from ICMP extensions. -a ADDRESS, --address ADDRESS: It is used to bind the outgoing socket to ADDRESS. -f NUM, --first-ttl NUM: It is used to specify the TTL to start. -m NUM, --max-ttl NUM: It is used to describe the maximum number of hops (max TTL value). By default, it is thirty. -U NUM, --max-unknown NUM: It is used to specify the maximum unknown host. By default, it is five. -u, --udp: It is used to specify the UDP datagrams instead of ICMP ECHO. -T, --tcp: It is used to specify the TCP SYN packets instead of ICMP ECHO. -S, --sctp: It is used to use the "Stream Control Transmission Protocol" instead of ICMP ECHO. -P PORT, --port PORT: It is used to specify the port number for TCP/SCTP/UDP traces. -L LOCALPORT, --localport LOCALPORT: It is used to specify the source port number for UDP traces. Examples of the mtr CommandLet's see the following examples of the mtr command:
Display traceroute ReportThe default behavior of the mtr command displays the traceroute report for a remote hostname or IP address. To display the traceroute report, pass the hostname or IP address with it as follows: Consider the below example: The above command will display the traceroute report for the 'javatpoint.com'. Consider the below output: 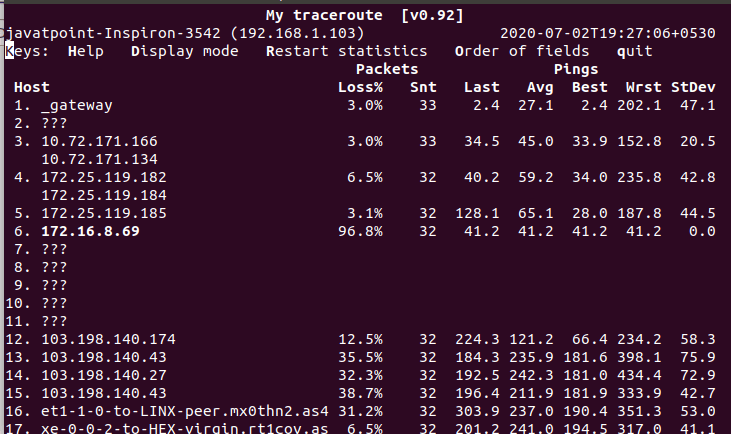
From the above output, the traceroute report keeps showing until its done. To interrupt it, press CTRL+C keys. Display CSV OutputTo show the CSV output, pass the '--csv' option with mtr command. A CSV file is a comma-separated file which delimits the columns by a comma (,). Consider the below command: The above command will display the CSV output. Consider the below output: 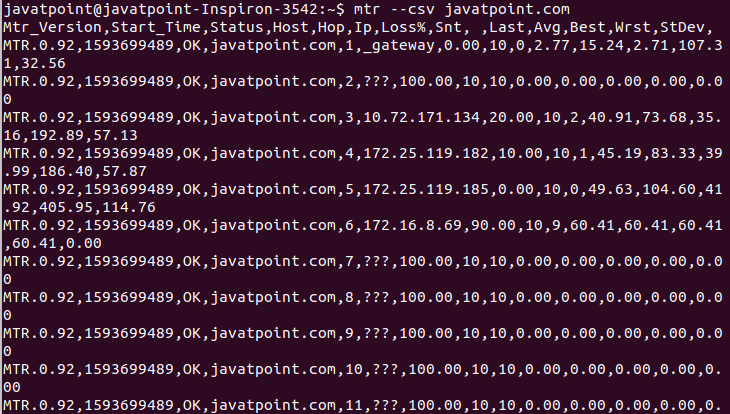
Display Xml OutputThe mtr command supports Xml format output. To display the Xml output, pass the '--xml' option with mtr command. The Xml format is useful for automated processing. Consider the below command: The above command will display the output in Xml format. Consider the below output: 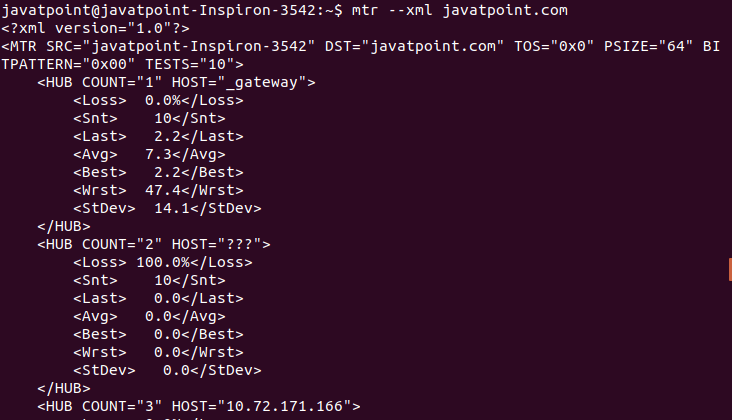
Display Json OutputAnother useful output format supported by mtr command is a Json file. We can display the output in Json format. To display the output, execute the command with '--json' option as follows: The above command will produce output like: 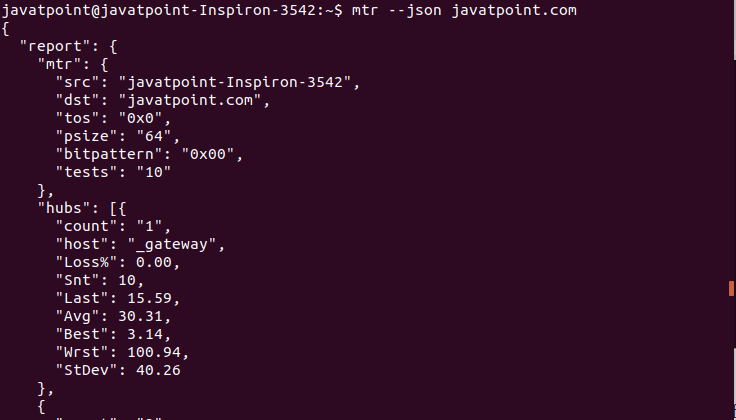
Specify Limit of PingWe can specify the limit of pings; it will automatically quit after completing the specified number of pings. The number of pings can be seen in the 'Snt' column. To determine the number of pings, execute the command with '-c' option as follows: The above command will display the traceroute report for the specified number of pings. Consider the below output: 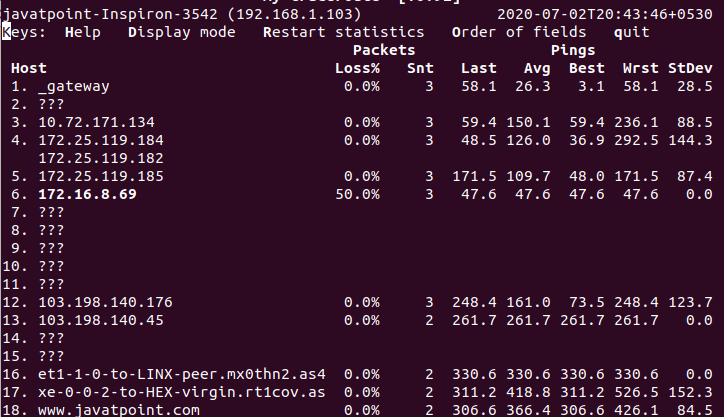
Read Hostnames From FileThe mtr command allows us to specify multiple hostnames in a file for reading. The various hostnames can be specified in a text file by putting in a new line. It will read them sequentially. To read file names from a file, execute the command with the '-F' option. Consider the below command: 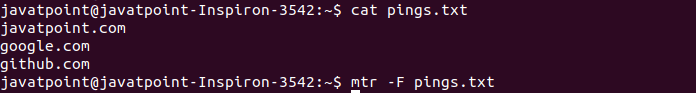
The above command will read the file names from the file 'pings.txt.' Consider the below output: 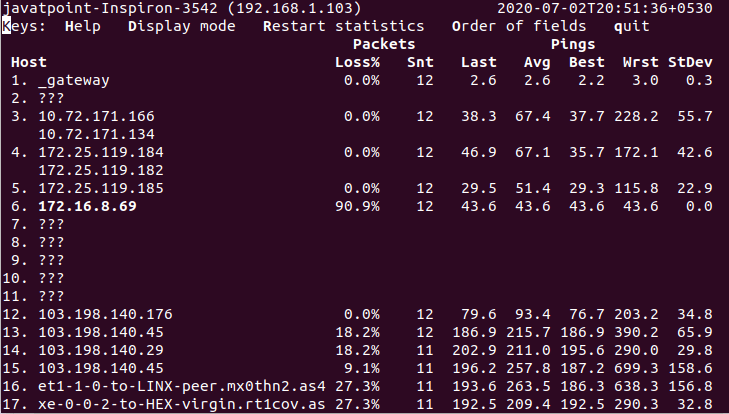
From the above output, the traceroute for the specified hostnames will be displayed sequentially. Disable DNS Resolving (Display numeric addresses only)The disabling of DNS resolving made the faster output, because it will reduce more traffic and wait time taken by DNS resolving. To disable the DNS resolving, execute the command with the '-n' option as follows: The above command will disable the DNS resolving and produce a faster output. Consider the below output: 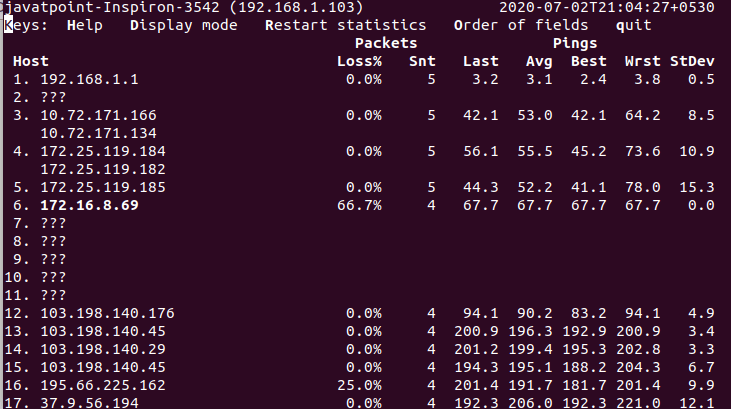
Getting Helpif you stuck during the use of mtr command, you could take the help from your terminal. There are 'help,' and 'man' command are available, which contains a summary of the usage and supported command-line options. To display the help, execute the command with '--help' option as follows: The above command will display a list of supported options as follows: 
To read the manual page, execute the below command: The above command will display the manual page. It will look something like this: 
To read more scroll the output and to exit from the manual, press 'q' key.
Next TopicLinux whois
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










