Linux hostname CommandLinux hostname command allows us to set and view the hostname of the system. A hostname is the name of any computer that is connected to a network that is uniquely identified over a network. It can be accessed without using a particular IP address. By default, the hostname of a system is set during the installation of OS. Even if we install a virtual machine, it is dynamically assigned by the system. But, there may be some conditions whenever we want to change the hostname. The hostname command will let us do so. Syntax:The basic syntax for the hostname command is as follows: Options:The hostname command supports the following command-line options: -a, --alias: It is used to display the alias name of the host ( If it is defined). However, the '-a' option is deprecated. -A, --all-fqdns: It is used to display the FQDNs of the system. The '-A' option lists all the configured network addresses on all interfaces and converts them to DNS names. It skips the addresses that can not be converted because they don't have proper reverse IP entry. -b, --boot: It allows to set a hostname for always. If any hostname is not specified, it will use the default hostname (i.e., localhost). -d, --domain: It is used to print the DNS domain name. Don't confuse between domainname and hostname command. The domainname command displays the NIS domain name, and it shows the DNS domain name. -f, --fqdn, --long: It is used to print the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). An FQDN contains the short hostname and the DNS domain name. The FQDN and DNS domain name can be changed in the "/etc/hosts" file, except for the BIND or NIS host lookups. -F, --file filename: It is used to read the hostname from a file. -i, --ip-address: It is used to print the network addresses of the hostname. This option will work only if the hostname is in resolving circumstances. -I, --all-ip-addresses: It is used to print the network addresses of the host. It will list all the configured addresses on all network interfaces. In this option, the loopback interface and Ipv6 local addresses are skipped. This option does depend on the name resolution like the '-' option. -s, --short: It is used to print the short hostname. If the hostname is too long, it will cut from the first dot. -V, --version: It is used to display the installed version information. -y, --yp, --nis: It is used to print the NIS domain name. If we pass a parameter or file name, then the root can set a new NIS domain. -h, --help: It is used to display the help manual that contains a summary about the usage and support options. What is the FQDNThe FQDN stands for the Fully Qualified Domain Name. It is the name of the system that returns for the hostname like abc.example.com. It is the hostname followed by the DNS domain name. The FQDN can be checked by executing the "hostname -fqdn" command. Examples of the hostname CommandLet's see the following examples of the hostname command:
Print the Hostname of the SystemTo display the system name, execute the basic hostname command. Consider the below command: The above command will display the system name. Consider the below output: 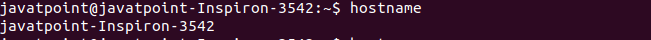
From the above command, the system name is displayed as 'javatpoint-Inspiron-3542', which is the default name created during the installation. Setting the hostnameWe can set the hostname by using the hostname command. It needs sudo privilege. To set the system name, execute the command as follows: Consider the below command: The above command will set the hostname as 'xyz.com.' Consider the below output: 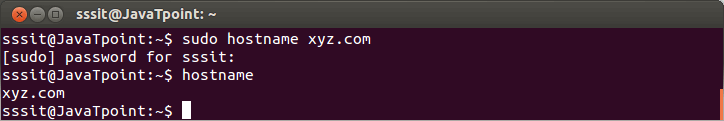
From the above output, we have set "xyz.com" as our hostname. The above system name is not permanent. The system name set with hostname command is not permanent. On rebooting the system, the name will change to the one specified in the hostname file. To permanently set the hostname, you have to save it in the hostname file present on the server. After setting, you have to reboot the system. For Ubuntu, /etc/hostname file is used. For RHEL, /etc/sysconfig/network is used. Print the IP Address of the SystemWe can view the IP address of the system by executing the hostname command. The '-i' option is used to display the IP address of the system. Consider the below command: The above command will display the IP address of the system. Consider the below output: 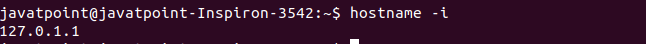
Print the hostname Alias Name (if any)The 'a' option is used to display the alias name of the host system (if any). If the system does not have an alias name, it will return an empty line. It lists all the configured addresses on all network interfaces. Consider the below command: The above command will display the hostname of the system. Consider the below output: 
The above output is returning a blank line, which means no alias name set for this system. Print the Associated Domain NameThe '-d' option is used to display the associated domain name with the system. It will display the local domain name (if set). It will not return anything if there is no domain name set for the system. Consider the below command: The above command name will display the associated domain name. Consider the below output: 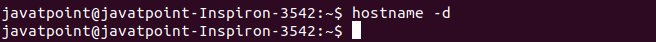
The above output is not returning anything, which means no domain name set for the Print the short hostnameThe '-s' option is used to print the short hostname. The short name is a part of the first section (before '.'). If the system does not have any short name, it will display the full name. Consider the below command: The above command will display the short name of the system. Consider the below output: 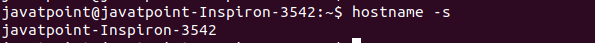
Getting HelpIf you stuck during the use of the hostname command, you could take the help from your terminal. The Linux commands support the '-help' and manual pages, which have a summary of the usage and support options. To get help, execute the below command: The above command will display the summary of usage and supported options. Consider the below snap of the output: 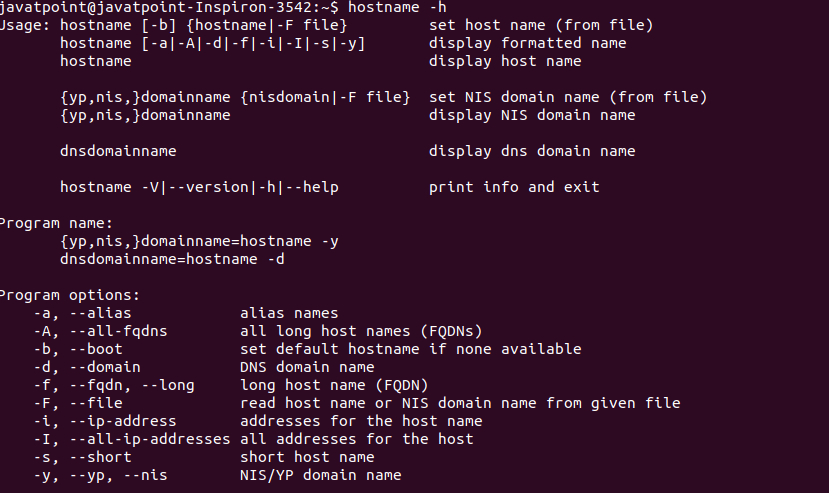
From the above output, we can see a summary of the hostname command is displayed. There is another way to take help from the command line, i.e. manual pages. To display the manual page of it, execute the below command: The above command will display the manual page of the hostname command. Consider the below output: 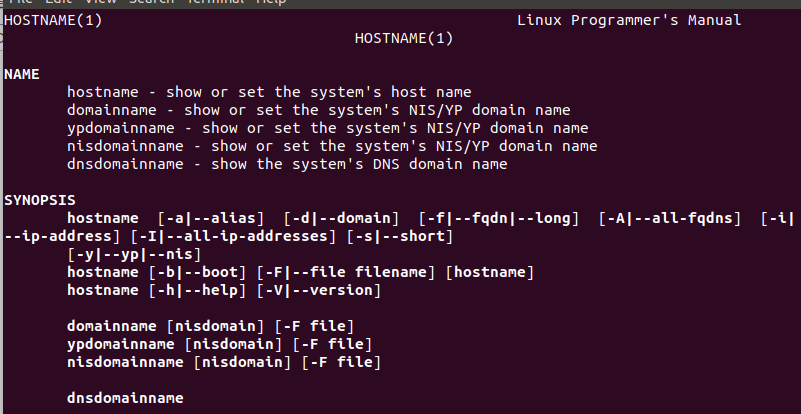
To read more scroll the output, press the 'q' key to quit from the manual page and back to the terminal.
Next TopicLinux curl & wget
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









