Check MySQL Version UbuntuIntroduction to MySQLMySQL is an open-source RDMS (Relational Database Management System). Its title is a set of "My" the title of the daughter of the co-founder Michael Widenius, and "SQL", stands for Structured Query Language. The relational database manages data into multiple data tables in which the types of data might be related to each other; the relations aid structure of the data. Structured Query Language is a language that programmers use to establish, change, and extract data through the relational database and control access of the user to the database. In addition to SQL and relational databases and RDMS such as MySQL operates with an operating system for implementing a relational database in the storage system of the computer. It permits network access and offers backup creation and testing of database integrity. Some key points are as follows:
Overview of MySQLMySQL is specified in the C++ and C programming languages. The SQL parser of SQL is specified in yacc, although it utilizes a home-brewed lexical analyzer. Besides, MySQL works on several system platforms, such as Tru64, Sanos, SCO UnixWare, SCO OpenServer, SunOS, Symbian, Oracle Solaris, QNX, OS/2 Wrap, OpenSolaris, OpenBSD, Novell NetWare, NetBSD, Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, IRIX, IBM i, eComStation, ArcaOS, HP-UX, FreeBSD, BSDi, and AIX. Also, a MySQL port to OpenVMS is available. The MySQL client libraries and server software itself apply dual-licensing distribution. They are provided under a proprietary license and GPLv2. Support can be achieved through the official manual. Additionally, free support exists in different IRC forums and channels. Oracle provides paid support from its MySQL Enterprise products. These products differ in price and service scope. Several third-party organizations are also available to give services and support. Brief History of MySQLMySQL was developed by MySQL AB, a Swedish company, founded by Finnish Michael "Monty" Widenius, Allan Larsson, and Swedes David Axmark. Original MySQL development by Axmark and Widenius in 1994. The initial release of MySQL was represented on 23 May 1995. Initially, it was built for personal use via MySQL which was the low-level language ISAM-based, which the creators acknowledged was inflexible and too slow. They made a new interface of SQL while keeping a similar API to mSQL. Several developers can use MySQL rather than the mSQL antecedent by keeping the API the same as the mSQL system. Some other MySQL development milestones included:
Features of MySQLMySQL comes in two different editions: the proprietary Enterprise Server and the open-source MySQL Community Server. MySQL Enterprise Server is characterized by a proprietary extension series which install as the server plugins, but shares the numbering system of the version and is created from a similar codebase. Some major features of MySQL are as follows: 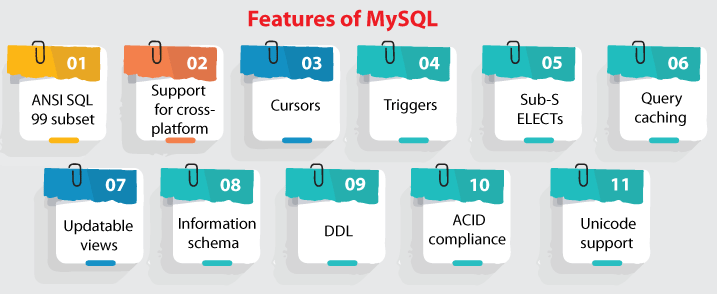
Limitations of MySQLWhen using the storage engines other than the InnoDB default, MySQL doesn't comply with the complete SQL standard for a few of the implementing functionality such as foreign key references. Also, check constraints are determined but avoided by every storage engine before the 8.0.15 version of MySQL. Deployment of MySQLMySQL can be manually created and installed from source code but it's more generally installed using a binary package unless unique customizations are needed. The package management system can install MySQL with basic efforts on almost all distributions of Linux, though the further configuration is needed for adjusting optimization and security settings. MySQL has evolved gradually for supporting higher-scale requirements as MySQL started as a low-end replacement for more robust proprietary databases. Still, it is more generally used in small-medium scale single-server deployment either as a standalone database server or a component within the LAMP-based web applications. Much of the appeal of MySQL originates in its corresponding ease of use and simplicity which is activated by an open-source tool's ecosystem like phpMyAdmin. Some key points are as follows:
Cloud deploymentMySQL can be executed on many platforms of cloud computing such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure, etc. A few basic MySQL development models on the cloud are as follows: 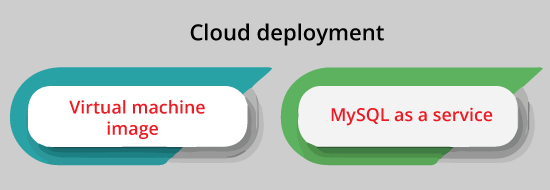
Virtual machine imageUsers of the cloud can upload their machine image using installed MySQL or apply a ready-made machine image using MySQL optimized installation on it like the one offered by Amazon EC2 with this implementation. MySQL as a serviceMySQL 'as a service' can be offered by a few cloud platforms. In this implementation, the owners of the application don't need to install and manage their MySQL database. The database service provider holds the responsibility to install and maintain the database rather, and the owners of the application pay according to their usage. Some remarkable services of cloud computing MySQL are the Jelastic, Heroku, HP Converged Cloud, Rackspace, Azure Database for MySQL, Oracle MySQL Cloud Service, and Amazon Relational Database Service. High availability applicationOracle MySQL provides a high availability solution along with a mix of tools such as the MySQL shell and the MySQL router. They are based on open-source, Group replication tools. MariaDB provides the same offer in product terms. User interface of MySQL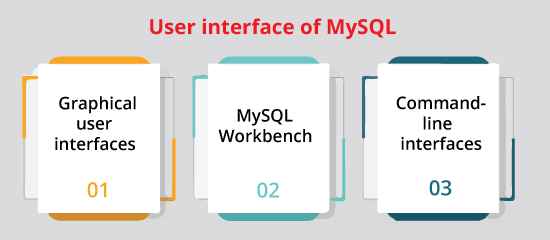
Graphical user interfacesA GUI is a kind of interface that permits users for interacting with programs or electronic devices through visual indicators and graphical icons like secondary notation, as disputed to text navigation, typed command labels, or text-based interfaces. Free graphical administration and third-party proprietary applications are available that develop with MySQL and let users visually implement data and database structure. MySQL WorkbenchFor MySQL, MySQL Workbench is the developed environment. It was integrated by MySQL AB and let users visually create database structures and administer MySQL database graphically. MySQL Workbench is present in three different editions. The first one is the basic open-source and free Community Edition which can be downloaded through the MySQL website, the second one is the proprietary Standard Edition which improves and extends the Community Edition's features set, and the third one is the MySQL Cluster CGE. Some other tools of GUI:
Command-line interfacesThe command-line interface is a definition of collaborating with a computer program in which the user problem commands to the program by entering successive text lines (command lines). MySQL moves with several command-line tools through which the primary interface is the mysql client. The utilities of MySQL are a group of utilities established for performing common administrative and maintenance operations. The utilities are the stand-alone download accessible from Oracle which was originally added as a part of MySQL Workbench. MySQL shell is interactively used for the MySQL database administration. It supports SQL, Python, or JavaScript modes and it can also be used for access and administration purposes. MySQL interfaces for application programmingSeveral programming languages include libraries to access MySQL databases with language-specific APIs. These include MySQL Net/Connector for CLI/.NET languages and the JDBC driver for Java. An ODBC interface known as MySQL Connector/ODBC permits extra programming languages that support the interface of ODBC for communicating with the MySQL database such as ColdFusion or ASP. The HTSQL (a method of URL-based query also ports with the MySQL adaptor, permitting direct interaction between any web client and a MySQL database by structured URLs). Several other drivers are also available for languages such as Node.js or Python. MySQL Project ForksA range of MySQL forks are available, including the below: 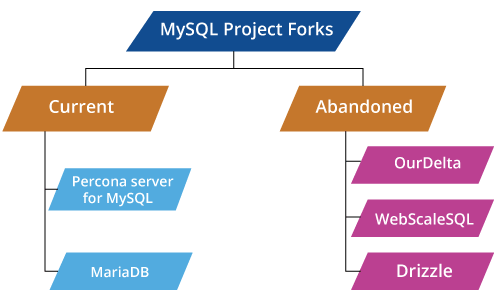
CurrentPercona Server for MySQL It was forked by Percona, which focuses on retaining close compatibility with the MySQL official releases. XtraDB was also added to the Percona server for MySQL which is the fork of Percona of the InnoDB Storage Engine. MariaDB It is a community-developed MySQL relational database management system fork intended for remaining free upon the GNU GPL. This fork has been led by the real MySQL developers who forked it because of some concerns about its execution via Oracle. AbandonedOurDelta It was created by the Open Query (an Australian company) but later inherited by Catalyst IT Australia. It had two different versions. The first one is the 5.0 version which was MySQL-based and the second one is the 5.1 version which was MariaDB-based. It added patches integrated by Open Query and other notable team members of the MySQL community including Google and Jeremy Cole. WebScaleSQL It was a MySQL 5.6 software branch and was published on 27 March 2014 by Twitter, LinkedIn, Google, and Facebook as a joint effort for providing a centralized development structure to extend MySQL with new aspects specific to its large-scale formations like building bigger replicated databases executing on server farms. Drizzle It was an open-source and free software relational database management system that was forked through the now-defunct 6.0 development branch of MySQL DBMS. Drizzle contains a client/server architecture and applies SQL as its main command language like MySQL. Drizzle was deployed upon the second and third versions of the GNU GPL with many portions including the replication messaging and protocol drivers upon the BSD license. Checking the MySQL version in UbuntuPrerequisitesBefore we start, ensure that we have:
We can get begun once we have the requirements which are mentioned above. Check Status of MySQL using SystemdSystemd is a robust Linux servicer manager and init system that permits monitors, stops, and starts the statuses of services and daemons. Additionally, it provides features such as tracking and logging usage, etc. So, it is a basic tool for all system administrators. We need to use the following command for using systemd to check the MySQL service: Once we run the above command successfully, systemd will begin the service thinking it doesn't execute into the errors. We need to use the following command for checking the service status: 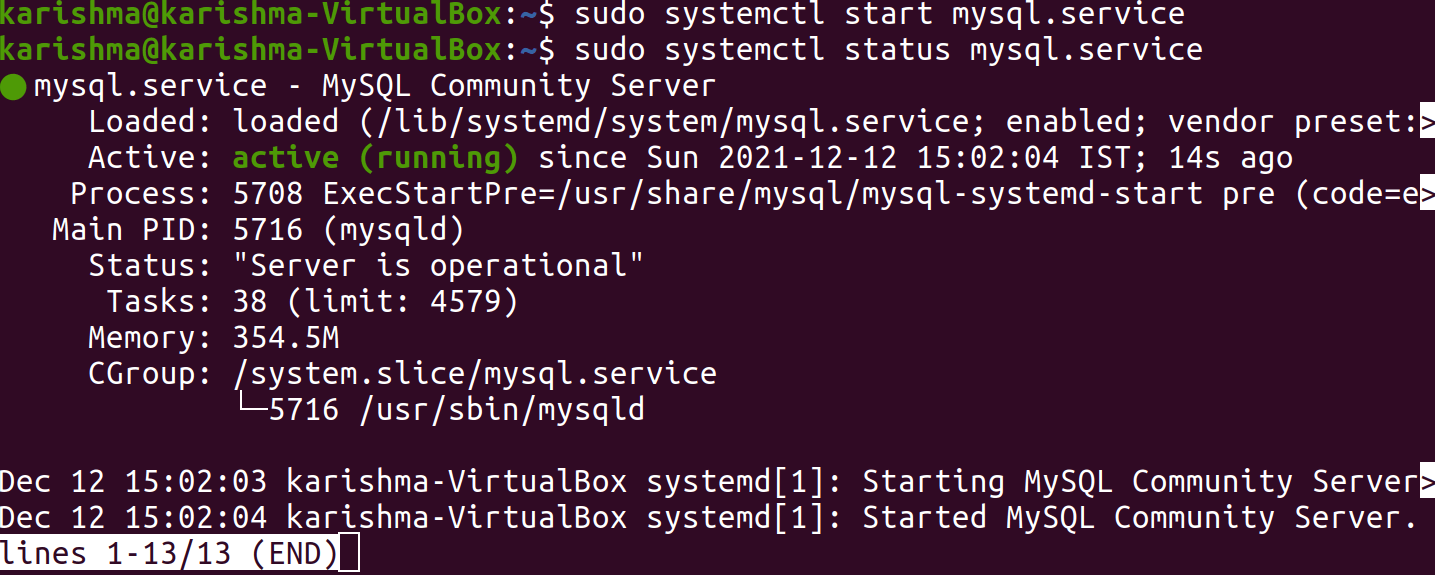
It will provide us with the output below displaying that the service is active. Check Status of MySQL using MySQLadminWe can use a tool like mysqladmin as well. MySQL admin is a command-line utility of the MySQL server administration for checking the MySQL server status. We can use the following command: 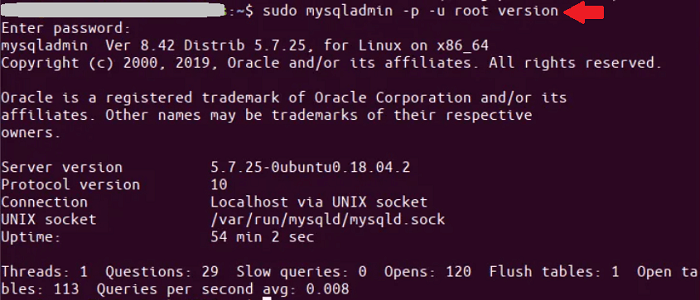
We will get the result if the MySQL server is active and running: Check MySQL VersionMethod 1 We can use the following command in the terminal window to see the version of MySQL: Method 2 We can use the command, i.e., mysqld with the option, i.e., -V to check the version of MySQL active on the local host system. The following examples can only be used for a localhost: Method 3 We can also get the version from inside the MySQL shell by entering the following statement: Method 4 We can also see the information of the MySQL version which is saved inside a variable called 'version'. We need to enter the following statement to see the server version of MySQL.
Next TopicExtract RAR File in Ubuntu
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share