Ubuntu Server vs. DesktopIntroduction to Ubuntu ServerUbuntu server is an open-source environment that does more than we might think. This operating system can work with everything with its capability for serving as an internal company server or scaling every way up and out to satisfy enterprise-level requirements. It is a server operating system integrated by Canonical that executes on every major architecture, such as POWER8, ARM64, ARM v7, x86-64, x-86, and IBM System z mainframes by LinuxONE. Ubuntu OS is a server environment that everyone can utilize for the below and much more:
Ubuntu server contains the following requirements:
One feature that makes the Ubuntu server so engaging is it is cost-effective. Everyone can download a copy of the current release of the Ubuntu server and run it on as various machines as essential at zero cost (minus time and hardware). The latest version includes essential updates to the environment. Now, Ubuntu Server supports ZFS, which is a file system using built-in snapshot abilities. Also, it includes the initial production version of the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) (a set of drivers and libraries for fast packet processing). If we run a small enterprise and we are looking for a simple-to-deploy web server or file server, the Ubuntu server can manage that and other things as well. If we are an enterprise-level company searching to scale out the OpenStack Cloud, a Hadoop cluster, or a massive render farm, Ubuntu has us covered. Ubuntu server has been authorized for HPE Cloud, IBM, Joyent, Microsoft Azure, and AWS if we are looking to operate with Ubuntu on a virtual environment as a guest. Why do we need Ubuntu Server?Over the few years, the cloud has become an important focus point for users and IT, and that transformation has been a big boon to Ubuntu and Chronicle. Ever since IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) has taken off, Ubuntu OS has become one of the greatest players in executing these services through the cloud. Ubuntu has become the initial choice for DevOps engineers and administrators looking to set up OpenStack. And then there is Docker, one of the most famous container deployment environments on the market. Ubuntu server set up Docker in an easy way. Containers can proceed a long way to support us expand our company offerings to customers, clients, and staff. The new snap package aspect is another benefit of the Ubuntu server, which has several platforms in its class. Snap packages are global packages that include every essential dependency and can be installed with an easy command (like sudo snap install nextcloud). Also, snaps can be easily updated with a command (like sudo snap refresh). Affected Areas of Ubuntu ServerUbuntu Server affects everyone from end users and CFOs developers to IT pros. Let's consider one component of Ubuntu Server: the cloud. Now, assume about it:
It means that ubuntu Server isn't only commanding the cloud, but it will be a big force for leading IT. If our enterprise has yet to set up Ubuntu Server, don't worry- it will. As users and companies become more reliant on the cloud, Ubuntu Server will become more essential. The environment makes rolling out clouds and containers incredibly simple, fortunately for IT pros. Release of Ubuntu ServerUbuntu Server made its initial appearance with the publication of Ubuntu 6.06 (Dapper Drake) on 1 June 2010. Ubuntu images can be installed for either a server platform or a desktop, as with all releases since. As the desktop, the server publication applies similar repositories, so there has been stability between the releases since inception. Ubuntu Server has been published sans GUI; because of the repository sharing, it's possible to get a graphical environment. Competitors of Ubuntu ServerOn the server platform, the competition is brutal, with proprietary and open-source solutions available. The main competition for the market is: 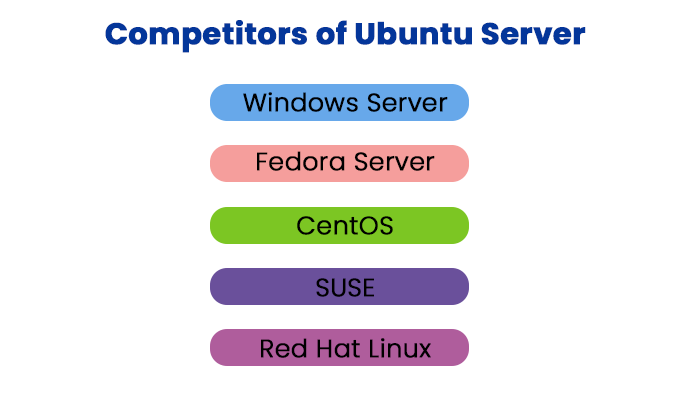
Only Fedora and CentOS servers are free from the above offerings. Introduction to Ubuntu DesktopUbuntu desktop is a distribution of Linux integrated by Canonical, and it is one of the most famous distributions due to its ease of use. Also, it is one of the top references for users who are getting started with these distributions. The server edition is also working in the internet server majority. Linux distro is an operating System integrated by the Linux kernel, a Unix-like system made by Linus Torvalds in 1991. Usually, Linux distributions are open-source and free, and several are great replacements for famous operating systems like macOS and Windows. In 2004, the Ubuntu Foundation was established by a South African-British entrepreneur and developer Mark Shuttleworth. He wished to make a more user-friendly Linux distro than Debian, which was very famous among Linux users. It was very difficult to install, although the Ubuntu Foundation operated to remedy that. Shuttleworth took Debian as a base for his operating system and named it Ubuntu because it was open-source. The word Ubuntu means "I am what I am because of who we all are" and "humanity to others". Why do we use Ubuntu Desktop?Let's look at every possible reason why Ubuntu may be worth giving a try: 
Different between Ubuntu Server and DesktopWe will discuss some important points about the differences between Ubuntu Server and Desktop: 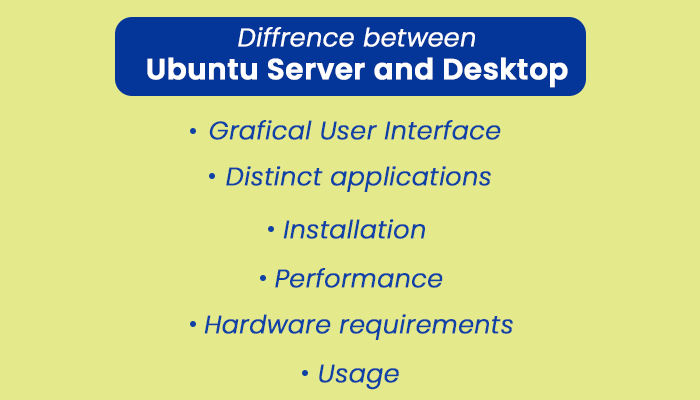
Graphical user interface The primary difference between Ubuntu Server and desktop is the desktop environment. Ubuntu server doesn't include a graphical user interface, while Ubuntu Desktop does. It's because almost all servers execute headless. It means they execute without a traditional mouse, keyboard, and monitor setup that enables users to interact with the device. Rather, servers are remotely managed by SSH. While SSH is established in Unix-based OSes, it is also easy to use SSH in Windows. However, a few Linux Server OSes offer desktop environments, and several lack a graphical user interface. So, Ubuntu Desktop thinks that our device uses video results and installs a DE. Meanwhile, Ubuntu Server lacks a graphical user interface. Distinct applications on Ubuntu Server and Desktop Additionally, Ubuntu Desktop includes applications suited to normal use: there is an office productivity suite, web browser, and multimedia software. Although, Ubuntu Server also contains distinct packages, and they concentrate on server requirements. Ubuntu Server can execute as a Samba server, web server, file server, and email server. Some specific packages are apacha2 and bind9. The packages of the Ubuntu server focus on permitting connectivity with users as well as security, whereas the applications of Ubuntu Desktop are geared towards utilization on the host machine. Installation of Ubuntu Server and Desktop The installation process of Ubuntu Server differs from Ubuntu Desktop because Ubuntu Server lacks a graphical user interface. Essentially, installing Ubuntu Desktop is like any software install. However, Ubuntu Server applies a process-driven menu rather. Performance of Ubuntu Server and Desktop Potentially, Ubuntu Server has better system performance because it does not have a graphical user interface by default. After all, there is no DE to handle. So, resources can be committed to server operations. However, it does not always succeed in practice. For instance, we might install a few specifically resource-intensive service applications, hence slowing the device down. Conversely, we might utilize Ubuntu Desktop for word processing. Installing Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Server using the default options on two different devices will always output in the server providing better performance compared to the desktop. But things will be changed when software arrives in the mix. Hardware requirements We need at least 4 GB of RAM to execute Ubuntu Desktop, and disk space should be at least 20 GB because the desktop version offers a graphical user interface. It is where it gets curious for Ubuntu Server. It doesn't have a GUI. The command line interface doesn't utilize a lot of system resources. As an outcome, we can run Ubuntu Server easily on a device with 512 MB and 5 GB of disk space. On the server, the disk space and RAM are subjected to the web service we execute. If a web software needs at least 2 GB of RAM, we should include that much RAM. But even 512 MB or 1 GB of RAM can work in the easiest scenario. Usage of Ubuntu Server and Desktop We should go for Ubuntu Server if it is specifically to deploy web services. Note: We need to have some common knowledge of the Linux command line for navigating from the terminal.If we wish to use Ubuntu as a normal computer, such as Windows, we should go for Ubuntu Desktop. If we wish to use it to learn Linux commands, LAMP, or Docker server installation, we should continue with Ubuntu Desktop. Ubuntu Server can be a good choice for server usage. For common computing usage, Ubuntu Desktop is better than Ubuntu Server. Similarities between Ubuntu Server and DesktopEven with every difference, there are still some similarities between these two:
Next TopicUbuntu VNC Server
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









