Gparted UbuntuGparted stands for GNOME Partition Editor. It is a front-end of GTK to GNU parted and the official partition-editing application of GNOME (alongside Disks). It is used to create, delete, resize, move, check, and copy disk partitions and other file systems. It is helpful to create space for new OSes, identifying disk usage, mirroring a single partition with other (disk imaging), and copying data that is residing on many hard disks. Partitions are logical segments of our actual hard disk space, specifying the file system and size format for the data and operating systems that are going to be positioned on them. It is one of the most common and important tasks for controlling the partitions. If we have the confidence and knowledge for manipulating the layout, changing it, deleting it, or creating it, then we can adapt our hardware to our varying requirements, without the need to blindly depend on the default setups specified by many vendors or other users. Background of GpartedGparted applies libparted for detecting and manipulating partition tables and devices while many file system tools offer support for many file systems not contained in libparted. These types of optional packages would be found at run time and don't need a re-creation of Gparted. It is specified in C++ and applies gtkmm for interfacing with GTK. The basic approach is to preserve the GUI as easily as possible and in obedience to the Human Interface Guidelines of GNOME. The Gparted project offers a Live OS containing Gparted which could be written into a Live USB, Live CD, and other media. The OS is based on Debian. Also, Gparted is present on other Live CDs of Linux including recent releases of Parted Magic, SystemRescueCD, Knoppix, and Puppy<. Gparted comes pre-installed if booting from the mode, i.e., "Try Ubuntu" on the installation media of Ubuntu. GNOME Disks is an alternative to this application. Features of GpartedGparted enables us to easily handle our disk partitions:
Gparted implements with the below storage devices:
Manipulate many file systems like:
Additional Information:It can find several file systems. Although, it might not run certain operations on a select some. Thus, to check what every file system is supported and to what extent. We require to execute the Package from the terminal or main menu of our system (type Enter and gparted). It will prompt us for the privileges of a superuser. How to install Gparted in the 20.04 LTS version of Ubuntu?We will discuss how we can install Gparted in the 20.04 LTS version of Ubuntu in this article. First, it was published on 26 August 2004. Installation Process of GpartedWe can install it using the command-line utility, i.e., apt because the package is present in the Ubuntu Repository. Hence, we are first required to update our Ubuntu repository. It ensures that we get the currently available release of the package. We need to open the terminal window and enter the following command: 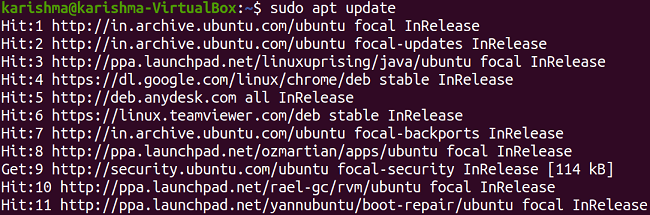
Then, enter the following command for installing Gparted: 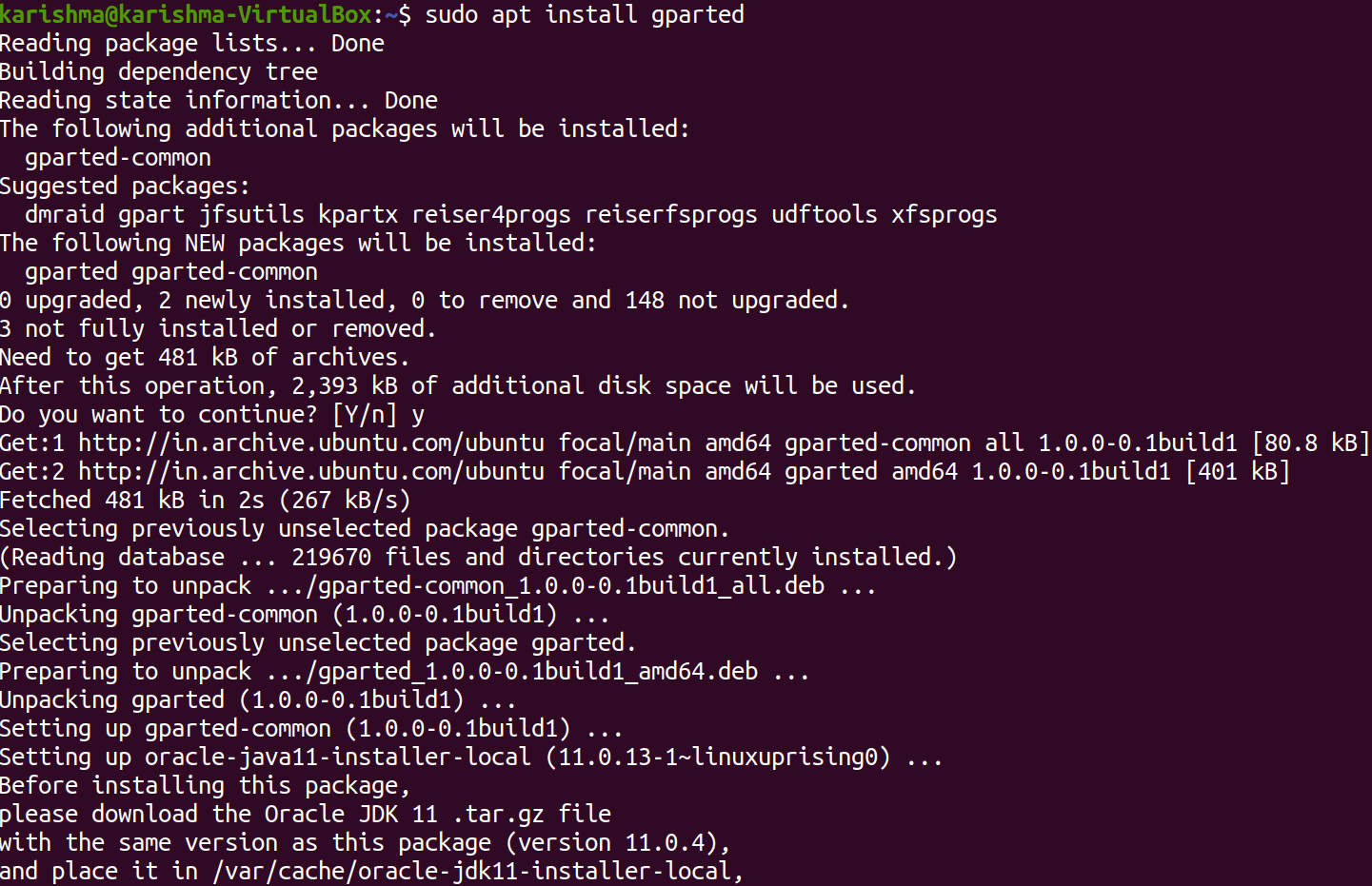
It will take care of every required dependency simultaneously. We can now use the package of Gparted from the main menu of our system. Note: Since we can handle the disk partitions using Gparted. Hence, we need superuser privileges to execute the application. If we do not know what do we do, we suggest taking the support of our System Administrator.Uninstalling GpartedThe Gparted software can uninstall from our Ubuntu computer by executing the following command in the terminal window: 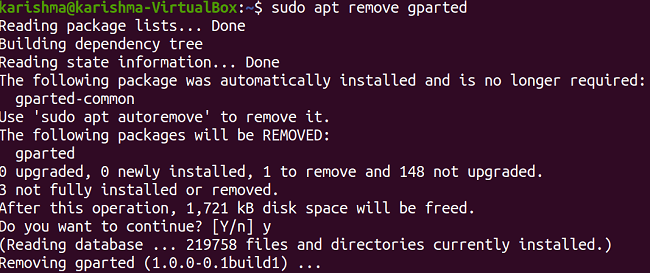
Next TopicIDM for Ubuntu
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









