Ubuntu ipconfigWhat is ipconfig?ipconfig stands for "Internet Protocol Configuration". It is a program of console application of a few computer OSes that shows every current value of TCP/IP network configuration and refreshes DNS (Domain Name System) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings. The ipconfig command shows IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 addresses, the default gateway for every adapter, and the subnet mask if applied without parameters. Implementations of ipconfigThe command is present in Apple macOS, ReactOS, and Microsoft Windows. The ReactOS release was developed upon the GPL license by Ged Murphy. Apple macOSIn Mac OS X, ipconfig serves as a cover to the IPConfiguration agent and could be used for controlling the DHCP and Bootstrap Protocol client through the command-line interface. Also, Mac OS X applies ifconfig for direct control on network interfaces like configuring static IP addresses like almost all Unix-based OSes. In Linux, the command, i.e., ifconfig has been substituted by the IP command. Microsoft Windows and ReactOSThe command, i.e., ipconfig supports the /all command-line switch. This outcome is more comprehensive information as compared to ipconfig alone. The ipconfig command contains an additional important feature where it forces refreshing the host computer's DHCP IP address to request a distinct IP address. It is done with two different commands in order. The first command is ipconfig /release which runs for forcing the client to immediately stop its lease by transferring the server a release notification of DHCP which updates the status information of the server and marks the IP address of an old client as "available". The second command is ipconfig /renew which runs for requesting a fresh IP address. In which a system is linked to a DSL modem or cable, it may need to be directly plugged into the modem network port for bypassing the router, before turning off the power and using ipconfig /release for a period, to make sure that the previous IP address is taken by other computers. The parameter, i.e., /flushdns can be used for clearing the DNS (Domain Name System) cache for ensuring future requests apply new DNS information by pushing hostnames to be fixed from scratch again. Parameters of ipconfigSome parameters of the ipconfig command are listed and mentioned below:
How to apply ipconfig and options?ipconfig is used for displaying details of our network configuration and refreshing the DNS and DHCP settings. The ipconfig command by default shows our IP address, default gateway, and subnet mask but we can get several details using this command with correct parameters. So, let's begin with something easier:
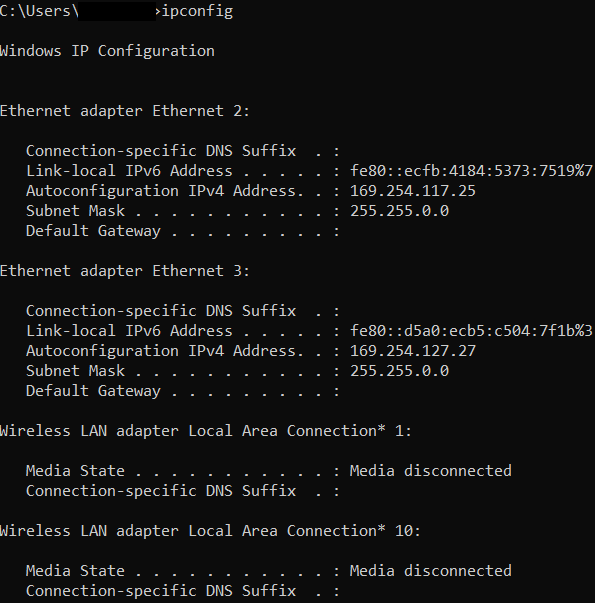
ipconfig /allThe command displays only the basic information of our network without using any parameter. But information about the DHCP and DNS servers is not shown by default. To display every detail of our network adaptor, we will need to enter the parameter, i.e., /all. 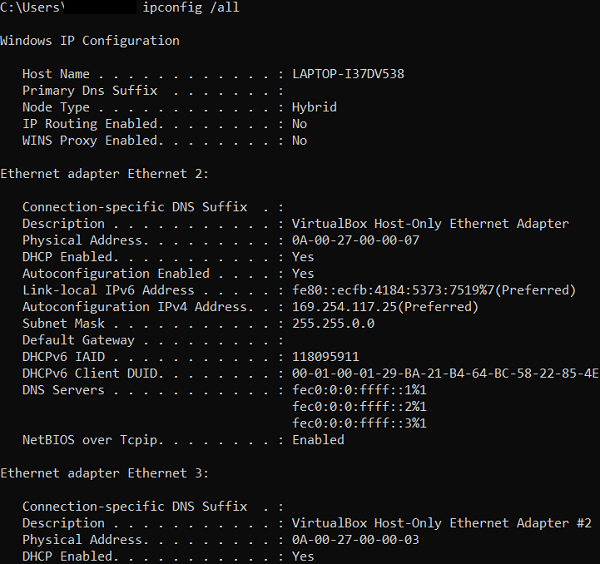
The above command will return the below information for all network adaptors in our device:
The command, i.e., ipconfig /all is often used for troubleshooting network connectivity issues. If we properly check out the outcomes of the ipconfig /all command, we can see 4 items that are essential and mentioned below:
ipconfig /releaseThe ipconfig command does not only display our information about our network settings, but it can also be used for resetting or refreshing our network settings. We can claim a new IP address through the DHCP server when we have enabled DHCP on our network card. The initial step to do it is to publish the current IP address. It means that we will alert the DHCP server that we do not no longer wish to apply the assigned IP address. 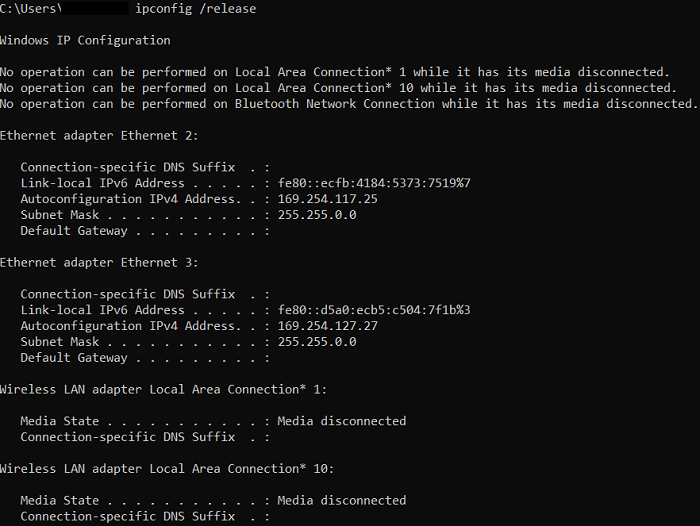
The above command will by default publish the IP Addresses for every network adapter. Also, we can specify an individual network adapter. To do so, we will need to type the adapter name that we find here inside the ipconfig results. For example, if we wish to publish only the IP address of our wireless network adaptor, we can enter the following command: It will publish the IP address of every adaptor in which the name begins with "Wireless". ipconfig /renewAfter we have published the IP address, we will need to claim a fresh one through the DHCP server. By using the command, i.e., ipconfig /renew, we can do it: 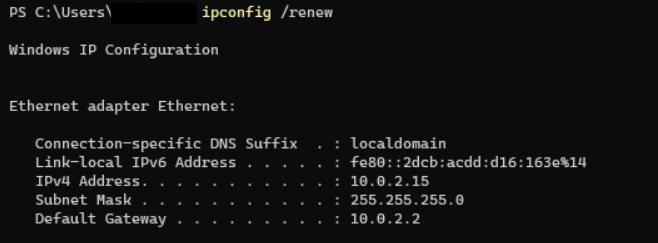
We will find a similar result as ipconfig command, gateway, subnet mask, and an overview of our new IP address when the renew command was successfully run. We can again specify an individual network adaptor by providing the adaptor name. ipconfig /displaydnsOur computer stores a local cache of every DNS record that it has visited. This cache is used for quickly translating the domain names into the correct IP address. In this way, our computer does not need to every time negotiate with the DNS server. For example, when we visit Google.com. We can run the following command in the terminal window for viewing the DNS cache content: 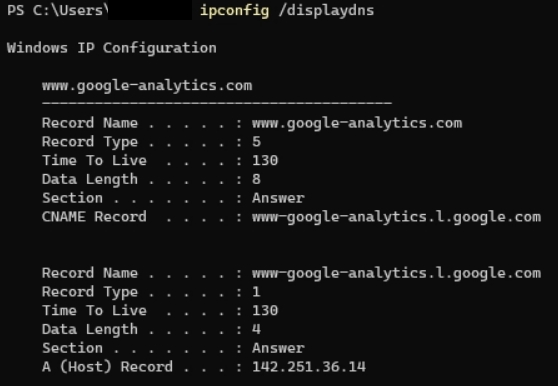
It will display all DNS records in our DNS cache. Often, we do not need to check the records, but we will discuss some important terms:
Flush DNSSometimes, our DNS cache includes outdated records which can give DNS-related errors (for example unable to reach websites), we can solve it by applying the command which is mentioned as follows: 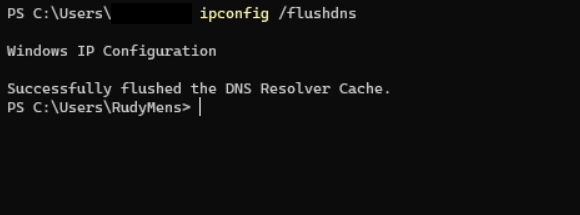
The above command will clear out our DNS cache. We can do it without any risk, our computer will simply claim an up-to-date and new DNS record through the DNS servers. ipconfig on UbuntuThe ifconfig command is equivalent to the ipconfig command. The ifconfig command will display us the basic information of the network of our adapters in Ubuntu. The command is as follows: 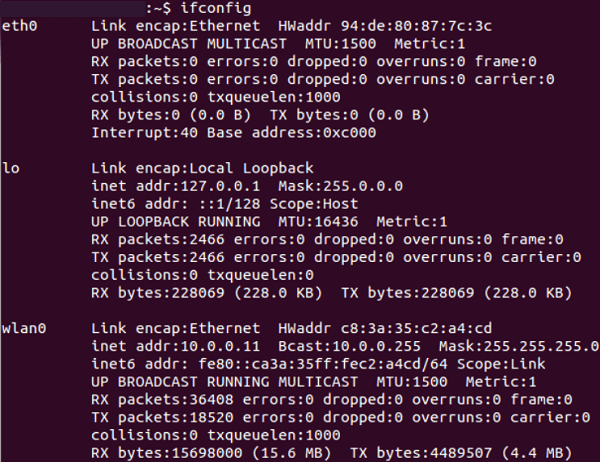
Next TopicUbuntu Packages
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









