Linux Text EditorsA text editor is a kind of computer program that can edit plain text. Sometimes, such programs are called "notepad" software. Text editors are offered software development and operating system packages and can be utilized to modify, including programming language source code, documentation files, and configuration files. Linux text editors can be used for editing text files, writing codes, updating user instruction files, and more. A Linux system supports multiple text editors. There are two types of text editors in Linux, which are given below:
A text editor plays an important role while coding. So, it is important to select the best text editor. A text editor should not only be simple but also functional and should be good to work with. A text editor with IDE features is considered as a good text editor. What is Rich text and plain text?There are essential differences between rich text (like that made by desktop publishing and word processor software) and plain text (made and edited by many text editors). Exclusively, plain text is composed of character representation. All characters are represented by one, two, or four bytes fixed-length sequence or as one-four bytes variable-length sequence, in accordance with particular character encoding conventions, including UTF-16, UTF-8, Shift-JIS, ISO/IEC 2022, or ASCII. These conventions specify several printable characters but non-printing characters that manage the text flow, including page breaks, line breaks, and spaces. Plain text includes no other text information, not only the character encoding convention applied.
Brief History of Text EditorsComputer text was inserted into cards using keypunch devices before text editors were available. Then, physical boxes of thin cardboard cards were embedded into the card reader. Dick card images, drums, and magnetic files made from these types of cards beautify generally had no line-separation characters and supposed 80- or 90- fixed-length character records. Punched tape was a replacement for cards. It could be made by a few teleprinters, which used unique characters to represent record ends. A few early OSes contained batch text editors, developed with language processors or as different utility programs; an example was the feature to edit source files, i.e., SQUOZE, for SCAT in SHARE OS.
O26 was one of the original full-screen editors, which was specified for the CDC 6000 series system's operator console in 1967. vi was another initial full-screen editor, which was specified in the 1970s; it's still a classic editor on Linux and Unix operating systems. Also, UCSD Pascal Screen Oriented Editor was written in the 1970s and was developed for both general text and sectioned source code. One of the initial open-source and free software projects, Emacs, is another previous real-time and full-screen editor that was ported to various systems. The speed and ease of use of a full-screen editor motivated several early video terminal purchases. In a text editor, the core data structure is the one that handles the string or list of records that indicates the current file state being edited. The ambition for text editors that can more quickly undo/redo early edits, insert text, and remote text led to the advancement of more complicated data structures while the departed can be stored in one long consecutive character array. A classic text editor utilizes a gap buffer, a rope, a piece table, or a line's linked list, as its data structure. Text Editor TypesA few text editors are simple and small, and others provide complex and broad functions. For instance, Unix-like and Unix operating systems contain the pico editor but several also contain the Emacs and vi editors. Microsoft systems provide the simple Notepad so that various people use other editors with additional features, especially programmers.
The file format (default) of these word processors generally features a markup language, along with the common format being visual formatting and plain text achieved with non-printing escape sequences or control characters. Later word processors, such as Microsoft Word, store the files in binary format and are mostly never utilized to alter plain text files. Typical Features of Text Editors
Advanced Features of Text Editors
The line command can also be described as a string that a user enters into the line number field and the editor identifies as a command working on that particular line or line's block. For example, LC to convert a line into lowercase. Regardless of the prefix command name, some editors permit the sequence field to occur after a text field. In this section, we are going to discuss the top 20 text editors for Linux. Further, we will talk about the latest text editors and will compare them with the traditional text editors such as Vi and nano. This will help you with selecting the editor of your choice.
1.Vi/VIM editorVim editor is one of the most used and powerful command-line based editor of the Linux system. By default, it is supported by most Linux distros. It has enhanced functionalities of the old Unix Vi editor. It is a user-friendly editor and provides the same environment for all the Linux distros. It is also termed as programmer's editor because most programmers prefer Vi editor. Vi editor has some special features such as Vi modes and syntax highlighting that makes it powerful than other text editors. Generally, it has two modes: Command Mode: The command mode allows us to perform actions on files. By default, it starts in command mode. In this mode, all types of words are considered as commands. We can execute commands in this mode. Insert Mode: The insert mode allows to insert text on files. To switch from command mode to insert mode, press the Esc key to exit from active mode and 'i' key. To learn more about Vi editor, visit the Vi editor with commands. To invoke the vi editor, execute the vi command with the file name as follows: It will look like below image: 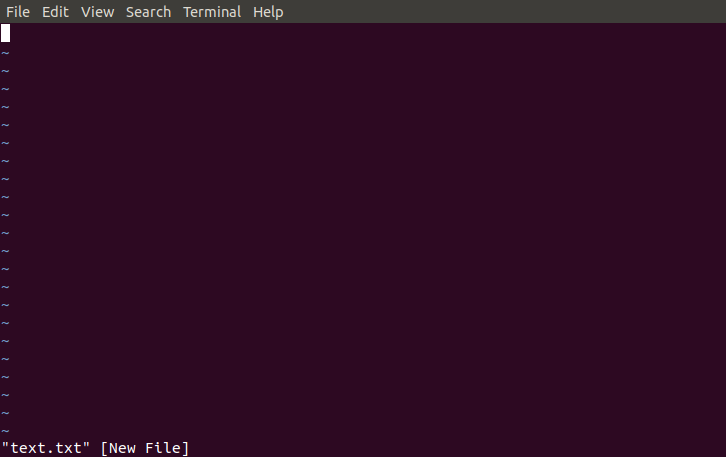
2. Nano editorNano is a straight forward editor. It is designed for both beginners and advanced users. It has many customization features. Some advanced features of a nano text editor are as following:
To open file with nano editor, execute the command as follows: The nano editor looks like: 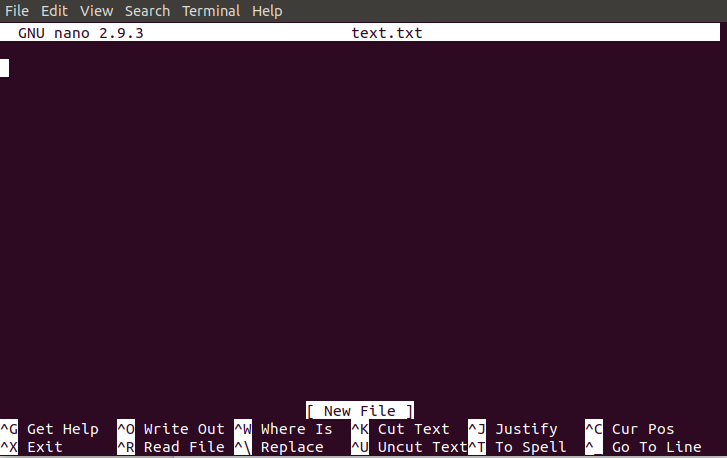
In the nano editor, the useful options are given at the bottom, use the CTRL+ option to perform an operation. For example, to exit from the editor, use CTRL +X keys. To learn more about nano editor, Visit Linux Nano Editor. 3. Gedit editorGedit editor is the default editor for the GNOME desktop environment. When we open a file, it will open with the Gedit editor. It provides straightforward functionalities like any basic text editor. It is a lightweight editor with a straight forward user interface. It was publicly released in the year 2000 with a GNOME desktop environment. It is developed using the C programming language and supports all font family. Some key features of the gedit text editor are as following:
To invoke the gedit editor from the terminal, execute the below command: It looks like: 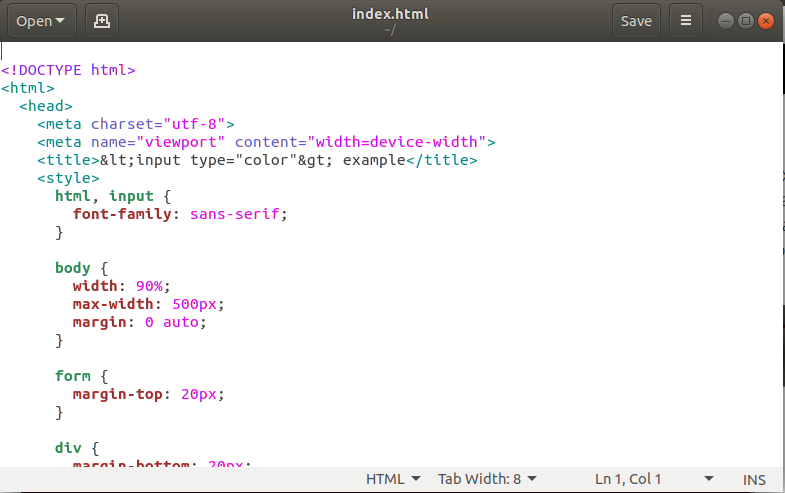
4. Sublime TextThe sublime text editor is also one of the most popular IDE-based text editors. It is used as a development environment tool more than a text editor. It has several features to support many programming and mark-up languages. Further, it supports numerous plugins to make it more than a text editor. Some key features of a sublime text editor are as following:
Execute the following commands to install the sublime text editor: To learn more about installation, visit Install sublime text editor on ubuntu. We can open the sublime editor by browsing applications. Also, we can open it from the terminal. To access the sublime editor from the terminal, execute the below command: It will look like below image: 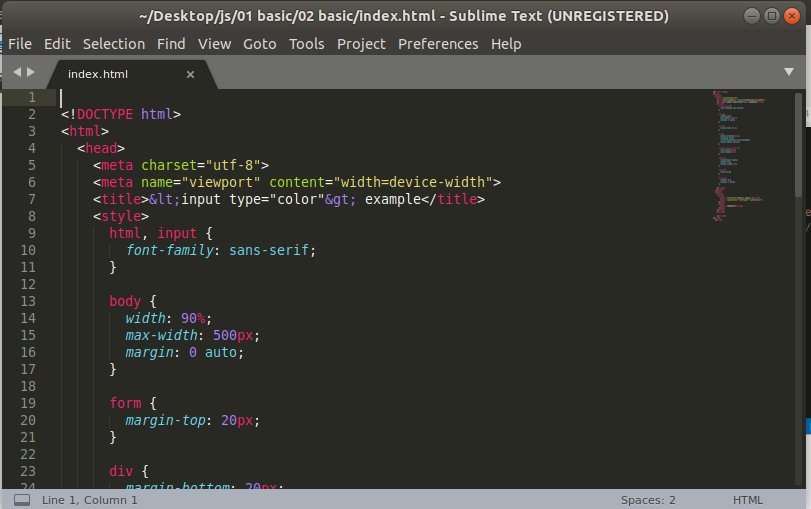
5. VSCode EditorVSCode editor is a modern and widely used text editor. It is built by Microsoft and has support for Linux, Mac and Windows OS. It facilitates with many powerful features to support many programming languages and markup language. To install the VSCode, download the binary package from Here. And, execute the below command for Debian and Ubuntu-based systems: Some key features of VSCode editor are as following:
The VSCode editor looks like the below image: 
6.GNU EmacsGNU Emacs is the oldest and simplest text editor for the Linux system. It is a part of the GNU project. It is still a popular text editor used by thousands of users because of its simplicity. It is written in C and LISP programming languages. Some key features of GNU Emacs are as following:
Execute the following commands to install GNU Emacs: To access it from the terminal, execute the below command: It will look like below image: 
7. Atom EditorAtom is a free and open-source code editor developed by GitHub Inc. It is cross-platform and supports several programming languages. It is also referred to as a "hackable text editor for the 21st century". It was developed for the development purpose. It is completely customizable using web technologies such as JavaScript and HTML. It facilitates with Node.js-based plugins and Git control. Some key features of Atom Editor are as follows:
To install Atom, download the binary package from the official site of Atom, and execute the below command: To know more about installation, Visit Here. It will look like below image: 
8. Brackets EditorBrackets editor is a free and open-source text editor developed by Adobe. It primarily focuses on web development. It provides a rich code editing experience with several free extensions. It is written in HTML, CSS, and JS. Some key features of Brackets editor are as following:
To install Brackets editor, execute the following commands: It will look like: 
9. Pico EditorThe Pico editor is a terminal-based Linux text editor. It has built-in support for pine news and email client. It is very straight forward to use and facilitates with some useful features such as justification, cut/paste, spell checker, and more. However, it is just a simple text editor, so it does not offer many features like other Linux text editors. It is not purely free text editor, so most Linux distributions do not provide pico as a text editor. It does not support working with multiple files simultaneously. Also, it cannot perform find and replace operation across multiple files. To open a file with a pico text editor, execute the command as follows: It will look like below command: 
10. BluefishBluefish is a free and open-source text editor for the Linux system. It is an advanced text editor having plenty of tools for programming. It is good for developing dynamic websites. It supports several languages and tools such as PHP, C, C++, JavaScript, Java, Google Go, and many more. Some key features of Bluefish text editor are as following:
To install Bluefish, execute the following commands: To know more about installation, visit Install Bluefish editor on Ubuntu. To open file with bluefish, execute the below command: it will look like: 
11. Kate/Kwritekate is an advanced and multi-document editor. It is part of KDE, since release version 2.2. The Kubuntu desktop environment ships it as a default editor. If you are familiar with the Kubuntu environment, then you must have known about kate editor. It provides working with multiple files simultaneously. It is considered as an IDE as it carries powerful features like an IDE. It is good for editing configuration files, viewing HTML sources from Konqueror, creating new applications, and many more tasks. Some key features of Kate editor are as following: Some of the unique features of Kate includes:
To install the kate editor, execute the below command: To open a file with kate editor, execute the below command: It will look like below image: 
12. Notepad++Notepad++ is a basic text editor having many customization options. It primarily focuses on speed and minimal program size. It is mostly used by Windows users. It supports several plugins to increase its functionality. Some key features of Notepad++ are as following:
To install notepad ++, execute the following commands: To know more about the installation process, visit How to install notepad++ on Ubuntu. To open a file with notepad++, execute the below command: It will look like the below image: 
13. EclipseEclipse is one of the most used IDE (integrated development environment) for development. It is a preferred choice of the Java developers as it is developed in Java and provides several features to develop advance java applications. It provides supports for other programming languages as well, and we need to install extra plugins to write code in other programming languages such as PHP, Python, C, C++, Ruby on Rails, COBOL, and more. Some key features of the eclipse are as following:
To install Eclipse, execute the following commands: To know more about the installation process, visit How to install Eclipse on Ubuntu. It will look like the below image: 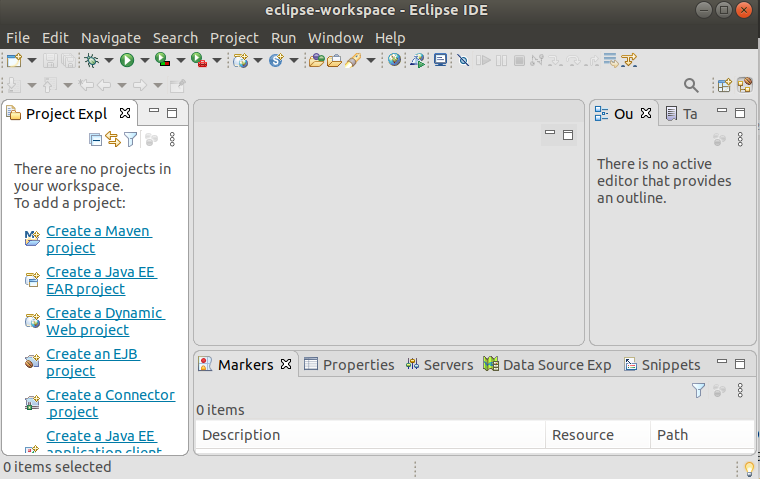
14. gVim EditorThe gVim editor is the GUI version of the popular Vim editor. It has similar functionality and modes as the command line editor Vim. It can be easily downloaded from the software store. To install it from the terminal, execute the following commands: To open a file with gVim from the terminal, execute the below command: It will look like the below image: 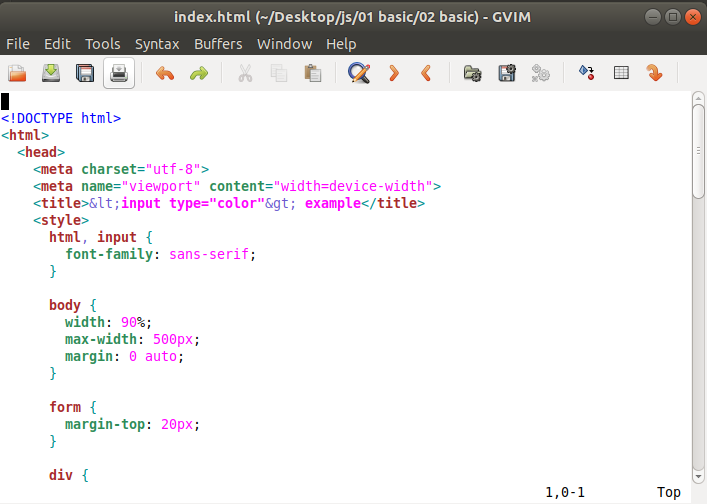
15. Jed EditorThe Jed is a command-line editor that supports extensive use of the S-Lang library. Jed supports its all flavors for different operating systems such as Linux and Windows. It is a lightweight editor, which makes it an ideal editor for the low configuration systems. Some key features of Jed editor are as following:
To install the Jed editor, execute the following commands: It will look like the below image: 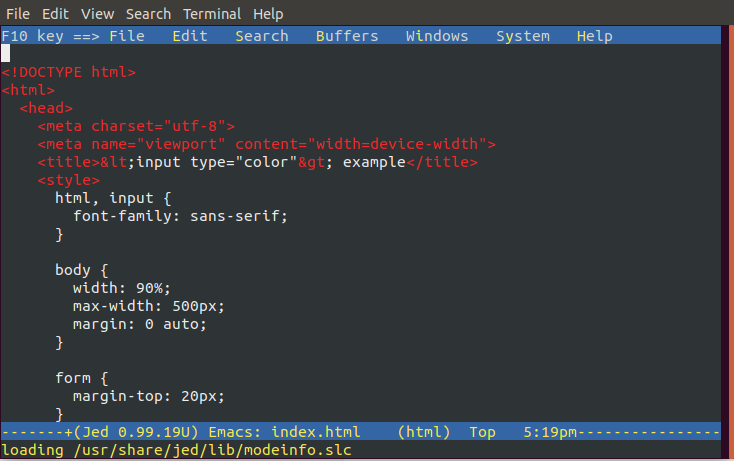
16. Geany EditorGeany is a powerful, lightweight editor for the Linux systems. It is stable and supports tons of features to make it useful. It has built-in support for several programming languages. It is supported by other operating systems such as Windows and Mac as well. Some key features of Geany editor are as following:
To install Geany editor, execute the following commands: It will look like the below command: 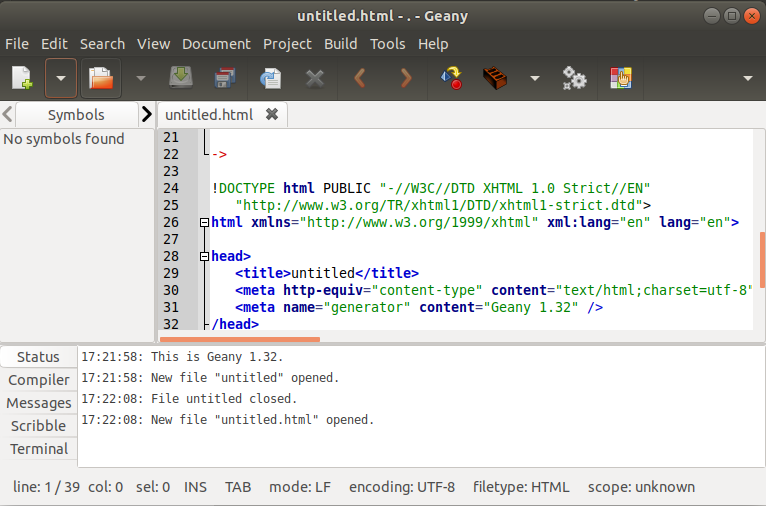
17. LeafpadLeafpad is a straight forward GTK based text editor. It is a popular text editor among Linux users due to its simplicity and lightness. The key features of Leafpad are as following:
To install Leafpad, execute the following commands: It will look like the below command: 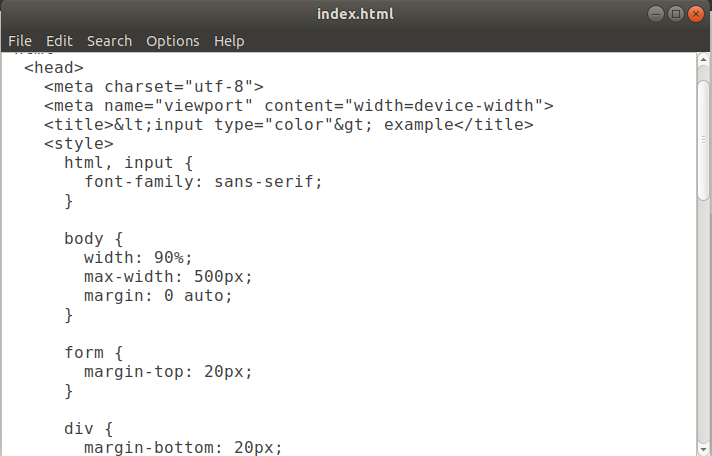
18. Light TableA light table is a modern open-source IDE based text editor. It is one of the best text editors of the Linux system. Some key features of Light table are as following:
We can simply download the light table from its official site. To install it from the terminal, execute the following commands: It will look like the below image: 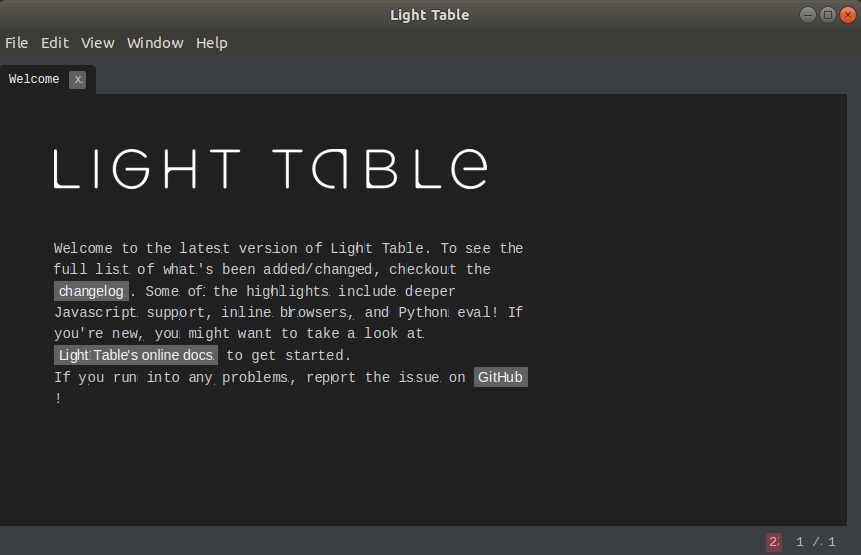
19. Medit text editorThe medit text editor is a lightweight open-source text editor. It is available for all major operating systems such as Linux, Mac, and Windows. It was started with a simple built-in component of CGAP, but it is now upgraded as a stand-alone text editor. Some key features of Medit are as following:
To install medit, execute the following commands: It will look like the below image: 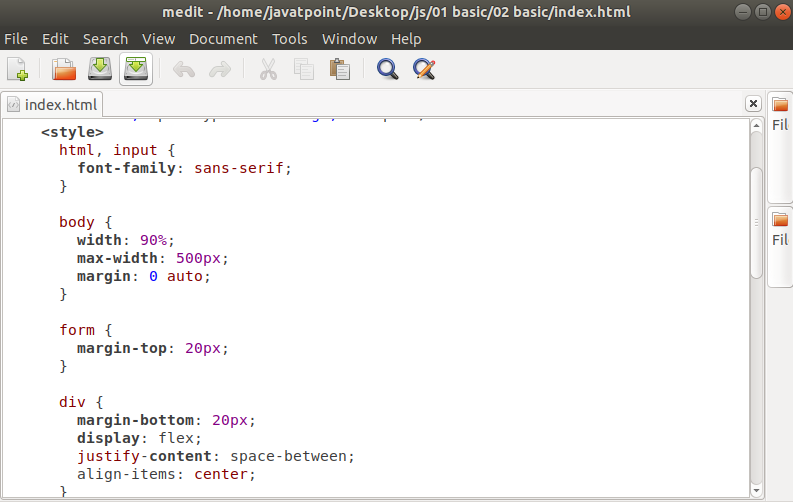
20. CodeLiteCodeLite is an open-source IDE that supports cross-platform. It supports several most used programming languages like C, C++, PHP, and JavaScript. It supports all major platforms such as Linux, Mac, and Windows. To install CodeLite, execute the following commands: It will look like the below image: 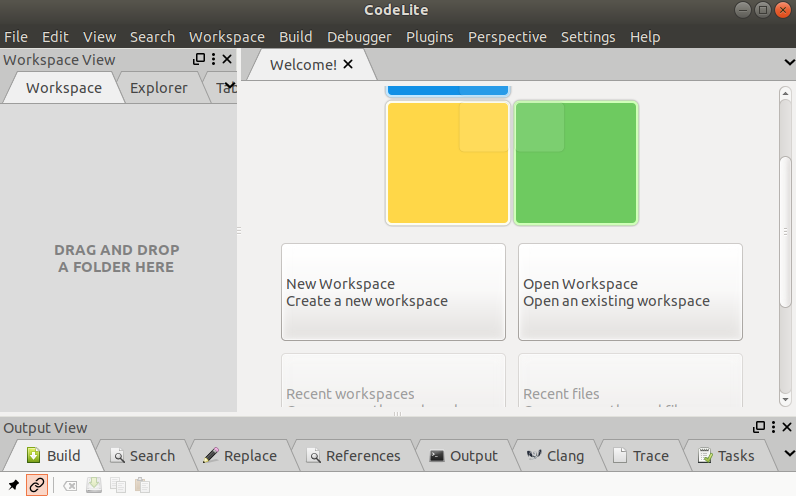
Some specialized editorsEditors contain extra functions and special features, for example,
Next TopicVi Editor
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









