Linux Data directoryData directory is used to store data of the system. Data directory contains following directories.
/homeThe '/home' directory stores users personnel files. After the '/home' there is a directory which is generally named at the user's name like we have '/home/sssit'. Inside this directory we have our sub-directories like Desktop, Downloads, Documents, pictures, etc. Example: 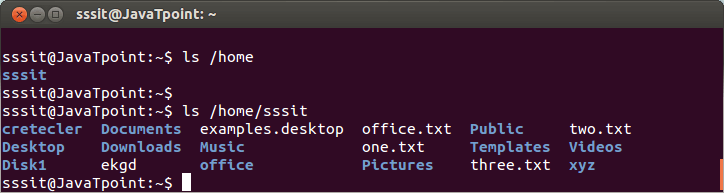
Look at the above snapshot, command "ls /home" displays 'sssit'. While command "ls /home/sssit" displays 'sssit' sub-directories. Note: Tilde (~) sign indicates "/home/sssit". For example, if you want to give the command "/home/sssit/Desktop" so instead of writing this you can also write "~/Desktop", both are same. /rootThe '/root' directory is the home directory of the root user. Please note that '/root' directory is different from (/) root. /srvThe term 'srv' is short for service. The '/srv' directory contains server specific data for services provided by the system like www, cvs, rysync, ftp, etc. /mediaThe '/media' directory acts as a mount point for removable media devices such as CD-Rom, floppy, USB devices, etc. This is newly introduced directory and hence a system can run without this directory also. Example: 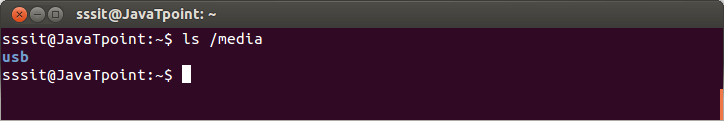
Look at the below snapshot, command "ls /media" displays '/media' content. /mntThe term 'mnt' stands for mount. The '/mnt' directory should be empty and sysadmins can only mount temporary filesystems. /tmpThe term 'tmp' stands for temporary. Data stored in '/tmp' is temporary and may use either disk space or RAM. When system is rebooted, files under this directory is automatically deleted. So it is advisable that never use '/tmp' to store important data.
Next TopicLinux Memory Directory
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










