GitHub Desktop for UbuntuBackgroundApplication development is all about specifying code and integrating solutions following processes and requirements. Handling code becomes not easy with time and more than one contributor. In the actual scenario, more than one developer operates on a similar project and specifies code on a regular basis. Tracking modifications and merging those codes are time-consuming and hassle without any proper platform or tool. Another problem is rollback which isn't possible without applying any version control tool. Source code management is another essential factor to examine when it comes to specifying code. Source code management is not just only storing the code but tracking the modifications, merging from more than one contributor, and solving the conflicts as well. There are many platforms and tools present for source code management along with executive aspects. We will elaborate on GitHub in this article which is one of the most utilized and open-source cloud-based communities for managing our source code with extensive aspects with Git repositories. Introduction to GitGit is a system of version control to manage the source code which records the track of it along with several options. It is basically software for tracking the modifications of files mostly utilized for coders to collaboratively work and source code management at the time of the software development. According to Git-SCM, "Git is an open-source and free distributed version control system developed to manage everything from a small project to a very large project with efficiency and speed". Git can be learned easily and contains a tiny footprint along with lightning-fast work. It beats SCM tools such as ClearCase, Perforce, CVS, and Subversion with features such as multiple workflows, convenient staging areas, and cheap local branching. Introduction to GitHubIn general terms, GitHub is an individual biggest cloud-based hosting service to manage git repositories which provides a huge variety of functionality for version control, source code management, and its features. One of the great things about GitHub is that it's completely free. We can make public and private repositories using GitHub at no cost with a few conditions. It's widely used for hosting open-source projects. The free plan of GitHub permits the establishment of unlimited private repositories along with unlimited collaborators as of now. However, there is a limitation of Git Actions of up to 2000 minutes for private repositories per month. With Git, GitHub offers features such as continuous deployment/continuous integration, code review, task management bug tracking, likewise several other features which enable this platform more interactive and useful professionally.Introduction to GitHub Desktop
What's the difference between GitHub and Git?GitHub: It is a web-based repository of Git hosting service which provides all of the distributed revision control and SCM (source code management) functionality of Git and adds its features as well. Git: It is a distributed version control system to track modifications in source code at the time of the software development. It's developed to coordinate work among several programmers but it could be used for tracking modifications in any group of files. The goals of Git include support, data integrity, and speed for non-linear distributed workflows. The following is the difference table between GitHub and Git:
About GitHub DesktopJust some of the several things we can do using GitHub Desktop or as follows:
Step 1: Install GitHub Desktop and verify our accountWe can install GitHub Desktop on the supported operating systems. We will require to sign in and verify our account on GitHub Enterprise or GitHub before we can make and clone any tutorial repository after we install the application. Step 2: Create a new repositoryIf we don't have any repositories related to GitHub Desktop, we will find a "Let's get started" option, where we can select to make and clone the tutorial repositories, include the existing repositories using our hard drive, make a new repository, or clone a previous repository using the internet. Important: When we create a new repository, we need to fill up some fields and choose our preferred options. These fields are listed and mentioned below: 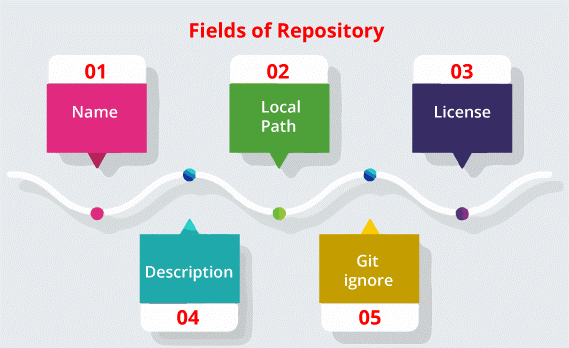
Installing and Using GitHub Desktop in UbuntuA GitHub Desktop is a Git software that is freely available. It's implemented with typescript. GitHub implements as the source code repository and it could be installed and used in distinct kinds of operating systems. The GitHub Desktop was developed by Brendan Forster for the users of Linux. This software can be used by executing AppImage and downloading it on the Linux OS. In this article, we will explain how to install GitHub Desktop in the Ubuntu system. Downloading the GitHub DesktopFirst of all, we need to open our terminal window and execute the below command for downloading the GitHub Desktop using the below URL address: 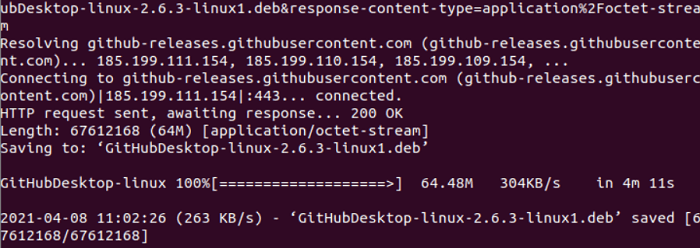
Launching the GitHub DesktopWe need to press the icon, i.e., "Show Applications" from the left-hand side of the desktop and find "GitHub". The below dialog box will occur if the user presses the "github-desktop" downloaded option. Press the install button and give the root password for starting the installation procedure. 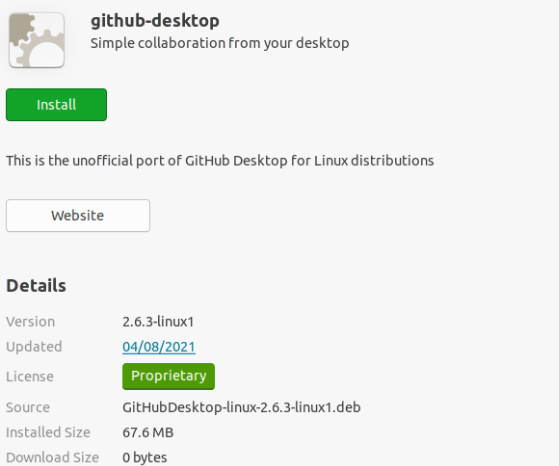
The dialog box will include the below button and the details after finishing the installation process. The 2.6.3 version of GitHub Desktop has been installed here. We need to press the Remove button if we wish to remove the software. 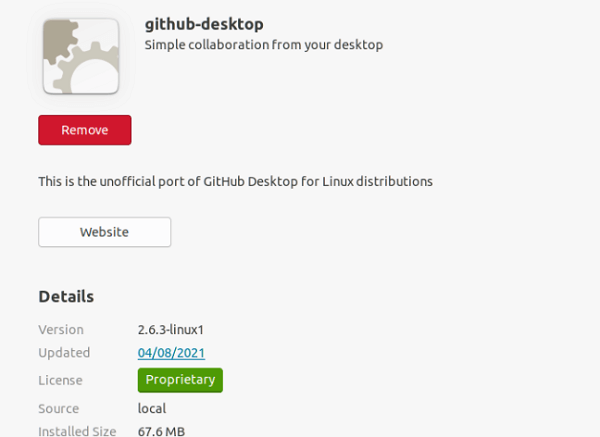
Next, press the "Show Applications" icon and find "GitHub" again. We will have the icon, i.e., GitHub Desktop if the application is properly installed. We need to press the icon to start the application. 
The below dialog box will occur when the software is opened for the very first time. If we have already an account on GitHub.com, press the "Sign in to GitHub.com" option and if we have already an account on GitHub Enterprise, press the "Sign in to GitHub Enterprise" option. If we are new users and wish to create a new account, press the "Create your free account" option. If we do not wish to access or make a new account, press the "Skip the step" option. 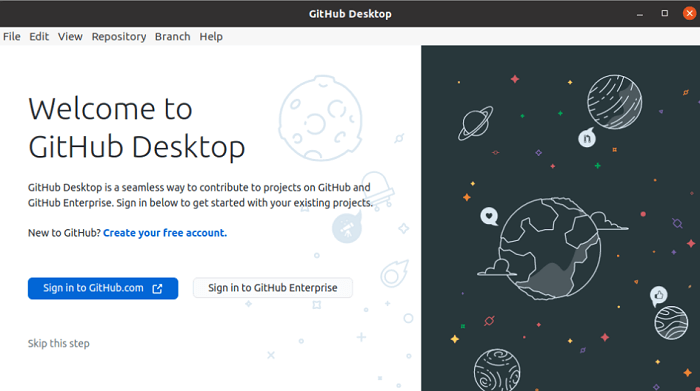
If we press the "Create your free account" option, the below page will occur within the browser. Press the "Create account" option after giving the valid details in the below form. 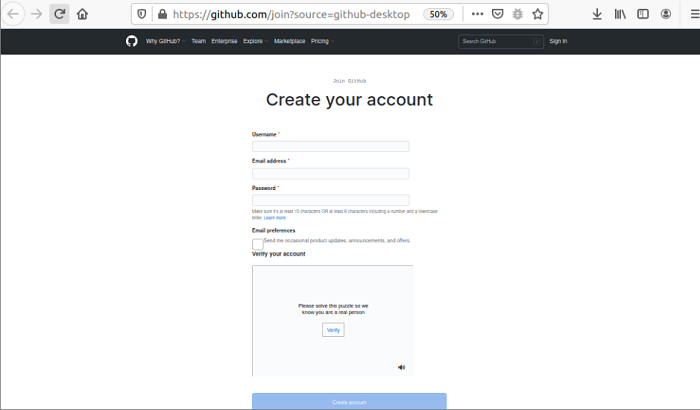
The below page will occur after establishing the account. The aspects of four applications are represented here for authorization.
The below pop-up screen will occur if we press the "Authorize Desktop" option. It is promoting permission to allow github.com for opening the link, i.e., x-github-desktop-dev-auth. Press the "Choose Application" option to choose the GitHub Desktop application. 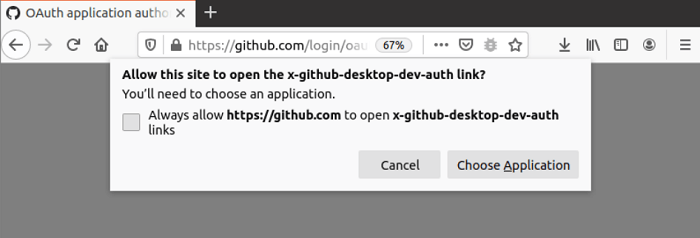
Choose the application, i.e., GitHub Desktop, and press the "Open Link" option. 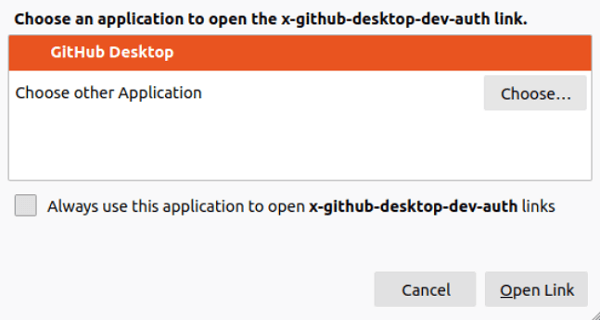
Now, if we open the installed application, i.e., GitHub Desktop, the below form will occur for configuring Git. The email address and the username of the GitHub account that was fixed during the creation of the GitHub account will occur here. Press the "Continue" option for configuring Git to identify the commits implemented by the GitHub user. 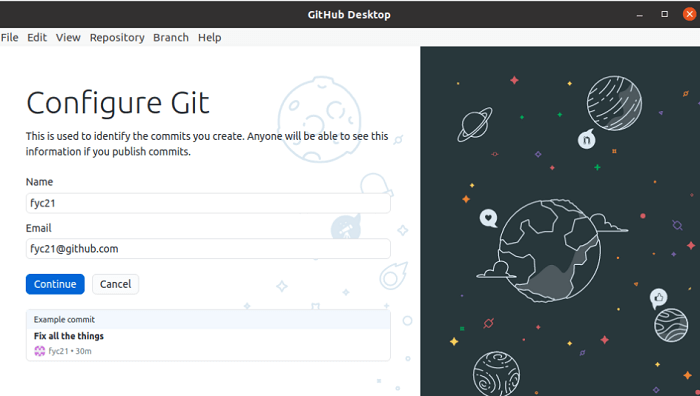
The below information will occur if everything is properly set up for the GitHub Desktop. Press the "Finish" option to finish the setup. 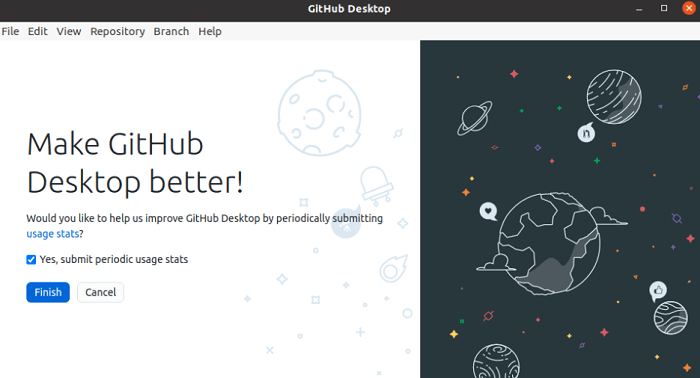
The below option will occur if the GitHub Desktop is properly installed and configured on the Ubuntu system. The ways of establishing four kinds of repositories have been explained here.
From the GitHub account, the repository can be found with the search box, i.e., "Filter your repositories" to clone the repository. The repository list would be empty if no repository is released in the GitHub account. After releasing any repository within the GitHub account, we need to press the refresh link for getting the recently released repository list. At the application window's top, a menu bar is there for doing the different kinds of repository-related functions. 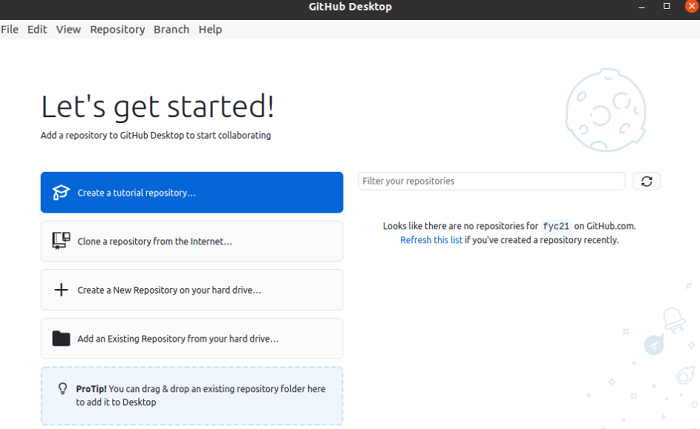
Next TopicInstall Yarn Ubuntu
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share