UML Object DiagramObject diagrams are dependent on the class diagram as they are derived from the class diagram. It represents an instance of a class diagram. The objects help in portraying a static view of an object-oriented system at a specific instant. Both the object and class diagram are similar to some extent; the only difference is that the class diagram provides an abstract view of a system. It helps in visualizing a particular functionality of a system. Notation of an Object Diagram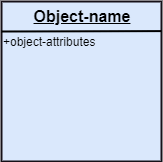
Purpose of Object DiagramThe object diagram holds the same purpose as that of a class diagram. The class diagram provides an abstract view which comprises of classes and their relationships, whereas the object diagram represents an instance at a particular point of time. The object diagram is actually similar to the concrete (actual) system behavior. The main purpose is to depict a static view of a system. Following are the purposes enlisted below:
Example of Object Diagram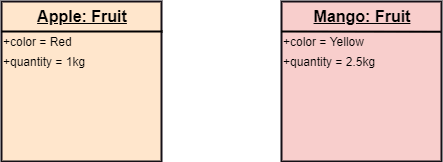
How to draw an Object Diagram?
Applications of Object diagramsThe following are the application areas where the object diagrams can be used.
Class vs. Object diagram
Next TopicUML Component Diagram
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










