What is the full form of ARDSARDS: Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeARDS stands for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. It is a severe lung condition in which the lungs become severely inflamed, and fluid fills up in the tiny, elastic air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. It may occur due to severe pulmonary injury or infection. In the beginning, it manifests as dyspnea, tachypnea or hypoxemia, then over time, evolves into respiratory failure. 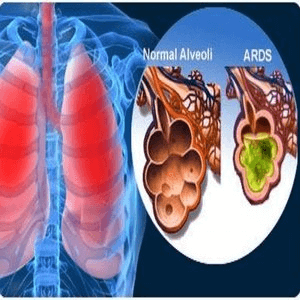
As fluid accumulates in the lungs, less space is left for the air, so less oxygen is passed to the bloodstream. It leads to low oxygen levels in the blood. The organs don't get sufficient oxygen to perform their functions properly. Common SymptomsThe symptoms of ARDS usually appear within a few hours or a few days after the injury or infection. Some of the common symptoms are:
Common CausesThe ARDS may occur due to a number of reasons; some of the most common causes are:
Risk componentsMost ARDS patients also are hospitalised for another illness, and many of them are in critical condition. You are more vulnerable if you have sepsis, a broad disease in your bloodstream. Individuals who have a past of chronic alcoholism have a higher risk of developing ARDS. ComplicationsWhile in the hospital, someone with ARDS may experience various health issues. The most typical issues are: Clots in the blood: These are the most frequent problems. Blood clots are more likely to form when you are in the hospital, especially in the leg veins. When you are on ventilation and resting still, if a blood clot develops in your leg, it may fragment and go to one or both of your lungs, where it might obstruct blood flow (pulmonary embolism). Lung collapsed (pneumothorax): A breathing apparatus called a ventilator is typically used in ARDS cases to raise oxygen levels in the body and push fluid out of the lungs. However, the ventilator's pressure and air volume can drive gas to pass through a tiny hole in a lung's very outer layer, leading to the collapse of that lung. Infections: Because the ventilator is directly attached to a tube implanted in your oesophagus, it is much simpler for germs to infect and worsen your lungs. Scarring (pulmonary fibrosis): Within just a few weeks of the onset of ARDS, the tissue in the space between the air sacs may become scarred and thickened. As a result, your lungs become more rigid, which makes it more challenging for oxygen to enter your circulation through the air sacs. Thanks to increasingly effective treatment, a lot more patients are surviving ARDS. However, many survivors experience potentially harmful and occasionally long-lasting consequences: Breathing issues: While many ARDS patients regain the majority of their lung function within a few months to two years, some may continue to struggle with breathing issues for the remainder of their lives. Even those who perform well frequently have weariness and shortness of breath, and they may require home oxygen therapy for a few months. Depression: The majority of ARDS patients also mention having episodes of manageable depression. Remembering and thinking clearly issues: After ARDS, sedatives and lower levels of blood oxygen may cause memory loss and cognitive problems. While in certain situations the consequences might fade with time, in others, the harm might be irreparable. Fatigue and weakened muscles: Your muscles may deteriorate if you are in the hospital and using a ventilator. Following therapy, you can have extreme fatigue.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










