What is the full form of ATA/PATAATA/PATA: Advanced Technology Attachment/Parallel Advanced Technology AttachmentATA stands for Advanced Technology Attachment. ATA is the older name of PATA. ATA was renamed Parallel ATA (PATA) when the newer Serial ATA (SATA) was introduced. ATA is a standard physical interface that connects the storage devices like hard-drive, CD-ROM, and other drives to the motherboard. ATA standards only allow cable up to 18 inches, due to which it works internally. It is designed to connect portable storage devices without using an external controller. ATA is the most common and low-cost interface that provides a reliable speed. It is basically made of thin wires and a cable bus. It is also known as Integrated Device Electronics (IDE). The ATA standards are backwards compatible. It means each newer version of ATA or new ATA drives can be used with older ATA interfaces. 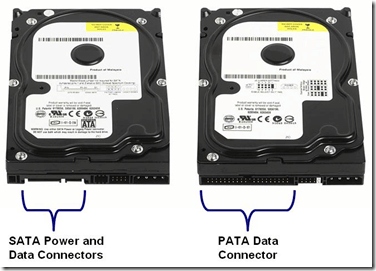
HistoryThe first version of ATA was developed by the company named Western Digital in 1986. Originally, it was known as ATA, but after the introduction of SATA (Serial ATA) in 2003, it became PATA. Both PATA and SATA are IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) devices. The task of creating all interface standards for the ATA interface, including ATA and ATA with Packet Interface, falls within the domain of NCITS Technical Committee T13 (ATAPI). FunctioningATA uses 40 pins connectors on either side of the cable and 40 or 80-wire designs. One end is connected to the motherboard, and the other is connected to the hard drive. PATA uses a single Bus but multiple wires. ATA can be connected to two devices at a time; one is called a slave, and the other is called a master. Systems can use ATA hard drives without the need for a specific controller to manage the device. Although an ATA connection must be supported by the motherboard, there is no necessity for an additional card (like a SCSI card for a SCSI hard drive). The different ATA standards include ATA-1, ATA-2 (also known as Fast ATA), ATA-3, Ultra ATA (33 MBps maximum transfer rate), ATA/66 (66 MBps), and ATA/100 (100 MBps). ATA drives are frequently referred to as "Integrated Drive Electronics," or IDE. ATA drives are occasionally labelled as "IDE/ATA" (to further confuse individuals purchasing hard drives). Technically speaking, ATA makes use of IDE technology, but what's crucial to understand is that they both relate to the same thing. New ATA drives (apart from SATA) can be utilised with previous ATA interfaces because the ATA standard is backwards compatible. Any newly announced feature is also included in all upcoming editions. For instance, ATA-4 supports PIO modes 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, although they were first implemented in ATA-1 and ATA-2.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










