What is the full form of BTBT: Bacillus ThuringiensisBT stands for Bacillus Thuringiensis. It is a Gram +ve bacteria. Belonging to the Formicates Phylum, the Bacillus Thuringiensis forms spore and is usually referred to as BT. Like other species of Bacteria, this belongs to the Bacilli class and is found on the soil, insect, water, insect faeces, plant surfaces, insect, etc. Further, it belongs to the Bacillales order, Bacillaceae family and Bacillus Genus. 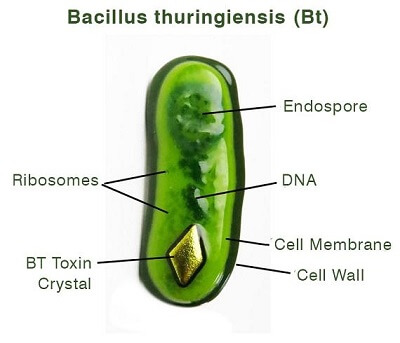
BT is more often used in organic farming. It is usually brought into use as a bioinsecticide. The toxin produced in by the BT was in use since the 1920s in the form of an insecticide spray. The Bacillus Thuringiensis is used to limit the spread of the butterfly caterpillars. As the caterpillars feed on the spores, which were spread onto plants and get killed. The toxins produced are very fatal to herbivorous insects. Origin of Bacillus Thuringiensis
BT was discovered on silkworms by Ishiwatari Shigetane and he named it Bacillus sotto. Many other subspecies are known of BT, such as the israelensis (Bti), kurstaki (Btk), etc. Ishiwatari Shigetane is a Japanese scientist, who discovered Bacillus Thuringiensis in 1901. Shigetane was researching the reducing silkworm population. It was rediscovered by a German scientist in 1911. It was when the use of the toxicity from the Bacillus Thuringiensis was found to be useful against pests. In 1958, for the first time, this product was commercially used, in the United States of America. Uses of Bacillus ThuringiensisDuring sporulation, Bacillus Thuringiensis creates an insecticidal protein. This is the Bt-toxin gene. This gene is then infused into the plants to let the creation of a variety of pest-resistant plants, with the help of genetic engineering. Such as Bt cotton, Bt corn, and others. The genes which are used to modify numerous food crops genetically are taken from the Bacillus Thuringiensis. The genes then independently produce the toxin. Although this toxin formed is harmful to many species of insects, still, a number of strains of BT are available to make it more target specific. Advantages of Bacillus Thuringiensis
Disadvantages of Bacillus Thuringiensis
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










