What is the full form of CABG in MedicalCABG in Medical: Coronary Artery Bypass GraftCABG stands for coronary artery bypass graft. A technique used to treat coronary artery disease is coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). The blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrition to the heart muscle are known as the coronary arteries, and coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing of these blood vessels. This accumulation makes the inside of the arteries smaller, which reduces the amount of oxygen-rich blood that can reach the cardiac muscle. 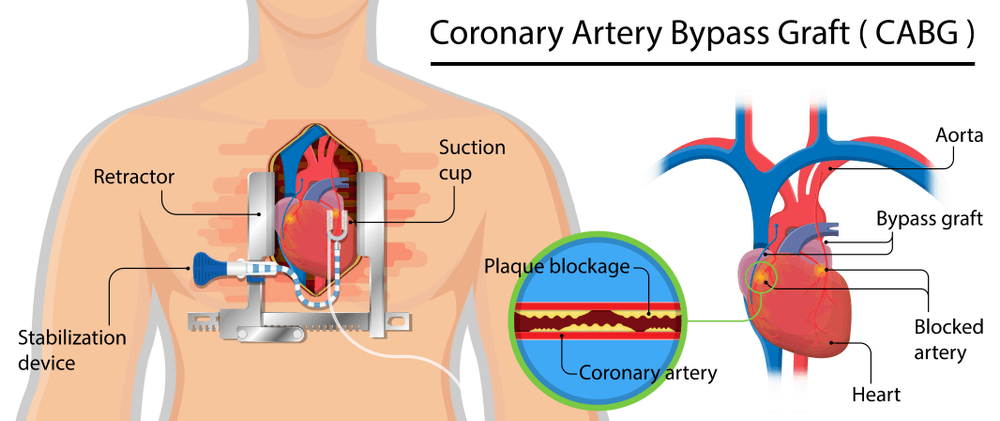
Bypassing the obstructed section of the coronary artery with a piece of a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body is one method of treating the blocked or narrowed arteries. Blood vessels, or grafts, from your leg's vein or an artery in your arm, may be used during the bypass operation. CausesA doctor might advise CABG for several causes, including: Severe Coronary Artery Disease When medication or other treatments are insufficient to improve blood flow, CABG is frequently advised for patients with substantial blockages or narrowing in numerous coronary arteries. Heart Attack If a person has had a heart attack, CABG may be advised to treat a blockage that contributed to the attack or to avoid further heart damage. Chest Pain (angina) CABG may be suggested to treat angina if it is not well managed by medication or lifestyle changes. High-risk Coronary Artery Disease For individuals with high-risk coronary artery disease, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or poor heart function, CABG may improve long-term survival and reduce the likelihood of complications. Emergency CABG CABG may rarely be carried out in cases where the patient's condition is life-threatening, such as a heart attack or unstable angina. CABG TechniquesThe following steps are usually included in the CABG procedure: Anaesthesia To guarantee that the patient is asleep and pain-free during the procedure, general anaesthesia will be administered. Incision To reach the heart and coronary arteries, the surgeon will create an incision in the chest, usually in the middle or on the left side. 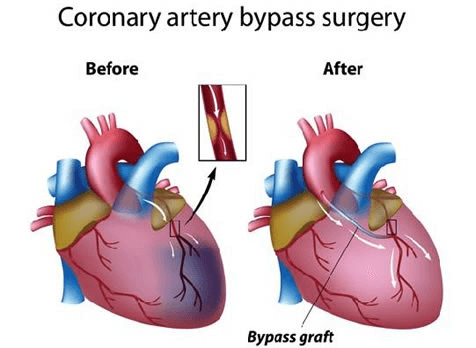
Harvesting Grafts The physician will take a healthy blood vessel out of the patient as a graft to go around the blocked or narrowed coronary artery, frequently from the leg or chest wall. Connecting the Graft After meticulously connecting the graft to the coronary artery, the surgeon will open a new passageway for blood to flow around the blockage. Finishing the Bypass The surgeon may repeat the procedure of harvesting and connecting grafts to bypass numerous coronary arteries depending on the number and position of the blockages. Closing the Cut Following the completion of the bypass, the physician will use sutures or staples to close the chest cut and cover it with sterile dressings. Recovery After being moved to a recovery area, the patient will be carefully watched as they emerge from anaesthesia and recover. The length of the CABG procedure can vary depending on the quantity and location of blockages, regardless of whether it is being done as an emergency or elective procedure. Usually, the procedure takes three to six hours. CABG Risks and ComplicationsCABG surgery entails risks and possible complications, just like any surgical procedure. The following are some of the most typical dangers and issues connected with CABG: Bleeding There may be significant bleeding during or after CABG surgery because the procedure entails cutting into the chest. Rarely, this bleeding might necessitate different surgery or blood transfusions. Infection Following CABG surgery, infection is dangerous, as with any surgical procedure. Longer hospital stays, additional treatments, and slower recovery times may result. Arrhythmia Following CABG operation, an irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, may occasionally develop. Sometimes, medication or other treatments can be used to address this. Stroke There is a tiny chance that blood clots or other surgical debris could fragment during CABG surgery and make their way to the brain, resulting in a stroke. Kidney Issues CABG operation can occasionally result in short-term or long-term kidney damage, especially in patients with kidney issues. Lung Issues CABG operation can occasionally result in lung issues, such as pneumonia or lung failure, especially in patients with lung issues. 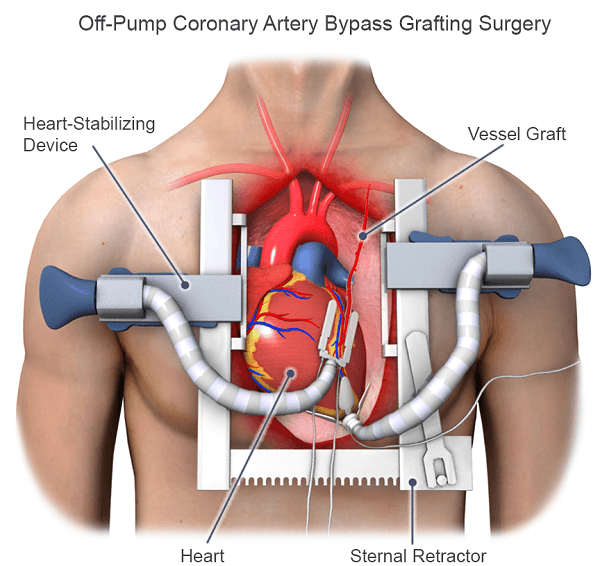
Death Although unlikely, there is a danger of passing away following CABG surgery, especially in patients with underlying medical conditions or very old. Recovery and Rehabilitation after CABGAn important step in the process is recovery and rehabilitation following CABG surgery, which typically includes several stages: Hospital Stays The patient will usually remain in the intensive care unit (ICU) or a specialized cardiac care unit for a few days following surgery. They will be carefully watched during this time and given medications to control pain, stop infections, and lower the possibility of complications. Transfer to a Normal Hospital Room The patient will be moved to a regular hospital room after a few days to continue their recovery. Under the guidance of a medical team, they will gradually start to sit up, move around, and partake in light exercise during this period. Discharge When patients are stable and can manage everyday tasks independently, they will be released from the hospital. They will receive directions on how to take their medications, care for any incision sites, and gradually increase their physical activity levels at home. Cardiac Rehabilitation The patient usually participates in a cardiac rehabilitation program after release. This program includes medically supervised exercise and education to enhance heart health and lower the risk of subsequent cardiac events. Following CABG surgery, recovery and rehabilitation times can differ based on the patient's age, general health, and the extent of the procedure. Generally speaking, patients can recommence light activities a few weeks after surgery and normal activities a few months later. To ensure a safe and successful result, the medical team will provide the patient with individualized advice on recovery and rehabilitation and carefully monitor the patient's progress. Living a Different Life After CABGMaking lifestyle adjustments after CABG surgery is essential for enhancing heart health and lowering the risk of subsequent cardiac events. Following CABG surgery, it's suggested that you make some of the following behavioural changes: Eating a Heart-Healthy Diet Eating a meal low in sodium, cholesterol, and saturated and trans fats can help lower the chance of future cardiac events. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and heart-healthy fats, like those in fish, nuts, and seeds, are usual components of a diet that promotes heart health. 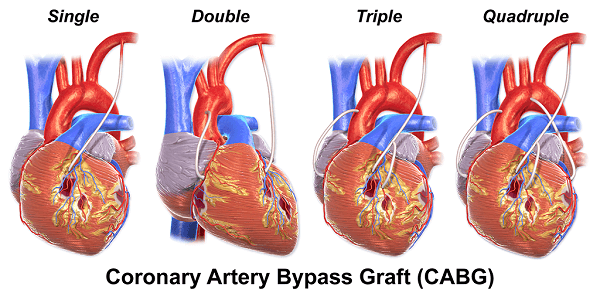
Regular Exercise Exercise can help decrease the risk of future cardiac events, lower blood pressure, and enhance heart health. The medical staff will give personalized physical activity and exercise advice based on each patient's unique requirements and capabilities. Quitting Smoking Quitting smoking can greatly improve heart health and lower the risk of future cardiac events because smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. The medical staff can offer tools and encouragement for quitting smoking. Managing Stress Stress can be a factor in heart disease, and methods like yoga, deep breathing, and meditation can all be used to reduce stress. Managing Other Medical Conditions Improving heart health and lowering the chance of further cardiac events require managing other medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. This may entail taking medications, altering food, and checking blood sugar levels. Patients must collaborate closely with their medical team to create a personalized plan for modifying their lifestyle following CABG surgery. After Care for CABGFollowing CABG surgery, follow-up care is a crucial step in the healing process and usually consists of several elements: Regular Doctor's Visits Following CABG surgery, patients will typically schedule routine follow-up visits with their medical staff to track their recovery and look for any indications of complications or recurrent heart issues. Medication Management Following CABG operation, patients may need to take medicines to control pain, avoid infection, and lower their risk of complications. Patients must adhere to the regimen of medications recommended by their healthcare providers and disclose any side effects or concerns. Cardiac Rehabilitation As it was already stated, participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program is crucial to healing from CABG surgery. The program usually includes supervised exercise and instruction to improve heart health and lower the risk of future cardiac events. Lifestyle Changes Following the CABG operation, it's crucial to make lifestyle changes like eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising frequently, quitting smoking, and managing other medical conditions. Monitoring Heart Health Following CABG surgery, patients may need to frequently check their blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels as advised by their medical team. Patients should carefully follow the advice of their medical team, show up at all follow-up visits, and report any concerns or changes in symptoms as soon as possible. Patients can effectively recover from CABG surgery and enhance their long-term heart health with the right aftercare. CABG Success RatesIn general, CABG surgery has very good success rates. The American Heart Association estimates that people with CABG surgery have a 98% overall survival rate. Additionally, after surgery, most patients notice a substantial improvement in their symptoms and overall quality of life. The extent of the artery blockages, the patient's general health, and the knowledge and expertise of the surgical team are all important considerations in determining whether a CABG operation is successful. Patients with more severe heart disease or other underlying medical problems may be more likely to experience complications or have less favourable surgical results. 
The safety and efficacy of CABG surgery have increased because of the recent developments in surgical methods and technology. Additionally, a multidisciplinary approach to care entails a group of experts, including cardiac surgeons, cardiologists, anaesthesiologists, and other medical personnel, who can help guarantee the best results for CABG surgery patients. Overall, CABG surgery is usually considered a safe and effective treatment option for patients with significant coronary artery disease, despite any surgical procedure's risks and possible complications. CABG AlternativesDepending on the patient's specific medical background, the severity and extent of their coronary artery disease, and other factors, a number of alternatives to CABG surgery may be considered. These options include, among others: Medication Medication may treat symptoms and lower the risk of developing future cardiac events in some people with mild to moderate coronary artery disease. Medications may include nitro-glycerine, blood pressure medications, antiplatelet medications, and cholesterol-lowering pharmaceuticals. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Also known as angioplasty, PCI is a minimally invasive treatment in which a small balloon or stent is inserted to open an obstructed or narrowed artery. For individuals with less severe blockages, PCI is frequently used as an alternative to CABG surgery to address blockages in one or more coronary arteries. Enhanced External Counter pulsation (EECP) The non-invasive procedure known as "Enhanced External Counter pulsation" (EECP) compresses and uncompresses the blood vessels in the legs to improve blood flow to the heart. Patients with mild to moderate coronary artery disease who are unsuitable for surgery may use this treatment. Lifestyle Changes A healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing other medical conditions are all lifestyle changes that can help improve heart health and lower the chance of future cardiac events. To choose the best course of treatment for their unique requirements and medical history, patients should consult closely with their medical team. A mix of therapies may be suggested in some circumstances. Causes of CABGPatients whose coronary arteries have substantial blockages or narrowing may benefit from CABG surgery. Atherosclerosis, a build-up of plaque in the arteries that obstruct blood passage to the heart, may be to blame. Patients with more severe or complicated coronary artery disease or those who have not responded to other treatments, such as medication or lifestyle adjustments, are frequently advised to undergo CABG surgery. Following are some typical justifications for CABG surgery:
Anaesthesia Options for CABG Surgery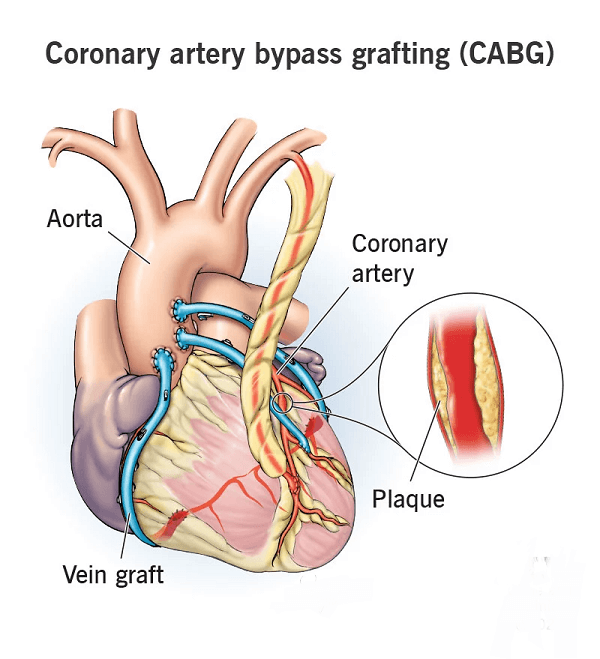
General Anaesthesia For CABG surgery, there are several anaesthesia choices. The patient's medical history, age, and other variables affect the choice of anaesthesia. The most frequent anaesthesia used for CABG procedures is general anaesthesia. It entails giving the patient drugs that make them sleepy so they can have surgery without experiencing any discomfort. Regional Anaesthesia A nerve block is another name for this kind of anaesthesia. Medication is injected into certain muscles to numb the region around the surgical site. For CABG operations, this can be combined with general anaesthesia. Epidural Anaesthesia A catheter is inserted into the spine's epidural region to administer epidural anaesthesia. Medication is given through the catheter to numb the nerves in the thorax and abdomen. For CABG operations, this can be combined with general anaesthesia. Conscious Sedation Conscious sedation is the anaesthesia that includes giving the patient medication to make them feel relaxed and sleepy but not asleep. Patients who cannot tolerate general anaesthesia or have minimally invasive CABG procedures usually use it. The anaesthesia staff will consult closely with the surgical team to choose the best anaesthesia for each patient. To ensure the patient's safety and comfort throughout the process, they will monitor their vital signs and modify the medication as necessary.
Next TopicFull Forms List
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









