What is the full form of CAPACAPA: Corrective and Preventive ActionCAPA stands for corrective and preventive action. The importance of corrective and preventive action (CAPA) in any quality management strategy (QMS) cannot be overstated. A crucial component of many legal requirements, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001 standard, CAPA is a tool for continuous development. To stop non-conformances or deviations from happening again, the CAPA process aims to find and resolve their underlying causes. This article will examine CAPA's fundamentals, significance, the crucial steps involved, and some best practices for putting one into reality. 
What is Corrective Action?A problem or nonconformity's root cause can be found, looked into, and eliminated using a systematic procedure called corrective action. Corrective action aims to stop the issue from happening again and guarantee that the process or product complies with the necessary standards. It is a crucial component of quality management systems, and businesses use it to enhance their operations, goods, and services. What is Preventive Action?A proactive strategy called preventive action is used to spot possible issues or nonconformities before they arise and to take steps to stop them from happening. Organizations use it as a key component of quality management systems to constantly enhance their operations, goods, and services. Finding and removing the causes of potential problems is the aim of preventive action to avoid them from happening in the first place. BackgroundCAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) is rooted in creating quality management systems and the requirement for ongoing growth within organizations. A quality management system, a structured and systematic strategy for managing processes, products, and services to meet customer requirements and regulatory standards, is fundamentally complete with CAPA. CAPA has its roots in the early days of manufacturing when quality control was mainly concerned with identifying and fixing errors as they occurred. This method, however, was expensive and ineffective because it frequently required scrapping or reworking defective goods. The Significance of Preventative and Corrective Action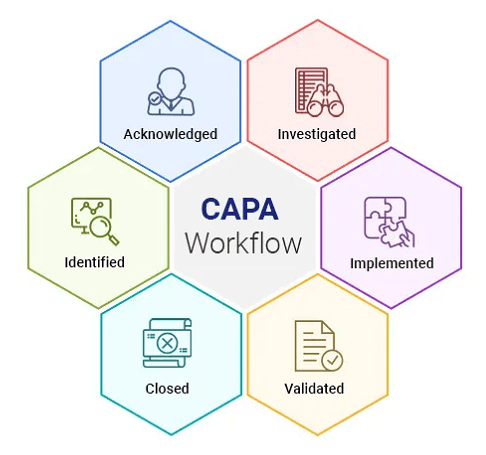
The main objective of CAPA is to locate and eliminate a problem's root source, not just to treat its symptoms. This strategy aids in preventing the recurrence of the problem, which eventually results in higher-quality goods and services. Additionally, a strong CAPA procedure can assist companies in meeting legal obligations and regulatory requirements. Key Stages in the Process of Corrective and Preventive ActionThe following steps are usually included in the CAPA process: 1. Finding the Issue Finding the issue or non-conformance is the first stage in the CAPA process. A production problem, an internal audit discovery, or a customer complaint could cause this. 2. Investigate the Issue After the issue has been identified, the next stage is to look into it to find out what caused it. This could entail gathering information, performing interviews, and reviewing records. 3. Choose the Appropriate Corrective Action Based on the investigation findings, the company must choose the best corrective action to deal with the problem's underlying causes. This might entail modifying processes, providing workers with training, or introducing new technology. 4. Execute the Corrective Action After the corrective action has been decided, it must be carried out quickly and efficiently. This might entail defining roles, setting deadlines, and informing pertinent stakeholders of the adjustments. 5. Verify the Effectiveness of the Corrective Action The company must assess the effectiveness of the corrective action after it has been put into place. This could entail gathering information to assess the effectiveness of the corrective action and watching the process to ensure the issue doesn't arise again. 6. Decide the Preventive Action As part of the CAPA process, preventive actions are identified and implemented to lessen the possibility of future occurrences of the same problems. This could entail adopting new technologies, changing working practices, or training staff. 7. Implement the Preventive Action After the precautionary action is chosen, it must be carried out quickly and efficiently. This might entail defining roles, setting deadlines, and informing pertinent stakeholders of the adjustments. 8. Verify the Preventive Action's Effectiveness The company must confirm its effectiveness after implementing it. This might entail monitoring the procedure to ensure the issue doesn't come up again and gathering information to gauge the effectiveness of the precautionary measure. Corrective and Preventive Action's Best PracticesThe main stages in the CAPA process are problem identification, investigation of the issue, selection of corrective and preventive actions, implementation of those actions, and evaluation of those action's efficacy. Organizations can increase the calibre of their goods and services, satisfy legal obligations, and comply with regulatory requirements by implementing an efficient CAPA programme. 
Organizations can create a strong CAPA programme that aids them in achieving their quality goals by adhering to these best practices. Careful planning and execution are necessary to implement a successful CAPA programme. Here are some recommendations for optimal practices: 1. Create a Clear Process It is crucial to create a CAPA method that is understandable to all parties. This entails outlining duties and responsibilities, setting deadlines, and ensuring everyone understand CAPA's significance. 2. Promote a Culture of Continuous Development A culture of continuous improvement is necessary for an efficient CAPA programme. This indicates that management is receptive to improvement suggestions and that employees are encouraged to spot issues. 3. Utilize Data to Inform Decisions Data is a crucial instrument for CAPA. Data collection and analysis can be used to find trends and patterns that point to fundamental problems. 4. Engage Cross-Functional Teams CAPA frequently entails problems spanning multiple functions or departments. To guarantee that all viewpoints are considered during the CAPA process, it is crucial to involve cross-functional teams. 5. Document the CAPA Procedure There are several reasons why the CAPA process needs to be documented. It serves as a record of the decisions and actions done and can be used as a guide for upcoming CAPA initiatives. 6. Monitoring and Reporting Monitoring and reporting on CAPA development are crucial to ensure that the corrective and preventive actions are being carried out successfully. This entails monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and informing management frequently. 7. Review the CAPA Program Regularly Regular reviews of the CAPA Program can assist in identifying areas for growth and ensuring that the program is accomplishing its goals. This entails assessing the success of the corrective and preventive measures and making any required adjustments. Any quality management strategy must include corrective and preventive action. Medical Devices and FDA Compliance on Corrective and Preventive actionCorrective and preventive action (CAPA) is vital to FDA compliance for medical device makers. The FDA mandates that businesses that produce medical devices have a CAPA programme to deal with any variations or non-conformances in production. This is being done to guarantee the effectiveness and safety of medical devices and prompt identification and mitigation of any possible risks. "Action to eliminate the cause of a discovered nonconformity or other undesirable circumstance," according to the FDA, is what corrective action is. While preventive action is described as "an action to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformity or other undesirable circumstance," preventive action is the opposite. These steps ensure the process or product meets the necessary standards and prevent recurring issues. Medical device manufacturers must create and keep CAPA implementation procedures following FDA regulations. These steps ought to consist of the following:
Manufacturers of medical devices must also keep track of all CAPA-related activities, including inquiry reports, reports on corrective and preventive actions, and verification reports. Depending on the sort of record and the requirements of the FDA, these records must be kept for a specific time. To ensure that CAPA rules are followed, the FDA also performs routine inspections of medical device makers in addition to these requirements. During these inspections, FDA examiners will examine the manufacturer's CAPA programme, including its practises, documentation, and effectiveness. Why do the Most Current ISO Standards Call for Corrective Action but Not Prevention?Even though the most recent ISO standards (like ISO 9001:2015) still call for organizations to take preventive action, they also strongly emphasize the necessity of corrective action to deal with problems discovered and enhance organizational performance. This shift towards corrective action is attributed due to the fact that it is typically simpler to recognize and solve current issues than it is to do the same for prospective ones. This is because existing issues are frequently more obvious and have already had unfavourable effects, making them more pressing to address. On the other hand, proactive action frequently entails identifying potential issues that may or may not materialize, which can be more challenging to identify and address. This change is also because corrective action stresses the value of root cause analysis, which assists in finding the underlying causes of issues and preventing their recurrence. Instead of merely addressing symptoms or surface-level problems, this method can result in more effective and long-lasting changes. Overall, even though preventive action is still a crucial component of quality management systems, the recent focus on corrective action emphasizes the significance of recognizing and resolving existing issues and the necessity of enhancing organizational performance over time by conducting root cause analyses and taking efficient corrective actions. How Should a CAPA Summary be Written?The steps made to address a problem or nonconformity found in a quality management system are summarised in a CAPA report (Corrective and Preventive Action Report), a formal document. The stages for writing a CAPA report are as follows: 1. Introduction State the problem or nonconformity found at the outset of the report, giving pertinent information like the time and place of discovery and the parties concerned. Give a thorough description of the issue, including any data or proof gathered and its effects on the quality management system, the product, or the service. 2. Root Cause Analysis 
Describe the root cause analysis that was carried out to ascertain the primary reasons for the issue. This might entail applying various techniques and instruments for solving problems, like process mapping, fishbone diagrams, or statistical analysis. 3. Remedial Action Strategy Describe the remedial action strategy that was created and put into place to deal with the issue. Along with the timetable for implementation and effectiveness testing, this should contain specific information about the actions done, such as modifications to equipment, training programmes, or existing processes. 4. Preventative Measures Describe any preventative measures that were done to make sure that the issue doesn't crop up again in the future. This might entail implementing new practices, providing more instruction, or changing current practices. Describe the procedure used to assess the success of the implemented remedial and preventative measures. This may entail running tests, gathering data, or keeping an eye on speed to ensure the issue has been resolved and won't happen again. 5. Summarize Summarize the report's key conclusions, including the issue, the root cause analysis, the corrective and preventive measures implemented, and the efficacy checks. Include any suggestions for potential modifications to the quality management system. 6. Appendices Place any pertinent files or information such as images, flowcharts, or statistical analyses. By following these steps, you can write a thorough CAPA report that summarises the issue, the root cause analysis, the corrective and preventive actions done, and the effectiveness verification. This report can be used to monitor development, spot patterns, and gradually enhance the quality management system. Where Can CAPA Values Be Used?When quality management methods are used, CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) principles can be applied to various fields and situations. Here are a few instances: 1. Manufacturing To handle product or process quality issues, CAPA principles can be used in the manufacturing sector. Manufacturers can increase the quality of their products and cut costs by locating and addressing the problem's underlying cause. 2. Medical Industry Medical errors, patient safety, and regulatory compliance are all problems that can be addressed using CAPA principles in the healthcare sector. Healthcare professionals can lower the chance of unfavourable events and enhance patient outcomes by implementing corrective and preventive measures. 3. Food and Beverage CAPA guidelines are crucial for the food and beverage sector because they can be applied to problems with product quality and safety. Food and beverage producers can enhance product safety and avoid recalls by determining and resolving the underlying causes of problems like contamination or spoilage. 
1. Information Technology CAPA concepts can be applied to problems involving software bugs, security lapses, and system failures in the information technology sector. IT companies can increase system reliability and decrease downtime by implementing corrective and preventive measures. 2. Service Industries To handle problems relating to customer satisfaction, regulatory compliance, and process efficiency, CAPA principles can be implemented in a variety of service industries, including transportation, hospitality, and banking. Service providers can increase the loyalty and retention of customers by determining and addressing the underlying cause of problems. ConclusionThe CAPA process offers a systematic strategy for locating the source of a problem, creating a corrective action plan, carrying it out, and assessing the measures' success. The manufacturing, healthcare, food and beverage, information technology, and service sectors all frequently use the CAPA method. Organizations can enhance their quality management systems, lower costs, boost customer happiness, and adhere to regulatory requirements by implementing CAPA principles. Organizations should create a culture of continuous improvement, educate staff, define clear roles and responsibilities, and track and evaluate the CAPA process' effectiveness over time to guarantee its efficacy. In conclusion, the CAPA process is an efficient tool for enhancing quality management systems and resolving problems. Organizations can succeed in their business operations and constantly improve their processes, goods, and services by adhering to the CAPA process.
Next TopicFull Forms List
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









