What is the full form of CBCCBC: Complete Blood CountCBC stands for Complete Blood Count. It refers to a common blood test that is performed to diagnose different medical conditions such as anemia, infection, dengue, malaria, etc. In this test, a trained person like a paramedic or lab technician usually takes blood from a vein that is visible from the skin, e.g., a vein on the back of the hand or the inner angle of the elbow. 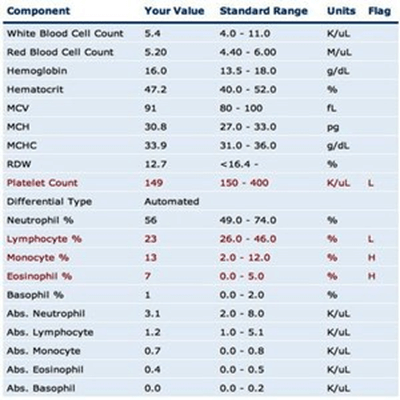
CBC analyzes and measures all the major components of the blood, like red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, etc. It shows the increase or decrease in the count of blood cell components. Typically, a CBC provides the following information:
CBC helps detect various disorders, some of which are as follows:
What can I anticipate from a complete blood count (CBC) procedure?To get ready for a CBC, there is nothing you need to do. Your doctor cleans your arm before sticking a needle in it. Although the needle may sting or pinch somewhat, it should not be painful. Typically, healthcare professionals will place the needle into an infant's heel. Your healthcare professional draws a sample of your blood through the needle, collecting it in a tube. After taking blood, your healthcare professional takes out the needle and wraps your arm in gauze. A lab receives the blood from your provider. Your body replenishes its blood supply fast. What may I anticipate after the test?Your arm will be covered in gauze and a bandage that is taped down. For a few hours, your arm might feel a little sore. Where your doctor inserted the needle, you might get a tiny bruise. What advantages does this test have?Your provider can see a picture of your general health thanks to a CBC. A CBC can aid in the early detection of hundreds of diseases, illnesses, and infections with only a small sample of blood. It enables your healthcare professional to keep an eye on your well-being, check for disease, and plan and modify treatments. What dangers could this test pose?A CBC is a routine, risk-free test. Your provider just removes a small amount of blood, and there are no hazards. Rarely do some persons experience slight dizziness or faintness after a CBC.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










