What is the full form of CVACVA: Cerebral Vascular Accident or Cerebrovascular AccidentCVA stands for Cerebral Vascular Accident or Cerebrovascular Accident. It is also referred to as stroke. It is a medical condition in which blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced. As a result, the brain cells don't get sufficient oxygen and nutrients and they start to die. CVA is a severe condition which is one of the leading causes of death in Australia. It usually affects one side of the brain. 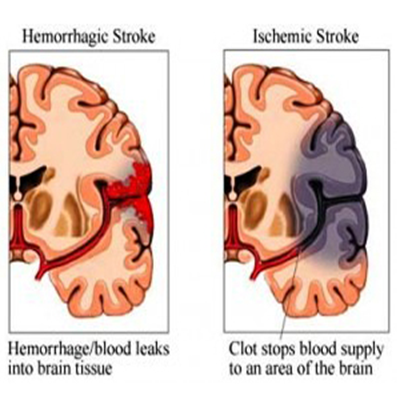
Types of cerebral vascular accident or stroke There are mainly two types of CVS: an ischemic stroke and a hemorrhagic stroke. 1) Ischemic Stroke: It is the most common type of stroke. It occurs when an artery is blocked due to a blood clot and the supply of oxygen and nutrients to a part of the brain gets interrupted. It can happen in two different ways:
2) Hemorrhagic stroke: It occurs when a blood vessel ruptures, as a result of which the blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted. Any blood vessel in the brain or a membrane surrounding the brain may rupture in this stroke. Common Symptoms
The diagnosis of CVA involves full physical examination and various diagnostic tests, some of which are as follows:
PreventionThere are many measures that may help prevent a stroke, some of which are:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










